If you’ve ever noticed red, itchy bumps suddenly appearing on your skin, you might have experienced urticaria, commonly known as hives. These bumps can be alarming and uncomfortable.
Hives are a reaction to allergens or stress and affect about 20% of people at some point in their lives. This fact highlights the wide impact of urticaria and underscores the importance of understanding this condition.
Our blog post offers a comprehensive guide on symptoms, treatments, medicines, and supplements for managing hives effectively. We’ll help you identify common triggers, recognize symptoms quickly, and explore both medical treatments and home remedies for relief.
Find out how simple changes can make a big difference in dealing with this skin issue. Keep reading for valuable insights.
Key Takeaways
- Hives, known as urticaria, affect the skin with red, itchy bumps as a reaction to allergens or stress. About 20% of people experience hives at some point in their lives.
- There are two main types of hives: acute and chronic. Acute hives last less than 6 weeks and often result from allergies to foods or medications. Chronic hives persist for more than 6 weeks and may not have an identifiable cause.
- Treatments for urticaria include over-the-counter antihistamines for immediate relief, prescription medications like omalizumab for chronic cases, and natural remedies such as colloidal oatmeal baths.
- Identifying triggers is crucial in managing hives effectively. Triggers can range from certain foods, stress, physical factors like temperature changes, to underlying health conditions such as autoimmune diseases.
- Complementary therapies including mind-body techniques like meditation can help manage stress-related outbreaks of urticaria by reducing inflammation and allergic responses.
Understanding Urticaria (Hives)
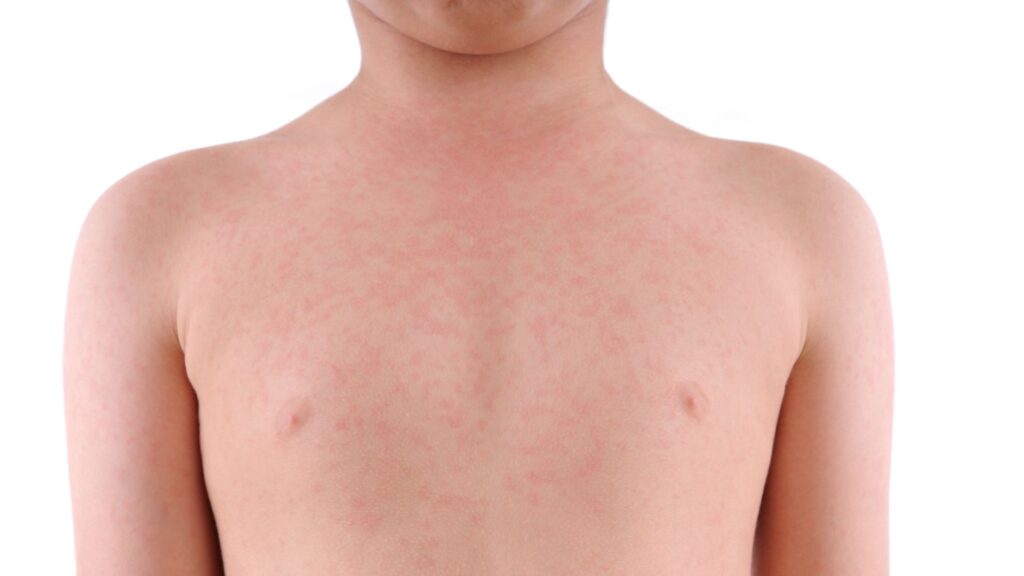
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, appears as an outbreak of swollen red bumps on the skin. These often result from the body’s reaction to certain allergens or conditions.
Definition and Overview
Hives, or urticaria, show up as red, sometimes itchy bumps on the skin. They usually happen because of an allergen. This skin condition involves erythematous, edematous plaques that can spread across the skin and mucous membranes.
These outbreaks might appear suddenly and can last for a short time or even become chronic.
