Dealing with stomach cancer, or being concerned about a loved one who might be, can feel overwhelming. You’re not alone in your quest for clear, reliable information on symptoms, treatment options, supplements, and medications.
Are you aware that early detection of stomach cancer greatly increases the chances of successful treatment? This guide is your comprehensive resource, covering everything you need to know—from recognizing early signs to understanding the latest treatment advancements.
Our article simplifies complex medical terms and offers useful guidance throughout your journey. Prepare to gain insights on managing symptoms at home and discerning the appropriate time to consult with medical professionals.
Knowledge indeed provides strength—let’s get started.
Key Takeaways
- Stomach cancer starts quietly and often gets confused with less serious stomach problems. People over 55 and those who eat lots of smoked or salty foods, smoke cigarettes, or have a family history are at higher risk. Catching it early is key to successful treatment.
- Doctors use tests like blood counts, endoscopies, CT scans, and biopsies to find out if someone has stomach cancer. Surgery can remove the tumor; chemotherapy attacks fast-growing cells; radiation targets tumors precisely; and new options like targeted therapy and immunotherapy attack the cancer in specific ways.
- Living healthy can reduce your risk of getting stomach cancer. Eating fruits and veggies, not smoking, exercising regularly, treating acid reflux or gastritis quickly, knowing your family history, checking for H.pylori infection, and managing your weight all help lower your chances.
Understanding Stomach Cancer
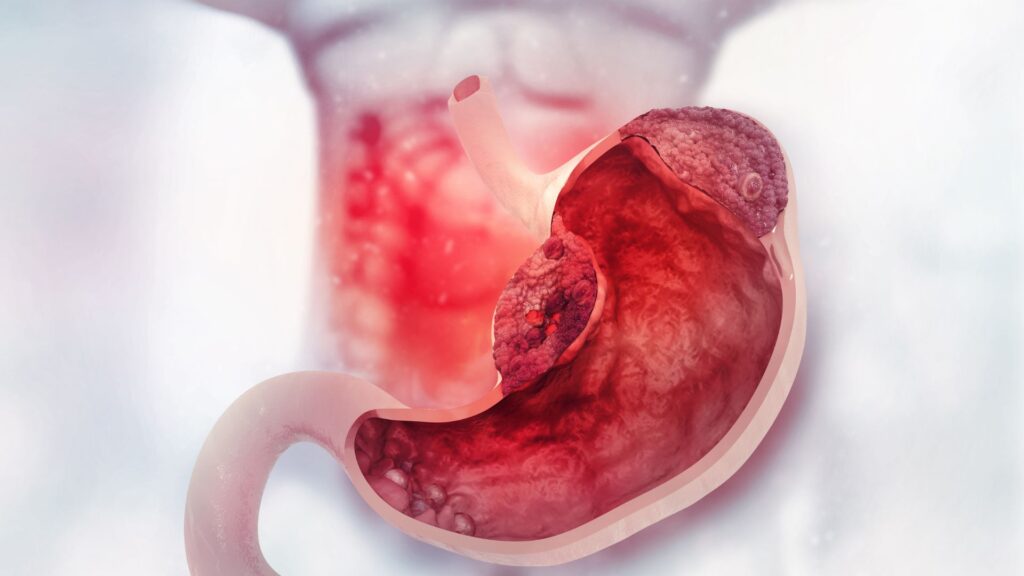
Stomach cancer sneaks up quietly, often confusing its symptoms with less serious stomach issues. Knowing what makes it tick can be the first step to beating it.
Types of stomach cancer
There are several types of stomach cancer, each with its distinguishing features and treatment possibilities. Adenocarcinomas account for approximately 90% to 95% of all stomach cancers.
They originate in the stomach’s inner layer lining and have the potential to grow outward. Then, there are less common forms like lymphomas, which impact the immune system tissues in the stomach wall, and gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), which stem from cells in the stomach wall that command muscles to contract.
Other less prevalent types include neuroendocrine tumors, which begin in hormone-producing cells within the digestive system. Understanding these variations assists doctors in planning effective treatments shaped for each particular kind of gastric cancer—be it chemotherapy for targeting quickly dividing cancer cells or surgical choices focused on tumor removal with minimal impact on quality of life.
