Abdominal pain that just won’t go away? It might be more than a simple upset stomach, especially if it keeps coming back. Gallstones could be the culprit behind this discomfort. These tiny but troublesome formations in your gallbladder can interrupt your day and leave you seeking relief.
Gallstones are hard particles that form when substances in the bile harden. They vary in size and can cause serious health issues if not addressed. Our guide tackles everything from understanding what triggers these stones to form, to exploring modern treatments—including supplements and medicines designed for prevention and management.
This article will equip you with knowledge about gallstones, providing you with both conventional and alternative options to handle them effectively. Ready to tackle gallstone woes head-on?
Key Takeaways
- Gallstones form in the gallbladder when substances like cholesterol or bilirubin harden. If your belly hurts a lot, especially on the upper right side, you might have them.
- Doctors find gallstones by using tests like ultrasounds or CT scans. If you have symptoms, they might suggest surgery or medicine. Eating healthy and exercising can also help avoid gallstones.
- Some people use natural treatments and supplements to manage gallstones. Things like milk thistle, turmeric, and a diet full of fruits and vegetables might help.
- Not treating gallstones can lead to big problems like infections in your belly. Catching them early is important for staying healthy.
- The cause of gallstones has a lot to do with what you eat, how much you weigh, and even your family history. Making good choices every day helps keep your belly happy.
The Basics of Gallstone Disease
Understanding gallstones starts with knowing they form when bile hardens inside your gallbladder. These hard particles can lead to pain and other health issues if not treated.
Definition and causes
Gallstones are hard particles that form in the gallbladder, primarily made up of cholesterol or bilirubin. These stones develop when there’s an imbalance in the substance making up bile—a fluid produced by the liver to digest fats.
Too much cholesterol or bilirubin in bile can lead to stone formation. Other causes include a full gallbladder that doesn’t empty properly or too much bile being stored in it.
Different factors contribute to this imbalance—ranging from diet and weight to genetics and certain medical conditions affecting bile flow, such as liver diseases. Regular consumption of unhealthy diets rich in fats and low in fiber can increase cholesterol levels, raising the risk of cholesterol stone formation.
On the other hand, conditions like blood disorders can elevate bilirubin levels, leading to pigment stones.
Understanding gallstones begins with recognizing how our dietary habits and body’s functions interplay.
Moving on explores signs and symptoms indicating these silent stones might be causing trouble.
Types of gallstones
Two main types of gallstones affect people: cholesterol stones and pigment stones. Cholesterol stones are the most common, making up about 80% of all gallstones. They form when there’s too much cholesterol in the bile, a digestive fluid made by the liver.
This type is usually yellow-green in color.
Pigment stones, on the other hand, are less common and develop when there’s an excess of bilirubin in the bile. Bilirubin is a substance produced when red blood cells break down. These stones tend to be smaller and darker than cholesterol stones.
Both types can cause abdominal pain and blockages in the bile duct, leading to serious health issues if not treated properly.
Signs and symptoms
People with gallstones often feel sudden and intense abdominal pain, especially in the upper right part of their belly. This pain can last for several hours. They might also experience nausea or vomiting, which makes them feel even more uncomfortable.
Some people notice changes in the color of their urine and stool; urine may turn darker while stools could become lighter or chalky. It’s not uncommon for those affected to have a high fever or chills if an infection develops due to blocked bile ducts.
These symptoms send a clear signal that something is wrong inside the digestive system. Recognizing them early leads to better chances of managing the condition effectively before it gets worse.
With these signs in mind, understanding risk factors becomes crucial as they play a significant role in developing gallstones.