Doctors often treat chronic hives with antihistamines that don’t make people sleepy to reduce itching and swelling. Other treatments include anti-inflammatory drugs, monoclonal antibodies like omalizumab, which is FDA-approved, and corticosteroids such as prednisone for more severe cases.
For quick relief from symptoms at home, taking a cool bath could also help manage the discomfort associated with hives.
Types of Urticaria: Acute vs. Chronic
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, affects the skin with red, itchy bumps. These reactions come in two main types: acute and chronic. Understanding them helps in managing symptoms effectively.
| Type | Description | Duration | Common Triggers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Urticaria | This type appears suddenly and is often a response to an allergen. | Less than 6 weeks | Food, medications, insect bites, or infections. |
| Chronic Urticaria | These hives last longer and may not have an identifiable cause. | More than 6 weeks | Often unknown, but can include stress, tight clothing, or illnesses. |
Acute urticaria can often be managed with over-the-counter antihistamines or a cool bath. Chronic hives, lasting more than 6 weeks, may require stronger medication. For chronic cases, doctors might prescribe antihistamines that don’t cause drowsiness, or even omalizumab, a once-monthly injection under the skin. Corticosteroids like prednisone are also an option. These treatments aim to ease itching and swelling, improving quality of life.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Hives
Identifying the symptoms of hives early can make a big difference in how you manage this skin condition. Hives typically appear as red, itchy bumps on the skin, signaling an allergic reaction or other underlying issue.
Common Physical Appearances
Hives, or urticaria, usually show up as red, itchy bumps on the skin. These bumps can appear suddenly and often in response to an allergen. They vary in size and shape but are generally swollen areas on the skin’s surface.
Sometimes hives form large patches that can cover significant parts of the body.
The appearance of hives is a key sign of this condition. These welts may turn white when pressed and are surrounded by an area of redness known as a flare. The rash typically lasts for a few hours to several days before fading away without leaving any marks.
Associated Symptoms Like Itching and Swelling
Itching and swelling are common symptoms of hives, also known as urticaria. These red bumps on the skin can cause discomfort. People often feel an urge to scratch due to the itchiness.
Swelling, or edema, accompanies these bumps, making the area appear larger.
Treatment options like over-the-counter antihistamines help with these symptoms. They reduce itching and swelling by blocking histamine in the body. Prescription medications offer stronger relief for chronic cases.
Moving on, let’s look at common triggers that might cause hives.
Common Triggers and Causes
Identifying the triggers of urticaria, commonly known as hives, plays a crucial role in managing this condition effectively. Allergens like pollen, certain foods, and even stress can provoke the immune system into an inflammatory response leading to red, itchy bumps on the skin.
Allergens and Physical Triggers
Urticaria, or hives, can flare up when your body reacts to allergens or physical triggers. This reaction leads to red, itchy bumps on the skin.
- Pollen: When inhaled, pollen can trigger allergic reactions leading to hives.
- Animal Dander: Pets like dogs and cats shed small flakes of skin that may cause allergic reactions in some people.
- Food Allergies: Foods such as nuts, shellfish, eggs, and dairy often trigger hives in sensitive individuals.
- Insect Bites and Stings: Reactions to bee stings or mosquito bites can cause swelling and redness around the bite site.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including aspirin and antibiotics like penicillin, can lead to an outbreak of hives.
- Latex: Exposure to latex products can trigger a reaction in people with a latex allergy.
- Physical Factors: Stress, cold temperatures, sun exposure, and exercise are known physical triggers of hives.
- Chemicals in Products: Cosmetics, soaps, and detergents contain chemicals that may cause hives upon contact with the skin.
- Dust Mites: These tiny creatures live in household dust and can provoke allergic reactions leading to skin rash.
- Mold: Breathing in mold spores from damp environments might trigger an outbreak of hives.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Sometimes, chronic urticaria is a sign of another health issue like thyroid disease or lupus.
Understanding these triggers helps manage and prevent future outbreaks by avoiding known allergens and factors that cause your body to react negatively.