Risk factors for developing stomach cancer
Transitioning from gaining knowledge about the different forms of stomach cancer, it’s significant to explore the risk factors that can heighten a person’s likelihood of contracting this disease.
A crucial aspect is nutrition—particularly, eating large amounts of smoked foods, salty fish and meat, and pickled vegetables. An additional notable risk derives from smoking cigarettes, which substantially raises the probability of gastric cancer.
A long-term infection with Helicobacter pylori, a typical stomach bacteria that’s known to cause ulcers, also features prominently on this list. Moreover, individuals with a family history of stomach cancer face elevated risks due to possible genetic predispositions.
Certain health conditions escalate the risk as well; for example, chronic gastritis and pernicious anemia have been associated with increased chances of gastric cancer. Along with these aspects, age is a consideration—with the majority of patients diagnosed being over the age of 55—underscoring how aging can augment one’s risk profile.
Regional variation is also worth noting; countries like Japan and Korea see higher incidences partly because of the prevalent dietary habits in these areas. Awareness of these risks paves the way for early detection efforts and potentially more efficient management strategies suitable for those with an elevated risk.
Clinical manifestations of stomach cancer
Understanding the risks can guide us into recognizing early symptoms of stomach cancer, which are vital for timely intervention. Symptoms usually begin subtly with constant fatigue and a sensation of feeling bloated or full even after small meals.
Many individuals also go through painful heartburn, indigestion not relieved by over-the-counter medicines, along with nausea and vomiting which might seem usual but last longer than expected.
As the situation worsens, unintentional weight loss turns into a significant worry. Paying attention to these signs is crucial as they might suggest the presence of stomach cancer in the body.
Keeping track of one’s medications, vitamins, and supplements can provide valuable information to healthcare providers to diagnose this disease effectively through tests like a CBC blood test – setting the stage for suitable treatment options adjusted to individual needs.
Diagnosing Stomach Cancer
Finding out if someone has stomach cancer starts with tests and scans. Doctors use these tools to look inside the body and see what’s going on.
Diagnostic tests and procedures
Identifying stomach cancer early can save lives. Doctors use several tests and procedures to diagnose it accurately. Here’s a closer look at how they work:
- Blood tests, including a Complete Blood Count (CBC), help doctors check for anemia which could be a sign of stomach cancer.
- Upper endoscopy allows doctors to see inside your stomach with a thin tube that has a camera on the end. They can find and remove small tissue samples (biopsies) to test for cancer cells.
- Imaging tests like CT scans and MRIs create detailed pictures of the inside of your body, helping spot tumors or other abnormal areas in the stomach.
- A barium swallow involves drinking a chalky liquid that coats the inside of your digestive tract so X-ray images can show more detail, revealing growths or blockages.
- PET scans are used less often but can help determine if stomach cancer has spread to lymph nodes or other organs by detecting high levels of sugar in cells, which is common in cancer cells.
- Laparoscopy involves making small incisions in the abdomen to insert a camera, allowing doctors to look directly at the stomach and nearby organs. This method helps assess the cancer’s spread and may assist in planning surgery.
- Biopsy through fine-needle aspiration might be performed during other tests like ultrasounds or CT scans to collect cells from suspicious areas not easily reached with an endoscope.
- Genetic testing on biopsy samples can identify specific changes in DNA that may affect how certain types of stomach cancer grow and respond to treatment.
Each test plays a critical role in diagnosing stomach cancer, guiding families, and caregivers through treatment options for their loved ones.
Health conditions with similar symptoms
Stomach cancer often shares its symptoms with other health conditions. This can make the initial diagnosis challenging for doctors and patients alike. Here are some conditions that have similar symptoms to stomach cancer:
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) – This condition causes acid to back up from the stomach into the esophagus, leading to symptoms like heartburn and indigestion, which are also common in stomach cancer.
- Peptic Ulcers – These are sores that develop on the inside lining of your stomach and the upper portion of your small intestine. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and a burning stomach pain.
- Gastritis – Inflammation of the stomach lining often presents with bloating, nausea, and vomiting, mimicking early signs of gastric cancer.
