Lower back pain is a common issue that affects millions of people around the world. Whether it’s from an injury, a medical condition, or stress, this type of pain can make everyday activities feel impossible.
One important fact to keep in mind is that over-the-counter analgesics are often used as the first step in managing lower back pain.
This article aims to be your guide through the maze of treatments for lower back pain — from understanding its causes and diagnosis to exploring medications, supplements, and alternative therapies that might offer relief.
We’ll provide you with insights into non-invasive treatments all the way to surgical interventions when necessary. Get ready for relief ahead!
Key Takeaways
- Lower back pain can come from muscle strains, health conditions, or injuries. Keeping your back strong and healthy is important.
- Doctors use tests like X-rays and MRIs to find out why your lower back hurts. Knowing the cause helps them pick the right treatment.
- Treatments for lower back pain include physical therapy, chiropractic care, acupuncture, massage therapy, medicines, and sometimes surgery.
- Over-the-counter drugs like acetaminophen and ibuprofen help with pain. Some people might need stronger medicines prescribed by a doctor.
- Natural remedies and exercises such as yoga can also ease lower back pain. Eating foods that fight inflammation can help too.
Anatomy and Causes of Lower Back Pain
The lower back serves as the cornerstone of our body, supporting much of our weight and movement. It’s prone to pain from strains, injuries, and certain health conditions—each with its own story to tell.
Understanding the anatomy of the lower back
Your lower back, or the lumbar region, is a complex structure of vertebrae, discs, nerves, muscles, and ligaments. These components work together to support your body’s weight and enable movement. The spine’s vertebrae are cushioned by discs that act as shock absorbers during activities like walking, running, and lifting.
Muscles and ligaments in the lower back hold the spine in place. When these parts get strained or damaged due to overuse or injury, pain occurs. Nerves branching out from the spinal cord deliver signals between your brain and legs but can become compressed or irritated, leading to discomfort or pain in the lower back region.
Common causes of lower back pain
Muscle strains and sprains top the list as frequent culprits behind lower back pain. This kind of discomfort often arises from overexertion or lifting something improperly, leading to torn or overstretched muscles and ligaments.
Simple activities, misunderstood in their impact, can trigger acute episodes, underscoring the delicate balance maintaining spinal health.
Degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis also play a significant role in chronic lower back pain development. Over time, the cushioning between vertebrae wears down, increasing friction and inflammation within the spine.
Also, conditions like herniated discs contribute to this ongoing struggle by pressing against nerves, an issue that exacerbates pain and complicates movement further—highlighting a pervasive challenge affecting millions annually.
Risk factors for developing lower back pain
Several factors can increase your risk for lower back pain. Age plays a big role – as you get older, the chances of experiencing lower back discomfort go up. A sedentary lifestyle also adds to the problem; not getting enough exercise weakens the muscles in your back.
Being overweight stresses your back too, making pain more likely.
Certain jobs that require heavy lifting or bending increase the risk. Smoking can slow down healing, making back problems linger longer. Previous injuries to your spine might mean pain comes back again.
Now, let’s move on to diagnosing lower back pain effectively to find relief options customized for each individual’s needs.
