Uterine cancer can be a scary topic. Many women may worry about what symptoms to watch for or how it’s treated. Uterine cancer, also known as endometrial cancer, affects the lining of the uterus and is something we should all be more informed about.
A key fact is that early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes. This blog will guide you through understanding the symptoms, exploring treatment options—including surgery and medication—and even looking at supplements that might help along the way.
Get ready to learn everything you need to know about tackling uterine cancer head-on.
Read on for clarity and support…
Key Takeaways
- Uterine cancer, also called endometrial cancer, starts in the lining of the uterus and is detected through symptoms like abnormal vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain.
- Doctors use various treatments for uterine cancer such as surgery to remove the uterus, radiation therapy to target cancer cells, chemotherapy to stop cell growth, hormone therapy to slow tumors, targeted therapy for specific cell traits, and immunotherapy to boost the immune system.
- Early detection of uterine cancer improves treatment outcomes significantly. Women should watch for symptoms and consult their doctor if they notice changes.
- Vitamins and supplements like Vitamin D and curcumin may help manage uterine cancer by boosting the immune system or slowing cancer growth. Diet changes and alternative therapies like acupuncture can support healing.
- Making informed decisions about treatment options involves discussing all possibilities with healthcare providers, considering benefits against side effects.
Understanding Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancer attacks the womb, where a baby grows during pregnancy. It shows up in different types, affecting women in varying ways.
What is uterine cancer?
Uterine cancer, or endometrial cancer, targets the lining of the uterus. It’s one of several types of cancers that affect a woman’s reproductive system. This condition presents various symptoms like abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and sometimes pain during sex.
Post-menopausal women face a higher risk, especially those on hormone supplements.
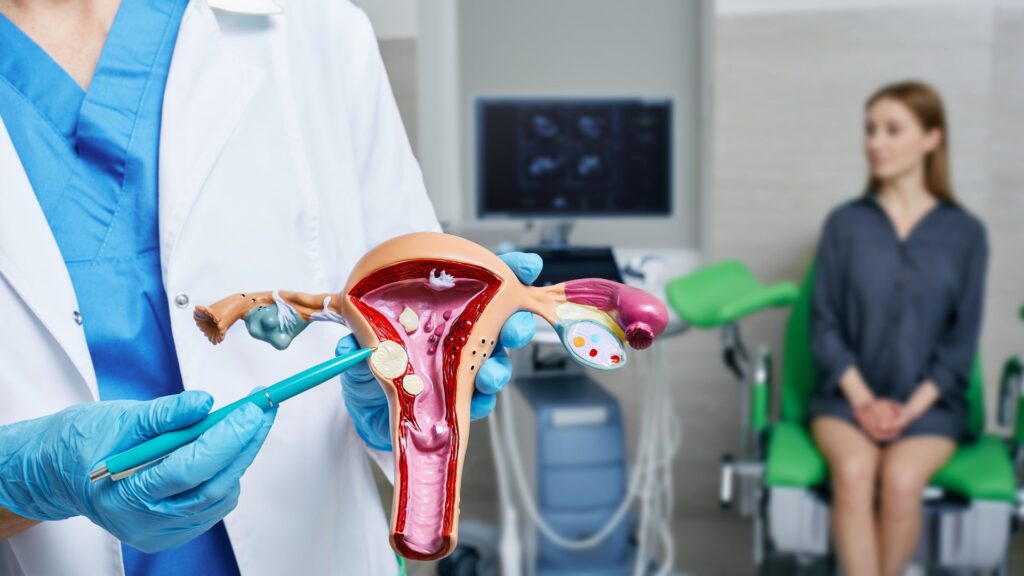
Uterine cancer affects the lining of the uterus and is also known as endometrial cancer.
Doctors use surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormonal drugs to fight this disease. Hormonal treatments may include progestins and tamoxifen among others. A common surgical option is hysterectomy—removing the uterus entirely.
