Dealing with diabetes can feel like a full-time job. From watching what you eat to keeping track of blood sugar levels, it’s a condition that requires constant attention. One relevant fact is that maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is crucial in managing both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes effectively.
Our guide provides the tools you need to manage your diabetes successfully, offering advice on everything from medication and supplements to lifestyle changes.
This article will walk you through understanding your condition better, exploring treatment options, and embracing comprehensive management strategies. Stay tuned for insights that could make all the difference.
Key Takeaways
- Managing diabetes involves understanding the types and symptoms, using medications like metformin and insulin, making lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, and considering supplements for nutritional gaps.
- Mental health support and joining support groups are crucial for coping with the emotional aspects of diabetes. Regular check-ups help adjust treatments over time.
- Special considerations are necessary for different groups such as women, older individuals, and coordinating care among various healthcare providers to effectively manage diabetes.
Understanding Diabetes
Getting to know diabetes starts with recognizing its types and how it affects your body. Next, you learn about the symptoms and what leads some people to get this condition.
Types of diabetes (type 1, type 2, gestational)
Type 1 diabetes happens when the body can’t make insulin. This kind needs insulin therapy for blood sugar control, making daily monitoring crucial. Experts find that creating a care plan with healthy eating and exercise plays a key role in managing Type 1.
Type 2 diabetes develops when the body struggles to use insulin right. Lifestyle changes like diet improvement and regular exercise are often first steps in treatment. Medicines such as metformin help keep blood sugar levels stable for those living with Type 2.
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually goes away after giving birth. However, it demands careful management to protect both mother and baby’s health. Blood sugar monitoring becomes essential, alongside following a doctor-recommended diet and exercise plan.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Feeling thirsty all the time, urinating often, losing weight without trying, and feeling tired are common signs of diabetes. Some people might also notice sores that heal slowly or frequent infections.
These symptoms can sneak up on you and start mild. To diagnose diabetes, doctors use blood tests like the A1C test, which shows your average blood sugar level over the past 3 months.
If your A1C is 6.5% or higher on two separate tests, you have diabetes.
Creating a care plan starts with recognizing these symptoms early and getting diagnosed. This involves learning how to manage your blood sugar levels through daily routines while being aware of factors that affect them.
Now let’s explore the treatment options available to keep diabetes under control.
Early diagnosis of diabetes is key to managing the condition effectively.
Risk factors
After understanding the symptoms and diagnosis of diabetes, it’s crucial to consider the risk factors that may increase someone’s chances of developing this condition. Genetics plays a significant role—if your family has a history of diabetes, your own risk goes up.
Age is another factor; people over 45 are more likely to be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Being overweight or obese directly impacts how your body uses insulin, making weight ciritcal in managing blood sugar levels.
A sedentary lifestyle adds to the risk as well—regular physical activity helps control weight and improves insulin sensitivity.
Diet also influences diabetes risk. Eating foods high in refined sugars and fats can lead to obesity, which is closely linked with type 2 diabetes. Stress management should not be overlooked either; chronic stress affects blood sugar control.
Lastly, high blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels can indicate an increased risk for type 2 diabetes as part of metabolic syndrome—a cluster of conditions including excess belly fat and elevated glucose levels—that affect heart health and blood sugar regulation.
Treatment Options
Finding the right path to manage diabetes involves exploring various treatments. From medications that help control blood sugar to lifestyle adjustments, each step is crucial for health.
Medications (oral, injectable)
Managing diabetes often requires taking medication. These medicines help control blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
- Metformin: This is the most common oral medication for type 2 diabetes. It works by reducing glucose production in the liver and improving insulin sensitivity.
- Sulphonylureas: Pills like glipizide, glyburide, and glimepiride increase insulin production from the pancreas.
- Prandial glucose regulators are fast-acting medicines that stimulate insulin release during meals, helping manage spikes in blood sugar.
- DPP-4 inhibitors such as sitagliptin and linagliptin work by increasing insulin release and decreasing glucagon levels after meals, without causing weight gain.
- GLP-1 receptor agonists: Injectable drugs like exenatide and liraglutide mimic a natural hormone to lower post-meal blood sugar. They also slow stomach emptying and may promote weight loss.
- SGLT2 inhibitors: Empagliflozin and canagliflozin are oral medications that help the kidneys remove glucose from the bloodstream via urine.