Underlying Health Conditions
Hives, or urticaria, often have triggers rooted in various underlying health conditions. These issues can range from autoimmune disorders to infections and often require a health professional’s attention for proper management. Here’s a list of common health-related triggers:
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like lupus or thyroid disease can cause the body to attack its own tissues, leading to hives.
- Infections: Both viral and bacterial infections, such as the common cold or urinary tract infections, might trigger hives.
- Internal diseases: Issues with the liver or kidneys, as well as some cancers, have been connected to chronic hives.
- Hormonal imbalances: Changes in hormone levels, particularly due to thyroid problems or menopause, can instigate outbreaks of hives.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Diseases affecting the digestive tract, including celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), are linked to skin issues like urticaria.
- Allergic reactions: Not limited to external allergens, allergic reactions to medications or foods can cause hives as part of an immune response.
- Stress: Though not a direct cause, high stress levels can exacerbate existing cases of chronic hives.
Identifying and treating these underlying conditions is critical in managing urticaria effectively.
Diagnostic Approaches
Doctors often diagnose urticaria through a physical exam and reviewing the patient’s medical history. In some cases, they might perform allergy tests or blood work to identify the underlying causes of hives.
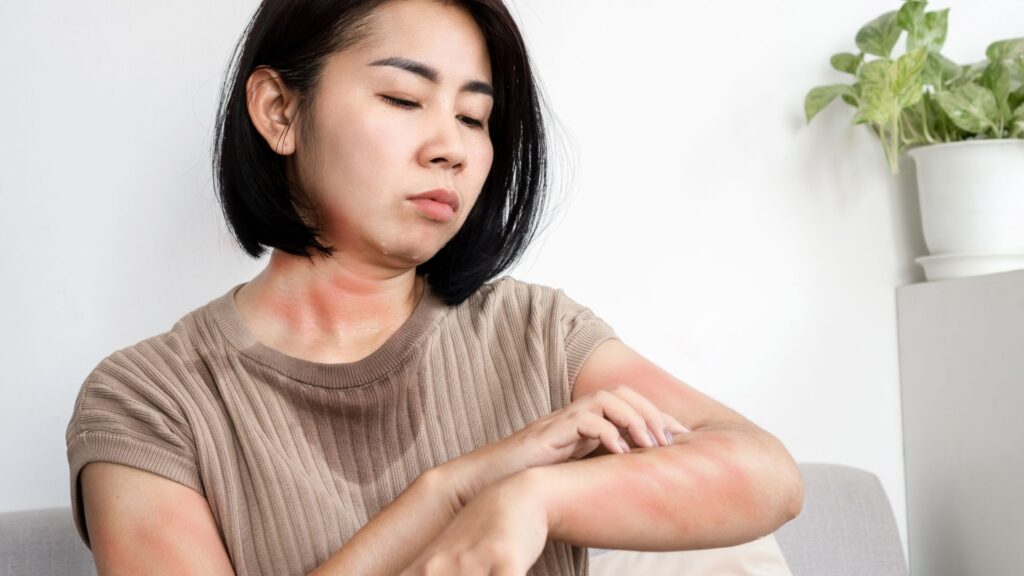

Clinical Diagnosis
Doctors use several methods to diagnose urticaria. They look at the skin and ask about any reactions to medicines, foods, or other allergens. A physical exam helps them see the hives and understand any related swelling or itching.
Sometimes, they might test for allergies or check if an underlying health condition is causing the hives.
Treatment begins with finding out what triggers your hives.
After diagnosing urticaria, knowing when to seek medical attention is crucial. This step guides patients on how to proceed in managing their condition more effectively.
When to Seek Medical Attention
You should seek medical attention for urticaria if the symptoms don’t improve with over-the-counter treatments. This includes antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs. If hives cover a large area of your body or last for more than six weeks, it’s time to see a doctor.
Omalizumab, an FDA-approved treatment, is available for chronic cases and requires a doctor’s prescription.
Emergency care is necessary when hives are accompanied by difficulty breathing, swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat. These signs could indicate a severe allergic reaction known as angioedema.