For detection, medical professionals rely on ultrasounds, MRIs, and biopsies where tissue samples are examined closely for signs of cancer cells.
Types of uterine cancer
Uterine cancer affects the lining of the uterus, also known as endometrial cancer. This disease can manifest in different forms, each with its own characteristics and treatment approaches.
- Endometrioid Carcinoma: This is the most common type of uterine cancer, making up about 80% of all cases. It starts in the glandular cells of the endometrium. Women with this type often have a better prognosis because it usually grows slowly.
- Serous Carcinoma: More aggressive than endometrioid carcinoma, serous carcinoma makes up about 10% of cases. It tends to spread more quickly and is found in post-menopausal women.
- Clear Cell Carcinoma: Representing around 4% of uterine cancers, clear cell carcinoma is rare and aggressive, known for its tendency to spread rapidly.
- Carcinosarcoma (Malignant Mixed Mullerian Tumor): Though rare, carcinosarcoma is particularly aggressive and often diagnosed at an advanced stage. It contains both carcinomatous (cancerous epithelial cells) and sarcomatous (cancerous mesenchymal cells) components.
- Uterine Sarcomas: Making up less than 5% of uterine cancers, these start in the muscle or connective tissue of the uterus. They are less common but tend to be more aggressive.
- Adenosquamous Carcinoma: This type features both squamous cells (thin, flat cells that line certain organs) and gland-like cells. It’s known for its high aggressiveness and poor prognosis.
Each type requires a specific approach for diagnosis and treatment, underlining the importance of early detection and customized care plans for patients battling uterine cancer.
Symptoms of Uterine Cancer
Spotting the signs of uterine cancer early can make a big difference. Keep an eye out for unusual symptoms, and don’t wait to talk to a doctor if you notice something off.
Abnormal vaginal bleeding
Abnormal vaginal bleeding stands out as a primary symptom of uterine cancer, especially notable in post-menopausal women. This condition can manifest in various ways, ranging from spotting between periods to heavier-than-normal menstrual flow.
For women who have gone through menopause, any instance of vaginal bleeding should prompt immediate medical attention, as it could signal the presence of endometrial cancer.
Different patterns such as prolonged bleeding during periods or bleeding after sex also fall under this symptom category. While hormonal supplements are common among post-menopausal women, they may elevate the risk of developing uterine cancer, underscoring the importance of monitoring for irregular bleeding as a precautionary measure against potential malignancies within the uterus.
Pain in the pelvic area
Pain in the pelvic area is a common symptom of uterine cancer. Women often feel this pain during sex or while going about their daily activities. It’s a signal from the body that something might be wrong with the uterus or other nearby organs.
Doctors pay close attention to this kind of pain when they’re checking for uterine cancer. If you tell your doctor about pelvic pain, they might perform tests like a pelvic exam or an ultrasound to see what’s happening inside.
These are important steps in diagnosing uterine cancer early, which can lead to more effective treatment options.
Unexplained weight loss
Losing weight without trying can be a sign of uterine cancer. This kind of weight loss often goes unnoticed at first because people usually don’t link it to serious illness. If you’re not dieting or changing your exercise habits but still dropping pounds, it could mean your body is fighting something as severe as uterine cancer.
Doctors pay close attention to unexplained weight loss in patients who also report other symptoms like abnormal vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain. These signals together may prompt further testing for uterine cancer.
Early detection through symptom awareness significantly improves treatment success rates, making knowledge about these signs crucial for women’s health.
Other potential symptoms
Uterine cancer symptoms go beyond the most commonly known signs. It’s essential to pay attention to your body and notice unusual changes.
- Feeling of fullness in the lower stomach area — This might be mistaken for bloating or gastrointestinal discomfort but can indicate something more serious.
- Difficulty urinating — Experiencing trouble when trying to urinate, or changes in frequency, could signal uterine cancer.