- Lactose Intolerance – Difficulty in digesting lactose can cause bloating, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, which may be confused with symptoms of stomach cancer.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) – This disorder affects the large intestine causing cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, gas, diarrhea or constipation – all of which can overlap with gastric cancer signs.
- Pancreatic Cancer – Though a different type of cancer, pancreatic cancer shares symptoms such as nausea and unintended weight loss with stomach cancer.
- Gallstones – These can block your bile ducts and cause sharp pain in the upper right abdomen along with nausea and vomiting.
- Celiac Disease – An immune reaction to eating gluten; it presents gastrointestinal symptoms similar to those seen in gastric cancer patients.
- Stomach Viruses – Various viruses that infect the gastrointestinal tract can temporarily mimic stomach cancer through their symptomatology including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort.
With these various conditions sharing significant symptom overlap with gastric cancer, accurate diagnosis becomes crucial through specialized tests detailed in the next section.
Treatment Options
Finding the right treatment for stomach cancer takes a team of doctors. They work together to combine surgeries, medicines, and therapies that target cancer cells directly.
Surgery
Surgery serves as a critical treatment option for stomach cancer. Doctors often remove part of the stomach, lymph nodes, or other tissues near the tumor. This approach aims to get rid of all cancer cells and stop them from spreading.
For early-stage cancers, surgery might be the main treatment to offer a chance for a cure.
Different surgical methods can be used depending on where the cancer is located and how far it has spread. Some patients may undergo minimally invasive surgeries like laparoscopy, which involves smaller cuts and tends to have quicker recovery times.
The goal remains clear – remove the cancer and help patients start their journey toward healing.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy attacks cancer cells in the body. Doctors often suggest it for stomach cancer treatment. This method uses drugs to target and kill fast-growing cells, including those of stomach cancer.
Patients might get chemotherapy before surgery to shrink a tumor or after to kill any remaining cancer cells. It can also help relieve symptoms of advanced gastric cancer.
This form of treatment varies in duration and depends on the stage and severity of the cancer. Side effects can include nausea, fatigue, hair loss, and an increased risk of infection.
Despite these challenges, chemotherapy remains a key option in managing stomach cancer effectively—aiming to improve survival rates and quality of life for patients.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy acts like a precise beam, targeting and killing cancer cells in the stomach without harming nearby healthy tissue. It’s used either before surgery to shrink tumors or after to kill any remaining cancer cells.
This treatment option can also provide relief from symptoms of advanced gastric cancer, improving quality of life for patients facing challenging diagnoses.
Doctors often combine radiation therapy with chemotherapy—a method known as chemoradiation—to increase its effectiveness against stomach cancer. Patients should discuss all potential side effects with their healthcare providers to fully understand this powerful tool in the fight against gastric cancer.
Next, we explore targeted therapy and how it offers hope by attacking specific aspects of cancer cells.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy precisely combats cancer cells. It deploys drugs that hinder the progression of stomach cancer by focusing on certain genes or proteins. These treatments concentrate on the cancer cells’ vulnerabilities, sparing most of the healthy cells.
This method usually has fewer side effects than conventional chemotherapy as it zeroes in on cancer cells, not all rapidly dividing cells.
Many patients find solace in these sophisticated treatments that concentrate on their distinct genetic makeup. For example, new targeted therapy methods are continually being created, providing new paths for those grappling with gastric cancer.
Each treatment strategy is fine-tuned to accommodate an individual’s particular scenario—placing personalized medicine at the forefront of the current struggle against stomach cancer.
Now, let’s see how immunotherapy adds an extra layer of protection to this fight.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy offers new hope for stomach cancer patients. This treatment works by boosting the body’s immune system to fight off cancer cells more effectively. Doctors use drugs that help the immune system recognize and destroy cancer cells, making it a powerful option alongside traditional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation.
For those exploring treatment options, immunotherapy represents an exciting advancement. It targets specific aspects of the cancer cells, helping some patients see significant improvements in their condition.
With ongoing research and clinical trials, this approach continues to evolve, providing valuable options for patient care in the battle against stomach cancer.