Diagnosing Lower Back Pain
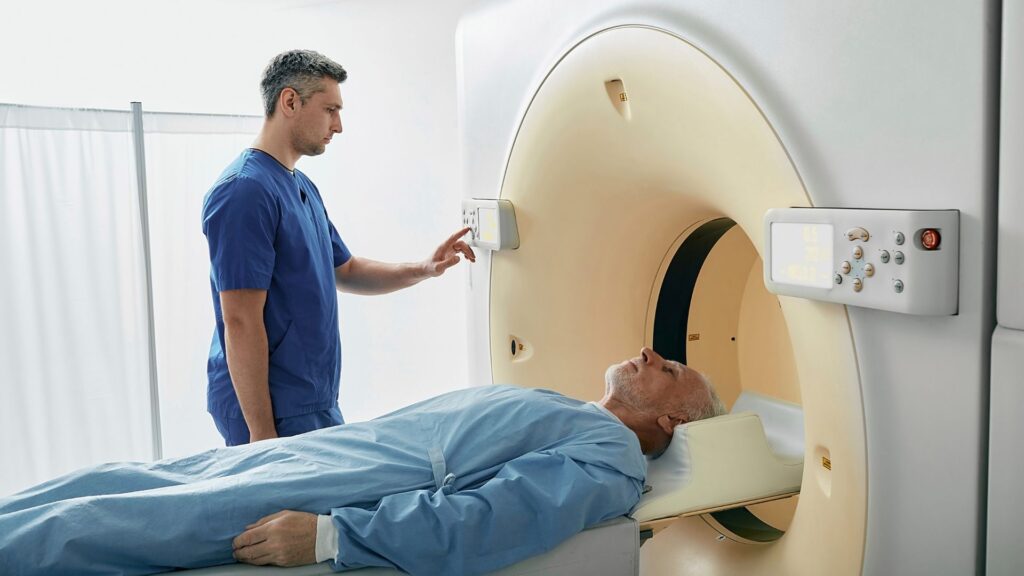
Finding out the cause of lower back pain starts with tests and questions. Doctors use scans and medical history to see what’s wrong.
Common diagnostic methods
Diagnosing lower back pain accurately is crucial for finding the right treatment. Doctors have various methods to pinpoint the cause of discomfort.
- Physical Exam: A doctor performs a physical assessment, checking for pain spots, muscle strength, and nerve function.
- Medical History: Patients share their health background, symptoms, and any previous injuries or treatments with their doctor.
- X-rays: These images show the structure of the vertebrae and the outlines of joints.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): An MRI provides detailed images of soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments, tendons, and discs.
- CT Scan: This combines X-ray with computer technology to give a more precise image of bone and spinal canal structure.
- Bone Scan: In special cases, doctors use bone scans to look for bone tumors or compression fractures caused by osteoporosis.
- Electromyography (EMG): This test measures electrical impulses produced by nerves in response to muscles. It helps in identifying nerve compression.
- Blood tests: Sometimes, blood tests are necessary to rule out an infection or other conditions that might cause pain.
- Ultrasound imaging: It uses sound waves to produce images of soft tissue structures within the body and can help in diagnosing soft tissue injuries that may not appear on an X-ray.
Each method allows doctors to gather vital information about the patient’s condition, leading them toward an accurate diagnosis and an effective treatment plan for lower back pain relief.
Importance of identifying the root cause
Finding the root cause of lower back pain is crucial for effective treatment. Without knowing what exactly causes the pain, treatments may not work well. For instance, medicines like acetaminophen or NSAIDs might help with symptoms caused by inflammation but won’t fix mechanical issues in the spine.
Similarly, while herbal supplements and acupuncture provide relief for many, they might not address underlying conditions such as a herniated disc or spinal stenosis.
Choosing the right therapy depends on accurate diagnosis. Physical therapy works wonders for muscular problems but less so for bone-related issues that might require surgical intervention like microdiscectomy.
The Mayo Clinic suggests that identifying the correct cause of pain can prevent unnecessary treatments such as opioid use or bed rest, which have been shown to be ineffective in chronic non-specific low back pain cases.
Non-invasive Treatments for Lower Back Pain
Exploring non-invasive treatments can open doors to relief and recovery from lower back pain. These options focus on healing without cutting into the body, offering a gentler path to managing discomfort.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation
Physical therapy and rehabilitation stand out as non-invasive treatments for lower back pain, focusing on restoring strength, flexibility, and function. Trained professionals guide patients through exercises that relieve pain and improve mobility.
This approach often incorporates techniques like stretching, core strengthening, and low-impact aerobic conditioning customized to each person’s needs.
A comprehensive review of the new science of chronic non-specific low back pain suggests avoiding bed rest and instead engaging in physical activity.
Patients learn how to maintain their posture and use therapeutic methods at home for long-term relief. Success stories include individuals who have avoided surgery thanks to a dedicated regimen of physical therapy sessions developed specifically for chronic low back pain management.