- Pain during intercourse — This symptom, often overlooked, can be a telling sign of uterine cancer’s impact on your reproductive system.
- Fatigue that doesn’t go away with rest — Persistent tiredness, even after getting enough sleep, might be your body signaling an underlying issue like cancer.
- Leg pain or swelling — Swelling in the legs or pain not caused by an injury can be linked to issues within the uterus.
- Changes in bowel habits — Look out for constipation or diarrhea that lasts for an extended time without any clear reason.
- Unintended weight loss is another red flag — If you’re losing weight without trying, it’s crucial to consider uterine cancer as a possible cause.
- Abnormal discharge from the vagina that isn’t blood — Discharge that is unusual in color, consistency, or smell should not be ignored.
Each of these symptoms could point to uterine cancer among other conditions. Always consult a doctor if you notice anything unusual about your health.
Diagnosing Uterine Cancer
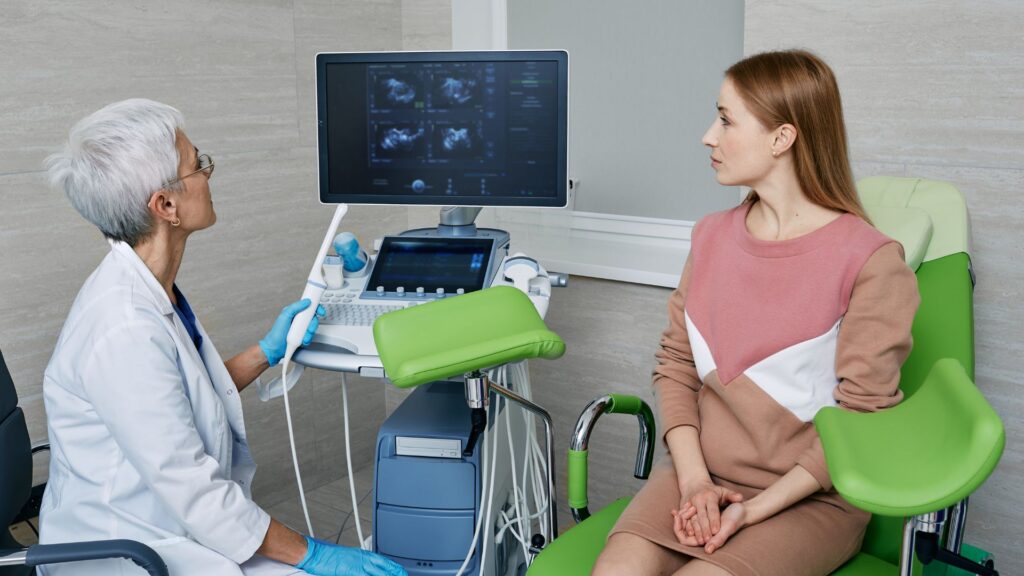
Finding out if someone has uterine cancer involves specific tests—each step guides doctors closer to the right diagnosis. Discover more about this crucial process.
Pelvic exam
A pelvic exam is a key step in diagnosing uterine cancer. Doctors perform this exam to check for any abnormalities or changes in the uterus, ovaries, and other nearby organs. During the exam, the doctor feels for lumps or changes in shape or size that might suggest cancer.
This process helps identify issues that may not be visible through imaging tests alone.
The importance of a pelvic exam cannot be overstated—it offers critical insights into a woman’s reproductive health. If symptoms like abnormal vaginal bleeding or pelvic pain are present, this examination can lead to early detection of uterine cancer.
Early detection dramatically improves treatment outcomes and survival rates for those affected by this condition.
Transvaginal ultrasound
Doctors use a transvaginal ultrasound to get a closer look at the uterus. They insert a small device into the vagina. This device sends out sound waves that create pictures of the uterine lining on a screen.
The process helps to find any abnormalities, like tumors.