- Insulin therapy: Various types of insulin manage blood sugar at different times of day—rapid-acting for mealtime, long-acting for overnight control, among others.
- Combinations: Some people might need a mix of oral drugs or both oral medications and injectables to effectively manage their diabetes.
These treatments must be part of a comprehensive care plan including diet, exercise, regular check-ups, and self-monitoring of blood glucose to effectively manage diabetes and reduce the risk of complications.
Insulin therapy
Insulin therapy plays a crucial role in diabetes management, especially for those with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2. This treatment helps control blood sugar by acting as a substitute for or supplement to the body’s own insulin.
Patients might use different types of insulin—rapid-acting, long-acting, or a mix of both—to mimic the body’s natural insulin patterns. The right dosage and timing are essential for effectiveness.
Doctors often determine these based on individual needs, taking into account food intake, exercise routines, and other medications.
Moving on from insulin therapy requires patients to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly. This ensures that they can adjust their insulin doses correctly and maintain healthy glucose levels in their bloodstream.
Monitoring also alerts patients to any sudden changes that might indicate problems like hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Next up is exploring lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise for comprehensive diabetes management.
Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise)
After exploring insulin therapy, we now shift our focus to lifestyle changes. Managing diabetes effectively goes beyond medication; diet and exercise play crucial roles.
- Eating a balanced diet is key for blood sugar control. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit foods high in sugar and fat.
- Regular physical activity helps the body use insulin more efficiently. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Keeping track of carbohydrate intake can prevent blood sugar spikes. Use food labels and measuring tools to stay within your daily carb goals.
- Stay hydrated by drinking water throughout the day. This helps remove excess glucose through urine.
- Monitor portion sizes to avoid overeating. Smaller, more frequent meals can help maintain steady blood sugar levels.
- Choose foods with a low glycemic index (GI) whenever possible. Low-GI foods raise blood glucose levels less than high-GI foods.
- Reduce stress through techniques such as yoga or meditation since stress can affect blood glucose levels.
- Get enough sleep every night—lack of sleep can disrupt blood sugar regulation and appetite control.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake, as these can worsen diabetes complications.
- Work closely with a healthcare provider or a dietitian to create a personalized nutrition plan that fits your specific needs and goals.
Each step toward healthier habits makes a difference in managing diabetes and enhancing overall well-being.
Comprehensive Management
Comprehensive management keeps you in control of your diabetes every step of the way—learn all about it to take charge of your health.
Blood sugar monitoring
Keeping track of blood sugar levels is crucial for anyone with diabetes. It helps you understand how well your care plan is working. Regular monitoring can show the effects of foods, exercises, and medicines on your glucose levels.
This data helps make necessary adjustments to keep your blood sugar within target ranges.
Doctors often recommend checking blood sugar several times a day using a home glucose monitor. The results guide decisions about diet, physical activity, and medications. Over time, patterns emerge that can lead to more personalized diabetes management strategies.
Managing diabetes effectively means understanding the fluctuations in your blood sugar and responding accordingly.
Let’s explore self-care practices next.
Self-care practices
Taking control of your diabetes is crucial for a healthier life. Self-care practices play a significant role in managing your condition effectively. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Schedule daily blood sugar monitoring to understand how foods, physical activity, and medications affect your levels.
- Create a balanced diet plan that includes nutrient-rich foods, focusing on controlling blood sugar as part of comprehensive diabetes management.
- Incorporate regular exercise into your routine, aiming for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days to help manage weight and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Take all prescribed medications, including metformin or insulin therapy, as directed by your healthcare team to maintain optimal blood glucose levels.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day, helping to lower blood sugar by flushing excess glucose through urine.
- Practice good foot care by checking for cuts, sores, or blisters daily—issues that can lead to complications if left untreated in people with diabetes.
- Manage stress through techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, reducing the negative impact stress has on blood sugar levels.
- Aim for quality sleep every night; poor sleep can affect blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity.
- Keep up with regular check-ups with your healthcare team to adjust your care plan as needed based on changes in weight or physical activity habits.
- Educate yourself about diabetes by reading up on management guidelines and treatment recommendations; knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about your health.
By following these self-care steps, individuals with diabetes can significantly influence their overall well-being and quality of life while minimizing the risk of complications associated with the condition.
