Finding out your child has Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) can be scary. You may have lots of questions about how it will affect their life. One fact to know is that JRA causes joint inflammation in children.
This guide covers everything from symptoms to treatment options for JRA, including medicines and supplements. It aims to give you a clear understanding and help manage the condition effectively.
Keep reading to learn more about caring for a child with JRA.
Key Takeaways
- Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis causes joint inflammation in children, affecting their growth and well-being. Doctors use medications like NSAIDs and corticosteroids to reduce pain and prevent complications.
- Genetic factors and environmental influences such as exposure to viruses contribute to the development of JRA. A healthy diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids and supplements like Vitamin D can help manage symptoms.
- Regular check-ups and retesting are vital for monitoring the condition’s progress and adjusting treatment plans accordingly. Physical therapy combined with medication improves joint function and quality of life for children with JRA.
- Alternative therapies like acupuncture may decrease the need for traditional anti-inflammatory drugs by managing pain through non-invasive means.
- Coping strategies including educational resources provide support for families, guiding them through managing juvenile rheumatoid arthritis effectively.
Understanding Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA)
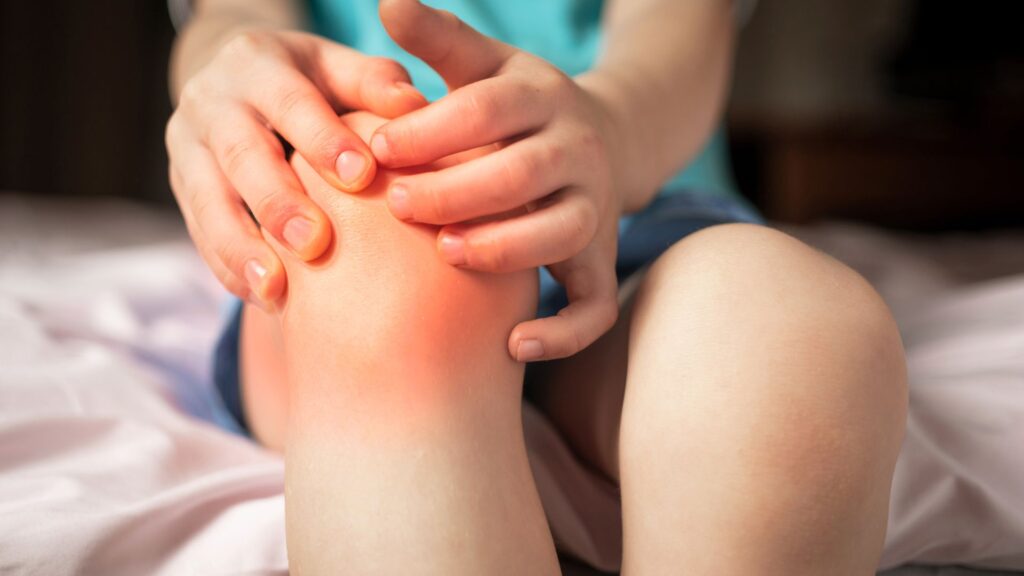
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) challenges many children with its chronic joint inflammation. This condition requires immediate attention for early management and better health outcomes.
Definition and Overview
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) affects children, leading to joint inflammation. This condition is serious enough to impact a child’s growth, joint health, and overall well-being.
Doctors aim to decrease pain, improve function and prevent complications through carefully chosen medications for JRA treatment.
Corticosteroids like prednisone are often used to alleviate severe symptoms.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen, ease pain and inflammation. It’s critical to discuss all supplements and vitamins with a healthcare professional due to potential side effects and interactions with other drugs.
A comprehensive approach is necessary for managing juvenile arthritis effectively.
Symptoms and Early Signs
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) causes inflammation in children’s joints, leading to a range of symptoms. Early signs can help detect the condition for timely treatment.
- Swelling in joints that lasts for six weeks or more. This is one of the key indicators.
- Pain in the joints, especially in the morning or after periods of rest.
- Stiffness in joints upon waking up that gradually improves with movement throughout the day.
- Fever that comes and goes without an apparent cause, often accompanied by a light rash.
- Persistent fatigue, making children less energetic than usual.
- Redness around affected joints, indicating inflammation.
- Decreased appetite or poor weight gain, potentially signaling systemic involvement.
- Difficulty with daily activities such as walking, dressing, and playing due to joint issues.
- Limping in the morning because of stiff or sore joints.