This kind of ultrasound is key in diagnosing uterine cancer. It shows details that other tests might miss. For anyone with abnormal vaginal bleeding or pelvic pain, this test can be very helpful.
It’s one way doctors check if symptoms are caused by uterine cancer.
A transvaginal ultrasound gives us clear images of the uterus, helping to detect uterine cancer early.
Hysteroscopy
A hysteroscopy is a key tool in the diagnosis of uterine cancer. This procedure involves inserting a thin, lighted tube through the vagina into the uterus. It allows doctors to look directly at the lining of the uterus and identify any abnormal areas that may indicate cancer.
The process is typically quick and provides valuable information without needing a more invasive surgery.
During a hysteroscopy, if suspicious tissue is found, a biopsy can be performed immediately. This means taking a small sample of tissue from the lining of the uterus to be examined under a microscope by pathologists.
Biopsies are crucial for confirming whether cancer cells are present and determining the exact type and grade of uterine cancer. This step is essential for creating an effective treatment plan specifically for each patient’s needs, considering options like surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy as mentioned in important facts about treating uterine cancer.
Biopsy
Doctors use a biopsy to confirm uterine cancer. They take a small tissue sample from the uterus to examine under a microscope. This test shows if cancer or abnormal cells are present.
It’s a key step in diagnosing uterine cancer, informing what treatment might work best.
After the biopsy, doctors often order more tests to understand the cancer better. These tests help plan out the patient’s treatment path, including options like surgery or chemotherapy.
Treatment Options for Uterine Cancer
Finding the right treatment for uterine cancer depends on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer. Doctors often use a combination of therapies to effectively combat this disease.
Surgery
Surgery plays a key role in treating uterine cancer. Doctors often recommend a hysterectomy, which means they remove the uterus. This procedure can be very effective for early-stage uterine cancer.
Other surgical options may include removing the ovaries and fallopian tubes, especially if the cancer has spread or if there’s a high risk of it spreading. The goal is to remove as much of the cancer as possible.
For many patients, surgery is just the first step. After surgery, treatments like radiation therapy or chemotherapy might be necessary to kill any remaining cancer cells and reduce the chance of the cancer coming back.
Each patient’s treatment plan will depend on their specific situation—like how advanced the cancer is and their overall health.
A hysterectomy isn’t just common; it’s often a lifesaving choice for those battling uterine cancer.
Next, let’s talk about radiation therapy and how it helps in fighting against uterine cancer cells left after surgery.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy plays a crucial role in treating uterine cancer, targeting the cancer cells in the uterus. Doctors use high-energy rays to kill these harmful cells, aiming to shrink tumors or eliminate any remaining after surgery.
This method is especially useful for patients who cannot undergo surgery or as an additional step to ensure all cancerous cells are addressed.
Patients undergoing radiation therapy might receive it externally from a machine outside the body or internally through a device placed inside the vagina. The choice depends on various factors, including the stage of cancer and overall health of the patient.
This approach helps minimize damage to surrounding healthy tissues while focusing on destroying the cancer cells effectively.
Chemotherapy
Moving from radiation therapy, doctors often consider chemotherapy for endometrial cancer treatment. This approach uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
Patients might receive these medicines through an IV or as pills. Chemotherapy aims to target rapidly dividing cancer cells, but it can also affect some fast-growing healthy cells.
Doctors may use chemotherapy alone or with other treatments like surgery and radiation therapy. The choice depends on the cancer’s stage and other health factors of the patient. For uterine cancer, this method helps slow the tumor’s growth and reduce symptoms when the disease has spread beyond the uterus or if there is a high risk of recurrence.
Hormone therapy
After exploring the benefits and processes of chemotherapy for endometrial cancer, it’s time to shift our focus to hormone therapy. This treatment uses hormonal drugs like progestins, tamoxifen, LHRH agonists, and aromatase inhibitors.
These medications aim to slow the growth of tumors by interfering with the body’s hormone levels. For many patients, hormone therapy serves as an effective method to manage uterine cancer.