Regular check-ups
Regular check-ups are crucial for keeping diabetes under control. Doctors use these visits to monitor blood sugar levels and adjust medications or insulin therapy as needed. They also check for any complications like vision problems or kidney damage.
These appointments are a key part of the diabetes care plan, ensuring patients stay healthy and manage their condition effectively.
During these visits, patients can discuss their lifestyle changes—such as diet and exercise—with healthcare professionals. This team approach helps individuals understand how different factors affect their blood sugar.
With guidance from their treatment team, patients learn to make adjustments that improve their health over time.
Importance of Supplements
Supplements play a key role in managing diabetes. They fill nutritional gaps and support overall health, making them vital for daily care.
Vitamins and minerals for diabetes management
Managing diabetes means keeping blood sugar levels under control. Vitamins and minerals play a key role in this process.
- Magnesium helps lower blood sugar levels by improving insulin’s ability to work in the body. Many people with type 2 diabetes have low levels of magnesium, so boosting intake can be beneficial.
- Chromium is important for fat and carbohydrate metabolism. It enhances insulin action, making it easier for your cells to take up glucose from the blood.
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) may prevent complications related to diabetes, such as nerve damage. People with diabetes often have thiamine deficiency, leading to high blood sugar levels.
- Vitamin D supports the pancreas in insulin production during prediabetes stages and in those already living with diabetes. Low Vitamin D levels have been linked to a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil supplements, improve insulin sensitivity. They also help reduce inflammation and risk factors for heart diseases—common conditions alongside diabetes.
- Calcium works alongside Vitamin D and is vital for healthy bones and teeth; a necessity since people with diabetes can have an increased risk of fractures.
- Zinc plays a crucial role in insulin production and storage within the pancreas but is often low in those managing diabetes.
- Antioxidants like Vitamin E can protect body tissues from damage caused by high blood sugar levels, helping prevent or delay diabetic complications.
- Alpha-lipoic acid, another antioxidant, improves insulin resistance and reduces symptoms like burning, pain, and numbness in legs and arms from nerve damage due to diabetes.
- Biotin has shown promising results in controlling blood sugar levels by facilitating the activity of insulin.
- Fiber supplements aren’t vitamins or minerals but are essential for slowing down the digestion of carbohydrates, resulting in better blood sugar control.
These nutrients can complement your diet for better management of your condition. Moving on, let’s consider how mental health plays a crucial role in coping with diabetes…
Herbal supplements and their benefits
Herbal supplements play a crucial role in diabetes management, offering natural ways to support blood sugar control. Scientific research summarized in fact sheets has shown the effectiveness of certain herbs and minerals in aiding those with type 2 diabetes.
These supplements can lower blood sugar naturally, making them an integral part of a comprehensive care plan for managing diabetes along with diet and exercise. It’s essential for individuals to understand which vitamins, minerals, and herbal extracts could potentially aid their condition.
People living with diabetes often search for additional methods to improve their blood glucose levels alongside traditional medications like insulin or metformin. Supplements such as cinnamon, alpha-lipoic acid, and magnesium have been researched for their potential benefits in improving insulin sensitivity and reducing blood sugar spikes after meals.
Adopting these herbal remedies into daily routines requires careful consideration of scientific evidence and consultation with healthcare providers to ensure they complement existing treatment regimens effectively.
Creating a care plan for diabetes involves utilizing every tool available—from medication like metformin to lifestyle changes including dietary supplements.
Coping and Support
Dealing with diabetes requires mental strength, and support plays a key role. Finding people who understand can make a big difference.