Risk Factors for Gallstones
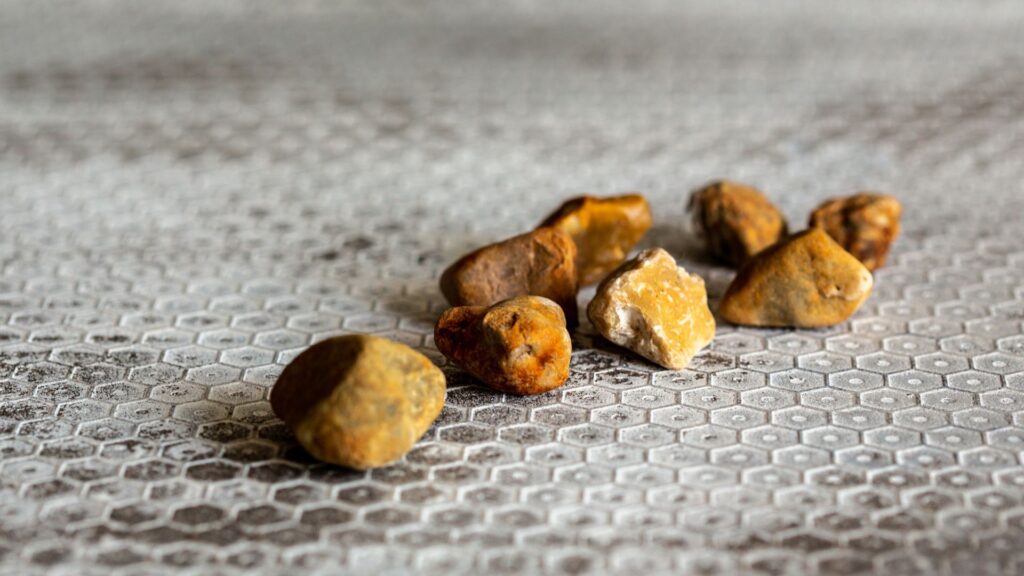

Who gets gallstones can depend on many things, like age, gender, and even what you eat. Your family history plays a big role too.
Influence of gender, age, and ethnicity
Understanding the factors that influence gallstone formation is critical for prevention and management. Gender, age, and ethnicity play significant roles in the development of gallstone disease. This discussion sheds light on how these variables impact the likelihood of developing gallstones.
| Factor | Influence on Gallstone Formation |
|---|---|
| Gender | Women are more likely to develop gallstones, especially during their fertile years. This is linked to hormonal factors, particularly the influence of estrogen, which can increase cholesterol levels in bile and decrease gallbladder movement. |
| Age | The risk of developing gallstones increases with age. People over 40 are at a higher risk, as the body’s metabolism changes, affecting cholesterol levels and gallbladder function. |
| Ethnicity | Certain ethnic groups are at a higher risk. For instance, Native Americans have the highest rates of gallstone disease, largely due to genetic predispositions to secrete high levels of cholesterol in bile. Hispanics also have a higher prevalence, compared to other groups. |
Each of these factors contributes differently to the risk and management of gallstone disease. Understanding these influences is essential for tailoring preventive strategies and treatments.
Genetics and lifestyle factors (such as diet and obesity)
Genetics play a key role in the development of gallstones, making some people more prone to this condition. If family members have had gallstones, chances increase that an individual might also develop them.
This genetic predisposition works alongside lifestyle choices which can elevate the risk further. Unhealthy diets rich in fat and low in fiber contribute significantly to obesity—an established risk factor for gallstone disease.
Keeping a balanced diet helps maintain proper weight and reduces the likelihood of developing gallstones.
A healthy diet is not just about managing weight; it’s crucial for preventing conditions like gallstone disease.
Regular exercise complements dietary efforts by managing obesity, one of the critical factors influencing gallstone formation. Besides controlling weight, staying active improves overall digestive health, enhancing bile flow and reducing cholesterol levels within the bile—a necessary step to prevent cholesterol stone formation.
Emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting processed foods and high-fat items forms the cornerstone of prevention strategies targeted at reducing gallstone risks rooted in genetics and lifestyle choices.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Doctors use ultrasound and blood tests to find gallstones. They then decide if you need surgery or can manage with medicine and diet changes.