Doctors often recommend this approach when surgery or radiation are not viable options or after these treatments to help prevent recurrence. It targets cancers that respond to hormones in the blood.
This makes it a powerful option for certain types of uterine cancer.
Understanding your treatment options empowers you in your fight against uterine cancer.
This process highlights how advanced treatments have become in targeting and managing diseases at a molecular level.
Targeted therapy
Moving from hormone therapy, doctors often turn to targeted therapy for treating uterine cancer. This approach uses medicines designed to attack specific cancer cell traits. For example, some drugs in targeted therapy block the action of certain proteins or genes that help cancer cells grow and spread.
Endometrial cancer treatment benefits from this method because it can be more precise and cause fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy.
Targeted therapy drugs reach out specifically to cancer cells without harming normal ones, making them effective allies against uterine cancer. They work by identifying and attacking the tumor’s growth mechanisms at a molecular level.
This means patients may experience better outcomes with potentially less impact on their overall health.
Immunotherapy
Shifting focus from targeted therapy, we explore the role of immunotherapy in treating uterine cancer. This approach strengthens the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Doctors use it to slow tumor growth and prevent it from spreading.
Immunotherapy comes into play when other treatments might not work as well. It targets specific parts of cancer cells, making the immune system respond more effectively.
Immunotherapy for uterine or endometrial cancer includes drugs that help the immune system identify and attack cancer cells. The treatment varies depending on how advanced the cancer is and if it has spread to other parts of the body.
Side effects can happen, but doctors work closely with patients to manage them. This method offers hope when conventional treatments may fall short, adding an essential tool in fighting against uterine cancer progressions.
Complementary and Alternative Methods
Explore the power of vitamins, special diets, and soothing therapies like acupuncture to boost your healing journey—each step offering a unique path to wellness. Discover how these methods can complement traditional treatments.
Vitamins and supplements
Vitamins and supplements can play a role in managing uterine cancer. They might help boost the immune system and manage symptoms.
- Vitamin D – Research suggests that high levels of Vitamin D may lower the risk of developing uterine cancer. It helps by slowing down the growth of cancer cells.
- Curcumin – Found in turmeric, curcumin has anti-inflammatory properties. Studies show it may prevent cancer cells from growing.
- Selenium – A mineral that enhances the immune system’s ability to fight off infections and protect against cell damage. Taking selenium supplements could support overall health during treatment.
- Green Tea Extract – Contains antioxidants known as catechins, which may inhibit cancer growth.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids – Found in fish oil, they reduce inflammation and have been linked to a lower risk of cancers.
- Probiotics – Help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which is vital for immune function and nutrient absorption during treatments.
- Calcium – Along with vitamin D, calcium keeps bones strong, especially important since some treatments can weaken bones.
- Iron – Essential for preventing anemia, a common condition in people with cancer due to blood loss or chemotherapy effects.
- Melatonin – Helps regulate sleep cycles disrupted by cancer treatment, improving quality of life and possibly enhancing the effectiveness of some treatments.
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) – An antioxidant that may improve energy levels and heart health during chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Taking these vitamins and supplements should always be discussed with a healthcare provider to ensure they are safe alongside uterine cancer treatments.
Special diets
Moving from the benefits of vitamins and supplements, exploring special diets can offer extra support for those dealing with uterine cancer. Certain foods might help slow the tumor’s growth or improve your body’s response to treatment.
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is key. This approach nourishes the body and strengthens it against the side effects of cancer treatments like surgery and chemotherapy.
Experts suggest limiting processed foods and sugars which can fuel inflammation. Some studies show that a diet low in fat and high in fiber may benefit people with uterine cancer, especially post-menopausal women at higher risk.
Each person’s needs are unique, so consulting a healthcare professional before making significant changes is crucial. They can provide guidance specifically to enhance one’s health during this challenging time.