Corticosteroids like prednisone might be recommended by healthcare professionals in these scenarios. Always consult a dermatologist if your condition worsens or doesn’t respond to initial treatments.
Treatment Options for Urticaria
Examining therapy varieties for urticaria introduces possibilities for comfort and mastery over this frequently unsettling condition. From easy-to-access over-the-counter solutions to customized prescription drugs, efficient treatments focus on reducing symptoms and controlling causes.
Over-the-Counter Solutions
Over-the-counter solutions offer immediate relief for many dealing with the discomfort of hives. These accessible treatments can ease itching and reduce inflammation without needing a prescription.
- Antihistamines: Common antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) block the release of histamine, a chemical in the body that causes allergy symptoms such as itching and swelling. Taking these can provide quick relief from urticaria symptoms.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Non-prescription anti-inflammatory medications, including ibuprofen (Advil) and naproxen (Aleve), help reduce swelling, redness, and pain associated with hives.
- Cool baths: A soothing cool bath or applying cool compresses to the affected area can help relieve the burning sensation and itchiness caused by hives.
- Calamine lotion: Applying calamine lotion directly to the skin can calm down the irritation and itching due to its cooling effect.
- Hydrocortisone cream: This mild steroid cream helps decrease inflammation on the skin’s surface, easing redness and itchiness caused by hives.
- Oral corticosteroids: For more severe cases, over-the-counter oral steroids like prednisone can be used for short periods to drastically reduce inflammation under medical guidance.
Each of these treatments aims at managing symptoms until hives naturally resolve or until one can see a physician for potentially more potent prescribed medicines if necessary.
Prescription Medications
Surpassing standard over-the-counter solutions, doctor-prescribed medications provide enhanced relief for individuals grappling with urticaria. These medications focus on more profound symptoms and aim to minimize inflammation and allergic responses.
- Physicians frequently recommend antihistamine pills that don’t induce sleepiness for persistent hives. These pills provide relief from itching and swelling by blocking the histamine that the body releases during an allergic response.
- Omalizumab, an FDA-approved drug, introduces a progressive treatment for persistent urticaria. This medication is administered through a monthly injection under the skin, significantly reducing hive outbreaks.
- For acute cases of urticaria, potent anti-inflammatory drugs such as corticosteroids like prednisone are utilized. Despite their ability to swiftly diminish inflammation, their use entails expert medical oversight due to potential adverse effects.
- If hives are caused by auto-immune responses, immune-suppressing drugs may be recommended by physicians. These drugs aid in regulating the immune system to prevent it from affecting the body’s tissues.
- Monoclonal antibodies, excluding omalizumab, belong to an advanced category of treatments that target distinct pathways in the allergy response mechanism. They provide specialized therapies and foster optimism for patients with challenging chronic urticaria conditions.
The selection of these prescribed alternatives necessitates thoughtful deliberation and professional medical counsel to guarantee they align with the patient’s distinct health condition and overall wellness profile.
Complementary Therapies
Complementary therapies offer additional relief for people dealing with urticaria. These include methods such as colloidal oatmeal baths and mind-body therapies, which can ease symptoms and improve overall skin health.
Colloidal Oatmeal Baths
Colloidal oatmeal baths are a great way for people with urticaria to soothe their skin. This natural remedy involves adding powdered oatmeal to lukewarm water. The unique properties of colloidal oatmeal help to calm the itching, redness, and swelling associated with hives.
Oatmeal acts as an anti-inflammatory and a moisturizer, providing relief from the discomfort caused by this condition.
Patients can easily prepare these baths at home by grinding plain oats into a fine powder and dispersing them in the bathwater. Soaking in this mixture for about 15 minutes can significantly ease symptoms of urticaria.
Many find that regular colloidal oatmeal baths contribute to managing their skin’s sensitivity and reducing flare-ups over time.
Mind-Body Therapies
Moving from the relief that colloidal oatmeal baths offer, we explore another avenue to manage urticaria: mind-body therapies. These therapies focus on the connection between your mind and body, aiming to reduce stress which often triggers or worsens hives.