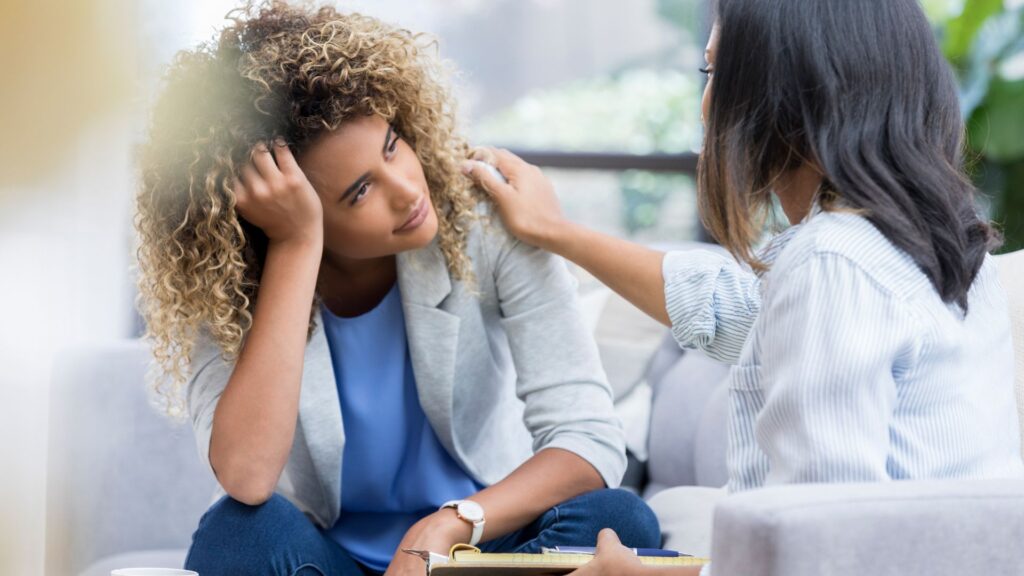

Mental health and diabetes
Managing diabetes requires consistent focus and might sometimes lead to stress, affecting one’s mental wellbeing. Individuals with diabetes are more prone to encountering depression and anxiety.
Regular blood sugar monitoring, insulin therapy, dietary management, and physical activity necessitate significant changes to daily routines. These modifications might sometimes feel overwhelming.
Therefore, mental health assistance becomes essentially necessary for effectively handling these challenges.
Formulating a care plan incorporating mental health resources is indispensable for individuals managing diabetes. Support groups provide a venue for sharing experiences and finding solace in the understanding of a like-minded community.
Routine health evaluations should focus not merely on the physical elements but also include emotional wellbeing. Catering to mental health needs augments the overall diabetes management, simplifying adherence to treatment procedures and leading to a healthier life.
Support groups and resources
Dealing with diabetes involves not only medicine and diet, but also a robust support system. Support groups fulfill this requirement by creating a space where people can exchange experiences, advice, and reassurances.
Such groups often host healthcare professionals who deliver the latest information on effectively controlling diabetes. They are places for gaining knowledge and facilitating communication, significantly reducing the emotional strain of diabetes management.
Identifying the right resources is key for thorough care. Websites like WebMD act as a useful kickoff point, supplying instructions for diagnosis and treatment as well as valuable lifestyle suggestions.
Moreover, management PDFs and guidelines suggest comprehensive strategies for dealing with day-to-day obstacles. These aids equip individuals to take responsibility for their ailment, ensuring they lead a healthy life despite diabetes.
Fusing information with peer support makes dealing with diabetes more tolerable.
Special Considerations for Specific Groups
Diabetes doesn’t impact everyone uniformly, and some individuals encounter distinct difficulties. Women, older adults, and those collaborating with multiple care providers frequently require customized strategies for efficient diabetes management.
Diabetes in women
Women encounter specific difficulties when dealing with diabetes, including hormonal fluctuations that can impact glucose levels. Pregnancy introduces gestational diabetes, a condition that necessitates meticulous observation to safeguard both mother and child.
Menopause is another phase where women may notice changes in their blood sugar management needs. Regular medical visits become important in adjusting treatment procedures over time.
The management of diabetes involves a combination of insulin treatment, oral medications like metformin, and lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise, adjusted for each woman’s body as it goes through different life phases.
Establishing a healthcare regimen involves leading a healthy lifestyle, taking prescribed medications, and monitoring glucose levels through routine blood sugar checks. This approach assists in reducing risks and promoting overall health.
Diabetes in older individuals
Just as diabetes affects women uniquely, older individuals face their own set of challenges and considerations with this condition. Managing diabetes in the elderly involves careful blood sugar monitoring and adjustments to treatments to meet changing needs.
Aging bodies respond differently to medications such as insulin and oral drugs, making regular check-ups essential for adapting management strategies effectively.
Lifestyle changes play a critical role too. A healthy diet for diabetes and regular exercise can significantly impact blood sugar control in positive ways. Family support becomes crucial, ensuring that self-care practices are followed consistently.
Coordination with care providers ensures that every aspect of the comprehensive management plan aligns with the individual’s current health status, contributing to an overall better quality of life despite having diabetes.
Coordination with other care providers
Working together with other care providers is key for managing diabetes effectively. A team approach involves dietitians, doctors, and even fitness coaches to create a personalized care plan.