Acupuncture and massage
After exploring how special diets can complement traditional uterine cancer treatments, it’s worth considering acupuncture and massage. These methods offer a different kind of support to those battling this disease.
Acupuncture involves placing thin needles at specific points on the body. This ancient technique can help reduce pain and alleviate some treatment side effects like nausea. Many find that including acupuncture in their care plan improves overall wellbeing.
Massage therapy also plays a significant role for individuals with uterine cancer. It provides relaxation, reduces stress, and helps manage pain without the use of drugs. Both options—acupuncture and massage—are beneficial in creating a more comprehensive approach to managing symptoms and improving quality of life during such a challenging time.
Coping with Uterine Cancer
Facing uterine cancer brings its own set of challenges. Finding the right support and exploring clinical trials can empower you on this journey.
Making treatment decisions
Deciding on uterine cancer treatment options involves careful consideration and understanding of the available methods. It’s essential to weigh the benefits and side effects to choose the best course of action for you.
- Discuss all treatment possibilities with your healthcare team, focusing on surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy as main options.
- Consider a hysterectomy—surgical removal of the uterus—as it is common for treating uterine cancer, especially in early stages.
- Evaluate using hormonal drugs like progestins and tamoxifen that help slow tumor growth in certain cases.
- Look into targeted therapy which attacks cancer cells without affecting normal cells too much—a newer form of treatment.
- Explore radiation therapy if surgery isn’t an option or to eliminate remaining cancer cells post-surgery.
- Ask about chemotherapy’s role in your treatment, especially for advanced or recurrent uterine cancer.
- Understand hormone therapy’s effectiveness against tumors that use hormones to grow.
- Research immunotherapy options, as they represent an emerging field showing promise in treating some types of uterine cancer.
- Review potential side effects for each treatment carefully with your doctors—knowing what might happen can help you prepare mentally and physically.
- Take into account how treatments might affect your fertility if future pregnancy is a consideration.
- Investigate clinical trials offering access to cutting-edge treatments not widely available elsewhere.
Seek a second opinion from another oncologist to confirm your treatment strategy and explore all options.
Prioritize your quality of life when choosing treatments—consider both the physical impacts and how they align with your personal values and lifestyle.
Clinical trials
After deciding on treatment options, exploring clinical trials becomes a crucial step. Clinical trials test new ways to treat uterine cancer. Doctors use these studies to find more effective methods for fighting this disease.
Patients might receive new drugs or treatments before they are widely available. Joining a clinical trial can offer access to cutting-edge therapies that could be more effective than current treatments.
Clinical trials also help doctors understand how treatments work against uterine cancer over the long term. Participants in these studies receive close monitoring and care from top cancer researchers.
This level of attention ensures any side effects are quickly addressed. Joining a trial contributes valuable information that will help future patients battling uterine cancer.
Support systems
Exploring clinical trials introduces a world of cutting-edge treatments for uterine cancer, but the journey doesn’t end there. Having a solid support system plays an equally crucial role in guiding through treatment and recovery.
Friends, family, and caregivers provide emotional comfort and practical assistance, making tough moments more bearable. Furthermore, joining uterine cancer support groups brings together individuals facing similar challenges.
Sharing experiences can offer invaluable insights and encouragement.
In the fight against uterine cancer, you’re not alone—support systems provide strength and hope.
Professionals like oncologists, nurses, and social workers also contribute to this network of support. They guide patients through each step of their treatment—explaining procedures such as hysterectomy or radiation therapy for uterine cancer—and help manage symptoms with medicines or suggest complementary methods like acupuncture.
These experts ensure that every person battling uterine cancer receives comprehensive care customized to their needs.
Conclusion
Uterine cancer presents a significant challenge yet brings hope through advancements in treatment and support. Dr. Clara Mendez—a leading authority with years of dedication to gynecologic oncology—shares her insights.