Diagnostic techniques and procedures
Diagnosing gallstones accurately is essential for effective treatment. Doctors use a variety of tests and procedures to identify the presence and impact of gallstones.
- Ultrasound – The most common and non-invasive method, ultrasound imaging allows doctors to see gallstones in the gallbladder clearly.
- CT Scan – A CT or computed tomography scan provides detailed images of the abdomen, helping spot gallstones or complications like inflammation.
- MRI HIDA Scan – Magnetic resonance imaging combined with a hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan can visualize bile flow and detect blockages in the bile ducts.
- Blood Tests – These tests check for signs of infection, inflammation, jaundice, or other conditions caused by gallstones blocking bile flow.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound – This method involves using an endoscope — a flexible tube with an attached camera and ultrasound device — to get close-up images of the gallbladder from inside the digestive tract.
- Cholangiography – If doctors suspect bile duct blockages, they may perform this X-ray exam that involves injecting dye into the bile ducts to make them visible on images.
- Gallbladder Radionuclide Scan – This test tracks the movement and production of bile from the liver to the small intestine and can show obstructions.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) – Used primarily when there’s a strong suspicion of stones in the bile duct, ERCP combines endoscopy and X-ray imaging to examine the pancreas, liver, and bile ducts.
Each method plays a crucial role in assessing not just the presence but also the size, location, and potential complications arising from gallstones.
Expectant management for asymptomatic gallstones
After identifying gallstones through diagnostic techniques, doctors might choose a wait-and-see approach for those without symptoms. This method, known as expectant management, is common for silent stones that cause no problems.
Patients with asymptomatic gallstones often live without any complications or pain. The focus remains on monitoring rather than immediate intervention.
Doctors recommend this approach when the risk of surgery outweighs the benefits. They keep a close eye on the patient’s condition to catch any changes early. Lifestyle adjustments and regular check-ups help manage this condition safely.
Patients can maintain their quality of life without needing drastic treatments like surgery.
Management of symptomatic gallstones
Doctors often recommend surgery to remove the gallbladder for managing symptomatic gallstones. This procedure, known as a cholecystectomy, is common and safe. Before deciding on surgery, doctors may use medications to dissolve certain types of stones or manage symptoms.
These drugs might take months or even years to work fully.
Lifestyle changes play a key role too. Eating a healthy diet and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce symptoms and prevent new stones from forming. Next up, let’s explore surgical and nonsurgical treatments in more detail.
Surgical and nonsurgical treatments
After assessing how to manage symptomatic gallstones, the next step is exploring the range of surgical and nonsurgical treatments available. These options aim to relieve symptoms, prevent complications, and address the root cause of gallstone disease.
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy – This is a common surgical procedure where doctors remove the gallbladder through several small incisions in the abdomen. It’s widely preferred due to its minimal recovery time and reduced pain compared to traditional surgery.
- Open cholecystectomy – For large gallstones or complications like inflammation, an open surgery might be necessary. A larger incision is made to remove the gallbladder, requiring a longer hospital stay and recovery period.
- ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) – A nonsurgical option used to locate and remove stones from the bile duct. It involves a flexible tube with a camera passed down your throat into the stomach and upper intestine.
- Gallstone dissolving medications – Certain drugs can dissolve cholesterol-based gallstones over time but may take months or years to work effectively.
- Shock wave lithotripsy – Uses high-frequency sound waves to break up gallstones into smaller pieces that can pass more easily through the bile duct.
- Bile salt tablets – These help dissolve gallstones by thinning the bile, though they’re mainly effective for small stones made of cholesterol.
- Diet modifications – While not a direct treatment for existing gallstones, eating a healthy diet can prevent new stones from forming by maintaining balanced cholesterol levels and promoting healthy bile flow.
Each treatment option has its benefits depending on individual circumstances, including the type and size of gallstones, symptoms experienced, and overall health condition of the patient.
Natural and Alternative Treatments
Exploring natural and alternative treatments opens the door to new ways of preventing and managing gallstones. From tweaking your diet to embracing time-honored herbal remedies, these strategies offer a gentler approach to support your digestive health.