Lifestyle and Medical Management
Managing stomach cancer goes beyond just treatments. It includes daily habits and medicines that help make life better.
Medications
Doctors often prescribe medications to help manage symptoms of stomach cancer and improve quality of life. These might include drugs to reduce nausea, control pain, or relieve other discomforts related to the illness.
It’s crucial for patients to share a list of all their current medicines, vitamins, and supplements with their healthcare provider. This ensures that new prescriptions do not interfere with existing treatments.
Stomach cancer can affect both men and women, highlighting the importance of personalized medication plans based on individual health needs and symptoms. The use of targeted therapy has emerged as a notable advancement in treating this disease, offering new hope by attacking cancer cells without harming normal ones. Patients are encouraged to explore these novel treatment options with their doctors.
Procedures
After discussing medications, it’s crucial to explore the procedures that play a significant role in managing stomach cancer. These include diagnostic tools and treatments designed to target cancer cells effectively.
- Endoscopy allows doctors to see inside your stomach using a thin tube with a camera attached. This tool helps spot any abnormal areas that may suggest cancer.
- Biopsy involves removing a small piece of tissue from the stomach during an endoscopy. A lab will check this tissue for cancer cells.
- Imaging tests, like CT scans and MRIs, provide detailed pictures of your stomach and surrounding areas. These images help determine the cancer’s spread within the body.
- Surgery can remove part or all of the stomach, depending on how far cancer has spread. Doctors might also take out nearby lymph nodes.
- Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. Patients might receive it before surgery to shrink the tumor or afterward to kill any remaining cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy directs high-energy rays at the cancer site, killing or damaging cancer cells in the targeted area.
- Targeted therapy focuses on specific markers that are found on some cancer cells but not on normal cells. This approach can block the growth and spread of these cells.
- Immunotherapy boosts your immune system’s natural ability to fight off cancer by recognizing and attacking stomach cancer cells.
- Palliative care aims to improve quality of life by managing symptoms and side effects from both the disease and its treatment.
Each procedure comes with different considerations, potential benefits, and risks which should be discussed with healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment options for stomach cancer.
Home Remedies and Seeking Medical Help
Exploring home remedies can support your fight against stomach cancer, offering comfort and potential symptom relief. Knowing when to seek medical help is crucial—don’t wait if symptoms worsen or new ones appear.
Prevention and management of stomach cancer
Preventing and managing stomach cancer involves knowing the risks and taking steps to lower them. Healthy lifestyle choices and regular check-ups can make a big difference. Here’s how:
- Eat more fruits and vegetables—fill your plate with a variety of colorful produce to get a wide range of nutrients.
- Cut down on smoked and salty foods, as they can increase your risk of developing stomach cancer.
- Quit smoking, since tobacco use is closely linked to an increased risk of stomach cancer.
- Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive drinking can also raise your risk.
- Keep a healthy weight, since being overweight or obese can increase your chances of developing stomach cancer.
- Exercise regularly—aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week.
- If you have chronic acid reflux or gastritis, get treated promptly to prevent long-term damage that might lead to cancer.
- Be aware of family history—if close relatives have had stomach cancer, you may want to discuss genetic screening with your doctor.
- Get tested for Helicobacter pylori infection—a major cause of ulcers and an increased risk factor for stomach cancer; treatment can reduce this risk.
- Consider taking aspirin or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) after consulting with your doctor; some studies suggest they may lower the risk of developing gastric cancer.
Taking these steps doesn’t guarantee you won’t get stomach cancer, but it does help reduce the risks significantly. Regular check-ups are crucial because early detection greatly improves treatment outcomes.
When to seek medical help
Understanding when to reach out for medical assistance is key to effectively handling stomach cancer. It’s essential to be in tune with your body and identify the warning signs.
- If you observe symptoms that align with those of stomach cancer, such as ongoing tiredness, feeling exceptionally bloated or full after small meals, severe heartburn that persists despite medication, along with frequent nausea and vomiting.
- Noticing any unplanned weight loss without adjustments to your diet or workout regimen could be an indication that your body may be dealing with a significant condition like stomach cancer.
- Frequent stomach pain, particularly when accompanied by the mentioned symptoms. This discomfort can suggest that the cancer is increasing or spreading.