Holding a PhD from Harvard University, she has led groundbreaking research while offering compassionate care to countless patients.
Dr. Mendez emphasizes the importance of understanding uterine cancer’s mechanisms—how it affects the body and the vital role of early detection and comprehensive treatment options.
“Recognizing symptoms like abnormal bleeding or pelvic pain can save lives,” she notes, underlining that treatments such as surgery and chemotherapy have evolved significantly, backed by scientific principles aiming at targeted cell destruction while sparing healthy tissues.
Safety, ethics, and transparency are pillars in managing uterine cancer, according to Dr. Mendez. She highlights the necessity for treatments to pass rigorous testing phases ensuring safety and effectiveness: “Patients deserve honesty about their condition, potential side effects, and outcomes.”.
Incorporating therapies into daily life requires balance; Dr. Mendez advises focusing on holistic well-being—embracing both medical treatments like radiation or hormone therapy alongside complementary methods such as diet changes or acupuncture for symptom management.
Balancing pros against cons reveals that though powerful options exist in combating uterine cancer—they come with considerations like side effects or long-term impacts on health which must be weighed carefully.
Comparing these treatments allows individuals to make informed decisions best suited to their unique situations.
Dr. Mendez concludes with optimism about the future of uterine cancer management: “While challenges remain—the blend of innovative surgeries, personalized medicine approaches like targeted therapy alongside supportive care offers a beacon of hope for those affected.” Her comprehensive evaluation underscores why staying informed is critical—it empowers patients along their journey while fostering developments toward even more effective solutions in battling uterine cancer.
FAQs
1. What are the first signs of uterine cancer I should watch out for?
Look out for unusual bleeding, especially if you’re postmenopausal, or any unexpected discharge – these can be early red flags.
2. Can taking certain supplements help prevent uterine cancer?
Yes, some studies suggest that vitamins and minerals like Vitamin D and calcium might lower the risk, but always check with a doctor first.
3. What’s the usual treatment path for someone diagnosed with uterinae cancer?
Treatment often starts with surgery to remove the tumor, followed by radiation or chemotherapy to target any remaining cells.
4. Are there medicines I can take to treat uterine cancer without surgery?
While surgery is common, some cases may use hormone therapy or targeted medication as part of the treatment plan.
5. How long does it usually take to recover from uterine cancer treatment?
Recovery time varies widely depending on your overall health, type of treatment, and how early the cancer was caught – it’s a journey unique to each person.
General Facts
- Uterine cancer, also known as endometrial cancer, is a type of cancer that affects the lining of the uterus.
- Symptoms of uterine cancer include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and pain during sex.
- Treatment options for uterine cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
- Hormonal drugs, such as progestins, tamoxifen, LHRH agonists, and aromatase inhibitors, can be used to slow the tumor’s growth.
- A hysterectomy, which is the surgical removal of the uterus, is a common treatment for uterine cancer.
- Post-menopausal women may be at a higher risk of developing uterine cancer, especially if they are taking hormonal supplements.
- Imaging tests, such as ultrasound and MRI, can be used to diagnose uterine cancer.
- Biopsy is another common test for diagnosing uterine cancer, where a small sample of tissue is taken from the uterus and examined under a microscope.
- Endometrial cancer can also be treated with targeted therapy, which uses drugs to specifically target cancer cells.
- It is important for women to be aware of the symptoms of uterine cancer and to seek medical attention if they experience any abnormal vaginal bleeding or pelvic pain.
Source URLs
- Cancer Treatment Centers of America – Uterine Cancer Information
- Mayo Clinic – Diagnosis and Treatment of Endometrial Cancer
- American Cancer Society – Treating Endometrial Cancer
- Cleveland Clinic – Uterine Cancer Overview
- WebMD – Uterine Cancer Slideshow
- MedlinePlus – Uterine Cancer Information
- Foundation for Women’s Cancer – Endometrial Cancer Guide (PDF)