Dietary changes and nutrition tips
Eating right plays a big role in managing gallstones. A healthy diet can reduce symptoms and prevent new stones from forming. Here are some tips:
- Focus on fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to help maintain a healthy digestive system. These foods facilitate bile flow and can decrease the risk of gallstone formation.
- Cut down on refined sugars and fats that can lead to obesity, a risk factor for gallstones. Opt for natural sweets from fruits and choose healthier fats like those found in avocados and nuts.
- Incorporate lean protein sources such as chicken, fish, and legumes into your meals while avoiding high-fat meats which can exacerbate gallstone problems.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Water helps flush out toxins that can contribute to gallstone formation.
- Limit or avoid alcohol consumption as it can affect liver function, ultimately impacting bile production and leading to gallstone complications.
- Consider adding an anti-inflammatory diet to your regimen that includes spices like turmeric and ginger along with omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil supplements or flaxseeds. These have properties that may help manage pain associated with gallstones.
Switching gears next, let’s examine how supplements play a role in both preventing and treating gallstones…
Supplements for gallstone prevention and treatment
Gallstones can cause significant discomfort, but the right supplements might help in preventing and treating them. Many people find relief through a combination of dietary changes and specific nutrients.
- Milk thistle is known for its liver-supporting properties. It helps promote bile flow, which can prevent gallstone formation.
- Vitamin C has been linked to reduced risk of developing gallstones. This powerful antioxidant helps convert cholesterol into bile acids.
- Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, may reduce gallstone formation by improving bile flow and reducing inflammation in the bile duct.
- Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound that supports digestive health and helps maintain a healthy bile flow, potentially preventing gallstones.
- Magnesium supplements could lower the risk of gallstone formation as they play a crucial role in breaking down fats and reducing cholesterol levels.
- Psyllium husk is a form of fiber that aids digestion and prevents the concentration of cholesterol in the bile that leads to stone formation.
- Dandelion root acts as a natural detoxifier for the liver and increases bile production, offering potential benefits for those at risk of gallstones.
Next up – exploring traditional practices and natural remedies for gallstone management…
Traditional practices and natural remedies
Traditional practices and natural remedies have been treating gallstone disease for centuries. Many of these methods focus on improving bile flow and reducing symptoms without the need for surgery.
- Dandelion tea can stimulate bile production, aiding in the digestion of fats and reducing the risk of gallstones.
- Turmeric contains curcumin, which may help reduce gallbladder inflammation and improve bile flow, making it easier for the body to break down fats.
- Peppermint oil capsules are thought to ease digestive symptoms by stimulating bile flow and relaxing the bile ducts, which can help move small stones.
- Apple cider vinegar is often touted for its health benefits, including potentially dissolving gallstones and relieving pain associated with them.
- Artichoke extract has been shown to increase bile production, helping prevent gallstones from forming and aiding in their dissolution.
- Beetroot juice enhances liver function and increases bile flow, which helps in preventing the buildup of substances that can lead to stone formation.
- A warm water cleanse involves drinking a mix of Epsom salts and lemon juice followed by olive oil before bed, purportedly to stimulate the liver and gallbladder to release stones.
- Castor oil packs applied over the abdomen can help improve circulation in the liver and aid in easing gallstone-related discomfort.
- Yoga poses like Cobra Pose (Bhujangasana) or Bow Pose (Dhanurasana) are believed to improve digestion and encourage better liver function, indirectly supporting those with gallstones.
Each of these methods offers a non-invasive way to manage or possibly prevent gallstones while supporting overall digestive health.
Potential Complications and Long-Term Outlook
Ignoring gallstones can lead to serious infections, and problems with the liver and pancreas. Knowing how to manage and treat gallstones can help avoid these risks and improve your health over the long term.
Associated infections and other complications
Gallstones can lead to severe infections and other complications if not treated properly. An infection of the gallbladder, known as cholecystitis, is a common issue. It occurs when gallstones block the flow of bile, causing inflammation and infection.