Techniques include meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises. They help calm the mind, leading to lessened symptoms in some individuals.
Practitioners believe that when you control your breathing and achieve a more peaceful state of mind, your body follows suit by lowering inflammation and allergic responses. Studies show meditation can significantly improve chronic skin conditions by reducing stress levels.
Reducing stress through mind-body therapies can ease urticaria symptoms.
Managing Urticaria at Home
Managing urticaria effectively at home involves adopting certain lifestyle changes and remedies. These strategies can help reduce flare-ups and ease symptoms, allowing individuals to maintain a higher quality of life despite their condition.
Lifestyle Changes
Making changes to your lifestyle can greatly improve the management of urticaria. These adjustments help in reducing the frequency and intensity of outbreaks.
- Stick to a diet that avoids known allergens. Common triggers include nuts, shellfish, eggs, and dairy products.
- Wear loose-fitting cotton clothes. This prevents irritation and allows the skin to breathe.
- Keep a diary to track your hives. Note what you eat, wear, and do before each outbreak.
- Reduce stress through activities like yoga and meditation. Stress can exacerbate urticaria symptoms.
- Maintain a cool environment at home. Heat can trigger or worsen hives.
- Exercise regularly but be mindful of your condition. Avoid workouts that make you overly hot or sweaty.
- Adopt good sleep habits to ensure adequate rest every night. Sleep helps regulate the immune system.
- Limit alcohol and caffeine intake, as they might trigger hives in some people.
Next, we explore home remedies and preventative measures for managing hives comfortably at home.
Home Remedies and Preventative Measures
After addressing lifestyle changes, it’s crucial to explore home remedies and preventive measures for urticaria. These strategies can empower individuals to manage symptoms more effectively.
- Apply cool compresses to affected areas to ease itching.
- Take a lukewarm bath with colloidal oatmeal or baking soda to soothe the skin.
- Use over-the-counter anti-inflammatory creams for immediate relief on small areas.
- Wear loose, soft clothing to prevent irritation from fabric friction.
- Avoid known triggers such as certain foods, medications, or stressors whenever possible.
- Keep a symptom diary to identify potential triggers and patterns of outbreaks.
- Incorporate stress-management techniques like yoga or meditation into your routine.
- Try natural supplements known for their anti-inflammatory properties, such as vitamin D or quercetin, but consult your doctor first.
- Maintain a cool environment at home and avoid sudden temperature changes to prevent hives from flaring up.
- Regularly moisturize your skin with hypoallergenic products to strengthen the skin’s barrier against allergens.
These measures can help manage the discomfort associated with urticaria and potentially reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
Are Hives Contagious?
Hives, known medically as urticaria, bring up a common concern: the fear of them being contagious. The truth is, hives themselves cannot spread from person to person. They manifest as red and sometimes itchy bumps on the skin caused by an allergic reaction or other triggers but do not transfer through contact.
This misunderstanding may arise because the symptoms of hives, such as swelling and redness, appear similar to conditions that are contagious.
Chronic hives can be managed with treatments like prescription antihistamines without causing drowsiness.
This quote highlights an important aspect of managing urticaria – focusing on treatment rather than worry about spreading it. Urticaria involves immune system responses to allergens among other causes but does not make it a condition others can catch.
Hence, while one might seek relief from symptoms through various medications or therapies mentioned in our guide, rest assured knowing the condition itself poses no risk of contagion to those around you.
Differences Between Hives and Other Skin Rashes
Hives stand out from other skin rashes due to their unique signs. These include red, sometimes itchy bumps that can appear because of an allergen. This reaction is not found in many other types of skin conditions.
For instance, chronic hives are a condition where such symptoms persist for long periods. They may require specific treatments like prescription antihistamine pills which do not make one drowsy.
Unlike eczema or psoriasis, which have more persistent and flaky patches, hives often manifest quickly and can vary in size. Each bump, or wheal, associated with urticaria typically has clear edges and can disappear or move to different areas within hours.