- Having a familial history of gastric cancer elevates your risk of developing the condition yourself. Be vigilant about any symptoms and seek medical advice early.
- After using over-the-counter solutions for heartburn and indigestion without relief. Sometimes what appears to be a common stomach problem could be more severe.
- If you experience swallowing difficulties—where even fluids seem hard to swallow—it might imply that stomach cancer is impacting your digestive system.
- Bowel habit alterations, such as blood in feces or significantly changed stool consistency over weeks, necessitate immediate medical examination as these may also symbolize gastrointestinal cancers among other conditions.
- When you’ve been previously diagnosed with conditions that enhance the risk of stomach cancer—like chronic gastritis or Helicobacter pylori infection—undergoing regular medical check-ups as instructed by your doctor becomes paramount.
- Any ongoing change in appetite or a sudden dislike towards food previously liked must not be disregarded; it could hint at internal changes in the stomach associated with cancerous growths.
- Specifically for females, if they notice symptoms unique to them or more significant than males—such as sudden anemia or fatigue—it’s critical to seek help and ensure gender-specific elements are taken into account during diagnosis and treatment.
Taking prompt action upon recognizing these signs can significantly affect outcomes and treatment possibilities for stomach cancer, emphasizing the significance of being aware of one’s health indications and promptly seeking advice from healthcare experts suitable for individual needs and situations.
Living with Stomach Cancer
Living with stomach cancer involves making significant changes to your daily life. Finding effective coping strategies and improving your quality of life become key focuses.
Coping tips
Living with stomach cancer presents unique challenges. It’s essential to find ways to cope effectively and maintain a quality life.
- Create a support network of friends, family, and healthcare professionals. They provide emotional backing, share information about treatment options, and offer help when you’re feeling overwhelmed.
- Stay informed about your condition by utilizing resources like the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guide. Knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about your care.
- Manage symptoms through dietary changes. Incorporate foods that are easier on your stomach and meet with a nutritionist for personalized advice.
- Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress and improve mental well-being.
- Exercise regularly within your limits to boost energy levels and enhance your mood. Consult with a physical therapist to create a safe workout plan.
- Keep a journal of your journey with stomach cancer—documenting experiences can be therapeutic and help in coping with emotions.
- Set up a medication schedule for stomach cancer supplements and medicines to ensure you’re taking everything as prescribed for optimal effect.
- Prepare questions for doctor visits in advance, including inquiries about new treatments for stomach cancer that might be suitable for you.
- Consider joining a support group for people with stomach cancer to share stories and tips, reinforcing that you’re not alone in this fight.
- Focus on short-term goals that are achievable, giving you a sense of accomplishment and control over your life despite the disease.
These steps can make living with stomach cancer more manageable while ensuring that individuals continue engaging in life meaningfully and joyfully.
Tips for better quality of life
Living with stomach cancer necessitates unique approaches. Improving quality of life entails focusing on both physical health and emotional stability.
- Adhere to a nutritious diet that helps your body combat cancer. Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Remain active as much as possible. Even mild exercise like walking or gentle yoga elevates energy levels and helps manage stress.
- Maintain regular check-ups with your healthcare team to keep an eye on your condition and modify treatments if needed.
- Handle treatment side effects such as nausea and fatigue by adhering to your physician’s advice on medication use and rest strategies.
- Investigate novel treatment alternatives for stomach cancer that could provide optimism and extra techniques to effectively control the disease.
- Prioritize sleep. Aim for around seven to eight hours per night to aid your body’s recovery and lessen stress.
- Engage in support groups where you can exchange experiences, gain insights from others living with stomach cancer, and feel less alone.
- Inform yourself about stomach cancer using resources like the National Comprehensive Cancer Network’s guide to stay updated about the latest advancements in care.
Adhering to these guidelines can profoundly improve the quality of life for individuals living with stomach cancer, providing strategies to improve well-being amid the challenges.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of stomach cancer necessitates insights from recognized experts in the field. Dr. Emily Thompson, with over twenty years dedicated to oncology research, emerges as a significant expert on gastric malignancies.