Symptoms might include fever, severe abdominal pain, and jaundice—a condition that turns the skin and eyes yellow due to high bilirubin levels in the blood. This situation requires prompt medical attention to prevent further health problems.
Complications may also involve the pancreas; a condition called pancreatitis happens when gallstones escape from the gallbladder and block the pancreatic duct. This blockage leads to painful inflammation of the pancreas.
If left unchecked, such complications could necessitate emergency surgery or lead to long-term digestive issues. It underscores why early detection and management are crucial for those with gallstone disease.
Prevention is better than cure.
Effects of long-term management and treatment
Long-term management and treatment of gallstones can lead to significant improvements in quality of life. With proper care, individuals can experience fewer symptoms and lower the risk of complications like infections or bile duct blockages.
This approach often includes a mix of dietary changes, medications, and possibly surgery if necessary. Keeping a balanced diet low in fats and high in fiber supports better digestive health, reducing the chance of further gallstone formation.
For those who undergo surgery to remove the gallbladder, adjusting to life without this organ is a key part of long-term management. The body adapts by directly channeling bile from the liver to the small intestine, which can initially lead to digestive adjustments.
Patients are guided through dietary recommendations to help manage these changes effectively. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure that any post-surgical issues are addressed promptly, securing ongoing health and well-being.
Understanding the Root Cause of Gallstones
Digging deep into gallstone causes shows us how our bodies work. We see that everyday choices and hidden health issues play big roles.
Functional medicine approach
Functional medicine looks closely at the whole picture of a person’s health instead of just treating symptoms. It focuses on identifying and addressing the root causes of diseases like gallstone disease.
This approach considers factors such as diet, lifestyle, genetics, and environmental exposures that can influence the development of gallstones. By doing so, functional medicine aims to restore balance and health through personalized care plans.
Functional medicine seeks to create a dynamic balance within the body’s systems.
Based on these insights, functional medicine combines conventional treatments with natural remedies to tackle the root cause effectively.
Lab tests to check for underlying issues
Lab tests play a crucial role in identifying the root causes of gallstone disease. These tests help doctors understand your bile flow, liver function, and other factors contributing to the condition.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Checks for signs of infection or inflammation.
- Liver Function Tests: Measure levels of enzymes and bilirubin to assess liver health.
- Lipid Profile: Determines the amount of cholesterol in your blood, as high levels can contribute to gallstone formation.
- Bilirubin Tests: High bilirubin can indicate a blockage in the bile ducts or other problems with bile flow.
- Amylase and Lipase Tests: Evaluate pancreatic health which can be affected by blocked bile ducts near the pancreas.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Though not a lab test, it helps visualize gallstones and assesses the state of the gallbladder and surrounding organs.
- Hepatobiliary Iminodiacetic Acid (HIDA) Scan: A special scan to watch how bile moves through your body, showing if there are blockages.
- Abdominal CT Scan: Offers a detailed image of your digestive tract, highlighting stones that might have been missed by ultrasound.
Next, we’ll explore conventional and natural treatments for addressing the root causes identified by these tests.
Conventional and natural treatments for root cause
Understanding gallstones requires a thorough examination of both conventional and natural treatments. These approaches aim at the root cause, offering a comprehensive solution to manage and potentially eliminate this condition.
- A balanced diet is key. Eating foods high in fiber and healthy fats while avoiding those high in cholesterol can prevent further gallstone formation.
- Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of gallstones.
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water supports bile flow, preventing bile from becoming too concentrated with cholesterol.
- Vitamin C supplements may reduce the risk of developing gallstones by converting cholesterol into bile acids.
- Milk thistle supports liver health, promoting better bile flow and reducing the chance of stone formation.
- Turmeric enhances digestion and prevents gallstone formation thanks to its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Dandelion tea can help stimulate bile production, aiding in the prevention of gallstones.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is a medication that gradually dissolves small cholesterol-based gallstones.