Treatment options also differ; while corticosteroids might be used across various rash types, Omalizumab injections target the immune response specifically related to chronic urticaria.
Conclusion
Urticaria, also known as hives, presents a significant challenge for many. This guide has aimed to cover crucial aspects from symptoms and triggers to treatments. Dr. Samuel Greene stands out in the field of dermatology with over 20 years of tackling skin conditions like urticaria.
His qualifications include a degree from Johns Hopkins University and numerous awards for his research on skin disorders.
Dr. Greene analyzes that understanding both acute and chronic forms of urticaria is key in choosing effective treatments. He highlights how antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs play central roles in managing this condition based on their ability to reduce itching, redness, and swelling.
On safety, ethics, and transparency points, Dr. Greene emphasizes the importance of FDA-approved medications like Omalizumab for chronic hives treatment. He insists on honest disclosure about possible side effects when using corticosteroids such as prednisone.
Incorporating treatments into everyday life requires adherence to prescribed regimens while monitoring triggers closely. Dr. Greene offers tips like keeping a symptom diary helps identify potential allergens or stress factors causing flare-ups.
His balanced evaluation considers both pros—such as immediate relief offered by over-the-counter solutions—and cons—including potential long-term side effects from corticosteroids.
Comparing these options shows that comprehensive management involves combining medicines with lifestyle adjustments.
Finally, according to Dr.Greene’s expert opinion, integrating standard medical treatments with careful attention to trigger avoidance provides the best approach for managing urticaria effectively Such an integrated method ensures individuals can maintain control over their symptoms while pursuing a quality life free from frequent discomfort.
FAQs
1. What are the symptoms of Urticaria, also known as hives?
Urticaria presents with a variety of symptoms including redness, itching, and swelling in patches on the skin. These symptoms can appear suddenly and may vary in severity from mild to severe.
2. How is Urticaria treated?
Treatment for Urticaria involves a combination of medications and supplements aimed at reducing inflammation and soothing the skin. This might include antihistamines, corticosteroids or other prescription medicines depending on the severity of your condition.
3. Are there any effective supplements for managing Urticaria?
Yes, certain dietary supplements such as Vitamin C and Quercetin have been found beneficial in managing Urticaria by boosting immune function and reducing inflammation.
4. Can lifestyle changes help manage Urticaria?
Absolutely! In addition to medication and supplements, making certain lifestyle changes like avoiding known allergens or triggers can significantly improve your condition.
General Facts
- Hives, also known as urticaria, are red and sometimes itchy bumps on the skin, typically caused by an allergen.
- Chronic hives can be treated with prescription antihistamine pills that don’t cause drowsiness, which can ease itching and swelling.
- Urticaria is characterized by erythematous, edematous, itchy, and transient urticarial plaques that cover the skin and mucous membranes.
- Urticaria can be treated with over-the-counter antihistamines, anti-inflammatory drugs, monoclonal antibodies, or even a cool bath.
- Omalizumab is an FDA-approved treatment for chronic urticaria and is injected under the skin once a month.
- Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can also be used to treat hives.
- Some people may seek ways to cure urticaria permanently, while others may be interested in self-care methods.
- WebMD provides information on the causes, diagnosis, treatment, and management of hives and angioedema.
- There are pictures of hives and their potential causes available for reference.
- There are questions related to the best medicine for urticaria, urticaria medication, and how to cure hives fast.
Source URLs
Here are SEO-friendly, easy-to-read versions of the links you provided:
- American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology – Hives Overview
acaai.org/allergies/hives - Medical News Today – Hives Information
medicalnewstoday.com/hives - Mayo Clinic – Chronic Hives Diagnosis and Treatment
mayoclinic.org/chronic-hives - NCBI – Chronic Urticaria Study
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/chronic-urticaria - WebMD – Hives (Urticaria) and Angioedema
webmd.com/hives - Verywell Health – Treating Urticaria
verywellhealth.com/treating-urticaria - American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology – Hives and Angioedema Overview
aaaai.org/hives