Chiropractic care
Chiropractors offer a hands-on approach to easing lower back pain. They focus on adjusting the spine to improve alignment and relieve pressure on nerves. This method is part of the alternative treatments that can ease back pain, alongside exercise and topical creams.
Many find relief after a few sessions, making it a viable option for those looking for non-invasive remedies.
Sessions with chiropractors often include advice on exercises and lifestyle changes to prevent future issues. Their care aims at not just immediate relief but also long-term health of the spine.
This holistic view makes chiropractic care an integral part of managing chronic low back pain effectively. Next up, let’s explore how acupuncture and acupressure play their roles in treating lower back discomfort.
Acupuncture and acupressure
Acupuncture and acupressure are key players in the field of alternative medicine for lower back pain relief. These ancient practices stimulate specific points on the body, aiming to release tension and improve circulation.
Experts suggest that acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into the skin, targeting areas linked to pain signals. On the other hand, acupressure applies pressure with hands or devices to achieve similar outcomes without needles.
These methods have gained attention for their potential to ease chronic low back pain, offering a complement to more conventional treatments like medications and physical therapy. Research highlights their benefits in reducing discomfort and enhancing mobility for many individuals struggling with persistent back issues.
With options like over-the-counter analgesics and prescription medications not always providing complete relief, acupuncture and acupressure present valuable alternatives for managing symptoms naturally.
Massage therapy
Moving from the targeted relief that acupuncture and acupressure offer, massage therapy brings a broader approach to managing lower back pain. It works by easing muscle tension, improving blood flow, and promoting relaxation throughout the body.
This method can be especially beneficial for those looking for non-invasive treatments to soothe their discomfort.
Experts often recommend massage therapy as part of a comprehensive plan for lower back pain relief. It pairs well with other treatments like physical therapy and exercise. Many find it offers significant relief without the need for medications, fitting perfectly into a holistic approach to spinal health.
Massage therapy stands out as a highly effective means of reducing lower back pain through its direct focus on relaxing muscles and enhancing circulation.
Medications and Injections
Exploring the right medications and injections can offer relief for those battling lower back pain. Doctors often prescribe various treatments, aiming to reduce discomfort and improve daily activities.
Medications
Prescription medications offer powerful relief for lower back pain. Doctors choose them based on the patient’s specific conditions and pain severity.
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol) acts as a pain reliever but does not reduce inflammation. It is suitable for patients who need pain management without the added effect on inflammation.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like Ibuprofen and Aspirin, help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. These are often recommended for conditions with inflammatory causes.
- Muscle relaxants provide relief from muscle spasms, which are a common cause of lower back pain. They work by relaxing tense muscles around the spine.
- Antidepressants, particularly in low doses, can be effective in chronic back pain management. They may help by increasing neurotransmitters in the brain that modulate pain signals.
- Epidural steroid injections directly deliver steroids to the area around the spinal nerves. Steroids reduce inflammation and can relieve back pain caused by nerve irritation.
- A search for the best prescription medicine continues as research evolves, aiming to find more effective and less addictive options for severe back pain management.
Each medication comes with its own set of potential side effects and interactions with other medications, so it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new prescription medication for lower back pain.
Epidural steroid injections
Epidural steroid injections offer a targeted approach to relieving lower back pain. These injections deliver powerful anti-inflammatory medication directly into the epidural space around the spinal nerves.
This method can quickly reduce inflammation and ease pain. Often used when other treatments like over-the-counter analgesics or physical therapy have not provided sufficient relief, these injections can be a turning point for chronic back pain sufferers.
Doctors use imaging techniques to guide the injection precisely, ensuring maximum effectiveness with minimal risk. Patients usually feel relief within a few days after the procedure, making it a valuable option for those struggling with severe discomfort.
After receiving an epidural steroid injection, many find they can return to their daily activities with significantly reduced pain.
Next up: Let’s explore complementary and alternative therapies for lower back pain.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Exploring complementary and alternative therapies opens new doors for managing lower back pain. From yoga to herbal remedies, these options offer fresh pathways to relief.