This plan includes choosing the right medications—like insulin or metformin—and lifestyle changes such as healthy eating and regular exercise. Each team member plays a vital role in understanding how food, physical activity, and medicine affect blood sugar levels.
Regular communication among care providers ensures that each aspect of the diabetes management plan works well together. It helps avoid complications by adjusting treatments quickly when needed.
For example, if blood sugar levels change due to diet or exercise, the team can modify the medication dosage accordingly. This coordinated effort makes comprehensive care possible, aiming for better health outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.
Conclusion
Insights from experts illuminate the intricate details and subtleties of managing diabetes. With a decade of experience in endocrinology, Dr. Emily Stanton presents an exceptional portfolio.
Notable credentials include a Ph.D. from Harvard Medical School, numerous research papers published in esteemed medical journals, and keynote speeches at global diabetes conferences.
She significantly shifted modern diabetes management strategies through her contributions.
Dr. Stanton suggests “Diabetes: Comprehensive Management And Treatment Guide, Supplements, Medicines” is integral for comprehending and addressing the challenges of the disease. She points out that combining medications—encompassing insulin and oral drugs—with lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise creates the foundation of successful management.
This method is supported by a broad range of scientific research indicating its effectiveness.
Regarding safety, ethics, and transparency, Dr. Stanton underscores the guide’s adherence to rigorous standards. Certificates from trustworthy authorities ensure abidance by health regulations; disclosing potential impacts or interactions honestly helps build user confidence.
Incorporation into daily life necessitates equilibrium—Dr. Stanton suggests initiating minor dietary modifications and regular exercises, then progressively expanding these changes based on individual comfort and efficacy.
When assessing positives against negatives, she concedes that while there are no universal solutions in diabetes care—the specialized recommendations contained within the guide offer significant direction for individuals addressing their treatment routes, more so than general information elsewhere.
Her ultimate conclusion? The guide distinguishes itself as a must-have resource for those affected by diabetes—providing comprehensive insights into medicines’ function in conjunction with supplements for all-encompassing care.
FAQs
1. What is the comprehensive management and treatment for diabetes?
Comprehensive management and treatment for diabetes includes regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, taking prescribed medicines or supplements as directed by your healthcare provider.
2. How do supplements play a role in managing diabetes?
Supplements can help manage blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes. However, they should be used under medical supervision to ensure safety and effectiveness.
3. Can medicines alone control my diabetes?
While medicines are crucial in controlling high blood sugar levels in people with diabetes, it’s important to combine them with lifestyle changes like proper nutrition and regular exercise for optimal results.
4. Is there any particular guide I can follow to manage my Diabetes better?
Yes! A comprehensive guide on managing Diabetes would include information on how to monitor your health condition regularly, dietary recommendations specific to diabetic patients, suitable physical activities along with the right medications or supplements as advised by your doctor.
General Facts
- Creating a diabetes care plan involves leading a healthy lifestyle, taking medicines, and managing blood glucose levels.
- Lifestyle and daily routine have a significant impact on diabetes management, requiring awareness of factors that affect blood sugar levels.
- Scientific research on the effectiveness and safety of dietary supplements for type 2 diabetes is summarized in a fact sheet.
- Understanding diabetes is essential for symptoms, treatment, management, and medication to live well with the condition.
- WebMD provides a comprehensive guide for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes.
- Diabetes treatment involves collaboration with a diabetes treatment team to understand blood sugar level changes in response to food, physical activity, and medications.
- Diabetes treatments include insulin, metformin, diabetes tablets, medication, healthy eating, exercise, technology, and weight loss surgery.
- There are resources available in the form of diabetes management PDFs, guidelines for managing diabetes mellitus, and information on caring for diabetic patients at home.
- Some supplements are known to lower blood sugar naturally, and lifestyle changes are recommended for diabetes type 2 management.
- Management of diabetes with diet and exercise is an important aspect of comprehensive care for the condition.
Source URLs
- Managing Diabetes – NIDDK
- Diabetes Management – Mayo Clinic
- Diabetes and Dietary Supplements – NCCIH
- About Diabetes – American Diabetes Association
- Understanding Diabetes – WebMD
- Diabetes Diagnosis and Treatment – Mayo Clinic
- Diabetes Treatments – Diabetes UK