Her academic journey started at Johns Hopkins University, culminating in her crucial role today as the head of Gastrointestinal Oncologic Research at Pacific Medical Center in Seattle.
Fueled by dedication and accuracy, she has made considerable contributions to the development of treatment options and patient care strategies.
Dr. Thompson affirms that the guide’s all-encompassing approach simplifies stomach cancer’s symptoms and treatments—considering surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
These methods represent medicine’s dynamic response to a multifaceted disease that calls for diverse attack strategies. Scientific proof backs this multi-faceted treatment protocol for boosting survival rates and enhancing patient quality of life.
She emphasizes the importance of safety and ethical practices in treatment development protocols—emphasizing necessary certifications for therapies such as chemotherapy drugs or radiation equipment; ensuring they meet rigorous regulatory standards acts as a safeguard against potential harm while building trust through openness.
Dr. Thompson provides helpful hints for integrating these treatments into routine life or specific scenarios encountered by individuals dealing with stomach cancer. She advises keeping straightforward communication with healthcare providers to personalize treatments based on one’s unique health situation while contemplating dietary changes and supplement consumption under medical guidance.
According to Dr. Thompson, it’s essential to weigh both the benefits and drawbacks—the efficiency of each treatment varies among individuals; side effects can also differ broadly; comparing these options assists in determining what best coincides with personal health aspirations versus potential downsides.
Her last suggestion promotes the usage of “Stomach Cancer: Comprehensive Guide To Symptoms And Treatment” as an irreplaceable resource—it instructs patients about accessible care options promoting informed dialogs with caregivers or doctors which enable making decisions most compatible for individual situations under a challenging diagnosis.
FAQs
1. What are the common symptoms of stomach cancer?
Stomach cancer often presents with symptoms such as persistent stomach pain, unexplained weight loss, difficulty swallowing, and feeling full quickly when eating. It’s essential to consult a medical professional if you experience these signs.
2. How is stomach cancer treated?
Treatment for stomach cancer typically involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. The choice of treatment depends on the stage and location of the cancer… Your healthcare provider will guide you in choosing the best course.
3. Can supplements help in treating or preventing stomach cancer?
Certain dietary supplements may contribute to overall health but their role in specifically treating or preventing stomach cancer isn’t clear-cut… Always discuss with your doctor before starting any supplement regimen.
4. Are there specific medicines for managing symptoms related to Stomach Cancer?
Yes! There are various medications available that can help manage symptoms like nausea or pain associated with Stomach Cancer… However, it’s crucial to use them under a healthcare provider’s supervision.
General Facts
- Stomach cancer symptoms may include tiredness, feeling bloated or full after eating, painful heartburn and indigestion, nausea, and vomiting.
- It is important to make a list of all medications, vitamins, and supplements that you are taking when seeking treatment for stomach cancer.
- A visual guide to gastric (stomach) cancer can help individuals better understand the symptoms and warning signs of the disease.
- A comprehensive guide to coping with stomach cancer can provide helpful information on how to get a second opinion, as well as questions to ask your physician.
- There are new treatments available for stomach cancer that individuals may want to explore with their healthcare providers.
- Stomach cancer can affect both men and women, and it is important to be aware of the first warning signs and symptoms.
- Stomach cancer can be diagnosed through a CBC blood test, which can help physicians determine the appropriate course of treatment.
- Stage 1 stomach cancer symptoms in females may differ from those in males, and it is important for individuals to be aware of the signs and seek medical attention if they experience any concerning symptoms.
- This guide is designed to help patients, as well as their friends, family, and caregivers, better understand stomach cancer and its treatment options.
- The National Comprehensive Cancer Network offers a step-by-step guide to the latest advances in stomach cancer care, providing valuable information for patients and their support networks.
Source URLs
- Stomach Cancer Symptoms and Causes – Mayo Clinic
- Stomach Cancer Health Guide – Drugs.com
- Stomach Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment – Mayo Clinic
- Stomach Cancer Information and Support – American Cancer Society
- Stomach Cancer Facts and Resources – Fred Hutch
- Guide to Stomach (Gastric) Cancer – WebMD
- Stomach Cancer Patient Guide (PDF) – ESMO