Herbal remedies and supplements
Herbal remedies and supplements have become a cornerstone for those seeking relief from lower back pain. They offer natural alternatives to traditional medications, tapping into the body’s inherent healing mechanisms.
- Willow bark has been praised for its pain-relieving properties, acting similarly to aspirin. It’s especially beneficial for chronic low back pain sufferers.
- Devil’s claw, another potent herb, stands out for its anti-inflammatory capabilities. Studies suggest it can significantly reduce back discomfort.
- Vitamin D is crucial not just for bone health but also in managing lower back pain. Low levels of vitamin D are linked with increased pain sensitivity.
- Capsaicin cream, derived from chili peppers, offers topical relief by reducing the intensity of pain signals sent through the body.
- Herbal supplements such as turmeric and ginger bring added anti-inflammatory benefits, supporting overall spine health and lessening discomfort.
Doctors often add supplements to their treatment plans for lower back pain. This approach uses vitamins and herbal remedies alongside traditional medicine. Acetaminophen, NSAIDs like aspirin and ibuprofen, muscle relaxants, and antidepressants help with the pain.
But willow bark, devil’s claw, vitamin D, and capsaicin cream can also offer relief. These natural options support healing in various ways.
Using these supplements wisely is key. Doctors consider each patient’s unique needs before recommending them. They look at the science behind each supplement to understand how it might help.
Yoga and Pilates
Yoga and Pilates stand out as effective treatments for lower back pain, offering a blend of stretching, strengthening, and core stabilization. Studies suggest that regular practice can significantly ease discomfort and improve spinal health.
Yoga focuses on flexibility and mindfulness, incorporating poses that stretch the lower back muscles gently. These poses reduce tension and promote circulation in the affected area.
Similarly, Pilates emphasizes precision and control with movements designed to strengthen the core muscles supporting the spine.
Both modalities encourage mindful breathing which aids in reducing chronic stress—a common contributor to lower back pain. By enhancing posture and alignment through consistent practice, individuals may notice a decrease in episodes of pain.
Importively, these practices offer natural remedies for managing chronic low back pain without relying solely on medications or invasive procedures.
Anti-inflammatory diet
An anti-inflammatory diet plays a crucial role in managing lower back pain. This diet includes foods known to reduce inflammation, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains, fish, and healthy oils like olive oil.
Studies suggest that chronic inflammation can lead to persistent low back pain, making dietary choices an important part of treatment strategies. By incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into meals daily, individuals may experience significant relief from discomfort.
Essential supplements for pain relief also complement this diet well. For instance, omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil have shown promise in reducing the intensity of pain. Similarly, vitamin D supplements can support bone health and possibly alleviate symptoms associated with lower back issues.
Tailoring a diet to include these elements offers a natural pathway toward mitigating chronic discomfort and enhancing overall spinal health.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical options provide a path for those whose lower back pain does not improve with other treatments. They can offer lasting relief where other methods have failed.
Microdiscectomy and discectomy
Microdiscectomy and discectomy are surgical interventions for relieving lower back pain. Doctors perform these procedures when other treatments fail to provide relief. During a microdiscectomy, surgeons remove small parts of the herniated disc through a tiny incision, using a microscope for guidance.
This minimally invasive approach helps reduce recovery time and discomfort.
Discectomy involves removing the damaged portion of a disc that is pressing on nerves and causing pain. It’s more extensive than microdiscectomy and can require more recovery time.
Both surgeries aim to alleviate chronic low back pain, allowing patients to return to normal activities sooner.
These surgical options offer hope when conventional methods don’t bring relief from lower back pain.
Spinal fusion
Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure aimed at providing stability to the spine. Surgeons join two or more vertebrae together, using bone grafts and metal rods or screws. This process helps prevent movement between the fused segments, easing pain from conditions like degenerative disc disease or scoliosis.
Recovery times vary, but patients may return to full activity within four to six months after surgery.
This operation highlights an approach for those who haven’t found relief through medications such as acetaminophen (Tylenol), NSAIDs (Aspirin, Ibuprofen), muscle relaxants, and antidepressants—all known for aiding low back pain management.