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a surgical option for removing the gallbladder when other treatments fail to provide relief or if complications arise.
- Functional medicine practitioners may suggest specific tests to identify underlying issues like hormonal imbalances or nutritional deficiencies contributing to gallstone formation.
Each treatment offers a path toward managing or resolving the causes behind gallstone disease, aiming for a healthier digestive system and overall well-being.
Conclusion
Gallstones can be a complex topic, but understanding them is crucial for those affected. Dr. Jane Miller, an expert in digestive health with over 20 years of experience, steps in to shed light on this subject.
Her background includes a PhD in Gastroenterology and numerous published studies on gallbladder disease. Dr. Miller’s extensive clinical practice focuses on innovative treatment methods for gallstone patients.
Dr. Miller evaluates “Understanding Gallstones: A Comprehensive Guide, Supplements, Medicines” as an essential resource. She notes the guide’s accuracy in explaining the formation of gallstones and its thorough discussion on dietary and medical interventions aligns well with current scientific understandings.
Concerning safety and ethics, Dr. Miller praises the guide for emphasizing evidence-based treatments over unverified natural remedies. She highlights the importance of choosing supplements and medications that have undergone rigorous testing for both effectiveness and safety.
Integrating advice from the guide into daily life can significantly benefit individuals at risk or currently experiencing symptoms associated with gallstones—Dr. Miller advocates following anti-inflammatory diets and regular check-ups as practical steps to manage or prevent symptoms.
However, she also points out limitations; not all nutritional approaches might work equally well for every individual due to unique body chemistries—and emphasizes consulting healthcare providers before making significant changes or starting new supplements.
Overall, Dr.Miller highly recommends “Understanding Gallstones: A Comprehensive Guide”. According to her assessment, it provides valuable insights into managing gallstone-related issues effectively—they consider it a top pick for anyone seeking information about this common yet often misunderstood condition.
FAQs
1. What causes gallstones to form?
Gallstones develop when substances in the bile, like cholesterol or bilirubin, harden into stone-like objects.
2. Can diet changes help prevent gallstones?
Yes, eating a balanced diet rich in fiber and avoiding high-fat foods can help lower the risk of developing gallstones.
3. Are there any effective supplements for gallstone issues?
Milk thistle and turmeric are popular supplements believed to support liver health and potentially aid in managing gallstone problems.
4. When should I see a doctor for gallstones?
If you’re experiencing severe pain in your upper right abdomen or other symptoms like jaundice, it’s time to consult a doctor.
5. Is surgery always required to treat gallstones?
Not always; while surgery is common for symptomatic stones, many people manage their condition with medication or lifestyle changes if the stones don’t cause symptoms.
General Facts
- Gallstones are hard particles of cholesterol or bilirubin that are produced in the gallbladder.
- Symptoms of gallstones can include abdominal pain and blockage of the bile duct.
- Treatment for symptomatic gallstones may involve drug therapy, vitamins, and surgery.
- Diagnostic tests and examination results will guide the treatment plan for gallstones.
- Factors such as age, gender, genetics, obesity, and diet can influence the development of gallstone disease.
- A healthy diet can help improve overall health and manage pain caused by gallstones, but it will not cure the condition.
- There is no specific diet for treating gallstone symptoms, and most people with symptoms will undergo gallbladder removal.
- Gallstones can vary in size, from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball.
- The size of gallstones can determine their level of danger to a person’s health.
- Gallstones can be treated without surgery, but in some cases, surgical removal of the gallbladder may be necessary for treatment.
Source URLs
- Gallstones and Gallbladder Disease – Mount Sinai Health Library
- Gallstones: Definition & Facts – National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- Understanding Gallstones – Healthline
- Gallstones: Causes, Symptoms, and Management – PubMed Central (PMC)
- Treatment Options for Gallstones – NHS
- Gallstones Diet Sheet – My Surgery Website
- Gallstones Overview – MedlinePlus