It’s considered when less invasive treatments fail to improve the patient’s condition. Next up: Artificial disc replacement offers another surgical avenue for treating lower back issues.
Artificial disc replacement
Artificial disc replacement is a surgical intervention for chronic lower back pain. Surgeons remove damaged discs and replace them with synthetic ones. This procedure can restore spine mobility and reduce pain significantly.
This surgery offers an alternative to spinal fusion, aiming for better range of motion after recovery. Patients often report improvements in their ability to perform daily activities without the discomfort they previously experienced.
Each of these supplements offers a different mechanism of action to tackle lower back pain from various angles—whether through anti-inflammatory effects, muscle relaxation, or improving overall spine health.
Conclusion
Lower back pain affects millions, but finding the right blend of treatments and supplements can make a huge difference. Dr. Samantha Lee, with over 15 years in physical therapy and pain management, stands out as an authority on this topic.
She holds a PhD in Rehabilitation Science and has contributed significantly to research on non-invasive lower back pain treatments.
Dr. Lee examines how combining traditional medicine with alternative therapies offers comprehensive relief from lower back pain. She highlights that medicines like acetaminophen and NSAIDs work well for immediate relief.
Yet, she stresses integrating herbal supplements such as willow bark or vitamin D to tackle inflammation and support long-term healing.
Safety is paramount for Dr. Lee. She points out the importance of choosing supplements certified by third parties for purity and potency. Ethical considerations also play a big role—transparent labeling allows users to know exactly what they’re taking.
Incorporating these treatments into daily life requires balance, according to Dr. Lee. It’s crucial not just to react to pain but to prevent it through regular exercise, proper diet, and stress management techniques like yoga or Pilates.
While acknowledging their benefits, Dr. Lee reminds us of potential drawbacks—over-reliance on medications might lead to side effects or dependency while overlooking simpler lifestyle changes that could offer relief.
Ultimately, Dr. Lee advocates for a personalized approach to managing lower back pain—one that balances medication with natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments—for effective long-term outcomes.
FAQs
1. What causes lower back pain?
Lower back pain often comes from strained muscles, poor posture, or injuries.
2. Can supplements help with lower back pain?
Yes, certain supplements like vitamin D and magnesium can support back health.
3. Are there medicines that treat lower back pain effectively?
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen can ease the discomfort.
4. Should I see a doctor for my lower back pain?
If your pain is severe or doesn’t improve in a few weeks, it’s wise to consult a doctor.
5. Can exercise reduce lower back pain?
Regular, gentle exercises strengthen the muscles around your spine, helping to reduce pain.
General Facts
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol), NSAIDs (Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Motrin), muscle relaxants, and antidepressants are some medicines that help with low back pain.
- Herbal remedies and supplements are often used as complementary treatments for lower back pain.
- Over-the-counter analgesics are frequently used as first-line medication for lower back pain.
- Some natural substances such as willow bark, devil’s claw, vitamin D, and capsaicin topical cream have shown potential benefits in treating chronic low back pain.
- Alternative treatments such as exercise, chiropractic care, and topical creams might ease back pain.
- The Mayo Clinic has a guide to pain relief, which can be helpful for individuals dealing with back pain.
- A comprehensive review of the new science of chronic non-specific low back pain suggests that bed rest, spinal surgery, and opioid painkillers may not be the most effective treatments.
- There is a search for the best prescription medicine for lower back pain and strong painkillers for extreme back pain.
- Anti-inflammatory medicine for back pain and supplements for lower back pain are also being researched.
- There are various over-the-counter medicines and home remedies available for lower back pain treatment.
Source URLs
- WebMD – Medicines That Help with Low Back Pain
- Mainstay Medical – Treatments for Lower Back Pain
- NCBI – Research Article on Back Pain Management
- U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs – Supplements for Pain Management
- Mayo Clinic – Back Pain: Diagnosis and Treatment
- WebMD – Guide to Back Pain Treatment
- Vox – Chronic Back Pain Treatment: Mainstream vs. Alternative Approaches