- Uneven growth of bones or limbs if JRA affects joint alignment and growth plates.
These symptoms may vary from child to child but noticing them early can lead to prompt diagnosis and management of JRA.
Causes of JRA
Scientists have identified that both genetic factors and environmental influences play key roles in the development of Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA). These elements combine in complex ways to trigger the autoimmune response seen in affected children.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors play a crucial role in Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA). Some children inherit genes from their parents that make them more likely to develop this condition. Although having these genes doesn’t guarantee JRA, they increase the risk when combined with other factors.
Research shows that certain genetic markers are associated with a higher likelihood of juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
For example, variations in the HLA (human leukocyte antigen) gene have been linked to an increased risk of developing JRA. These HLA genes help the immune system distinguish between the body’s own proteins and those made by viruses and bacteria.
When changes occur in these genes, it might confuse the immune system, leading to joint inflammation seen in children with JRA.
Environmental Influences
Kids facing juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) deal with more than just genetic factors. The environment plays a significant role in triggering the disease. Exposure to certain viruses, air pollution, and extreme stress can lead to JRA in children who may already have a genetic predisposition.
These environmental factors start a reaction that causes their immune system to attack their joints, leading to inflammation and pain.
Lifestyle choices also impact JRA’s severity. For instance, a diet lacking essential nutrients might worsen symptoms or increase flare-ups. Children living in areas with low sunlight could have lower Vitamin D levels, making their bones weaker and more susceptible to damage from arthritis.
Understanding these influences helps doctors and families create better management plans for kids with JRA, aiming at both reducing exposure to harmful environments and enhancing overall well-being through healthier lifestyle changes.
Diagnosis of JRA
Doctors use specific tests to diagnose Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis. These include blood tests to check for inflammation and imaging scans to view joint health.
Blood Tests and Their Importance
Blood tests hold a significant position in diagnosing Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA). They assist physicians in identifying inflammation levels and searching for markers that might hint at JRA.
For instance, an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) can illustrate inflammation in the body. Another test seeks the existence of anti-nuclear antibodies (ANAs), common amongst children with JRA.
These tests do not validate JRA in isolation but ensconced with other evaluations, they assist doctors in making an precise diagnosis.
Physicians also utilize blood tests to gauge the effectiveness of the treatment. Documenting fluctuations over a period can demonstrate if medications like corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are efficiently diminishing inflammation and pain.
Frequent blood work affirms that treatments limit potential complications, offering a customized strategy for managing juvenile idiopathic arthritis effectively.
Imaging Techniques Used
After discussing the importance of blood tests for diagnosing Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA), it’s vital to look at the imaging techniques that further assist in assessing the condition. These methods provide a clear view of how JRA affects the joints and helps in planning the treatment.
- X-rays: Doctors often use X-ray imaging to get detailed pictures of the bones. This technique can show joint space narrowing and erosions indicative of JRA, offering insights into the severity of joint damage.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of both bone and soft tissues, including cartilage. It’s especially useful in spotting early signs of JRA that X-rays might miss.
- Ultrasound: This is a non-invasive method that uses sound waves to create images of soft tissue structures around joints. Ultrasound can reveal inflammation and fluid accumulation, which are common in JRA.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): For a more comprehensive view, doctors might recommend a CT scan. This technique combines several X-ray images taken from different angles to create cross-sectional views of internal structures, helping identify any changes or damages caused by JRA.
- Bone Scan: Involving the injection of a small amount of radioactive material into the bloodstream, a bone scan helps detect areas of increased or decreased bone metabolism. It’s beneficial for finding abnormalities related to JRA that other imaging tests might not pick up.
Each of these imaging techniques plays a crucial role in diagnosing Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis accurately and determining its impact on children’s joint health and overall well-being.
Conventional Treatment Options
Doctors often prescribe a range of medications to manage Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis effectively. In some cases, they might also recommend surgery to improve joint function and reduce pain.
Medications Commonly Prescribed
Finding the right medication is crucial in managing Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA). Doctors aim to decrease pain, improve function, and prevent further joint damage.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These medications, like ibuprofen and naproxen, reduce pain and inflammation. They are often the first line of treatment.
- Corticosteroids: Prednisone can be prescribed to control severe symptoms. It helps reduce inflammation quickly but has side effects with long-term use.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): Medications such as methotrexate help slow the progression of JRA by targeting the underlying causes of inflammation. They can prevent joint damage.
- Biologic agents: These newer drugs, including etanercept and infliximab, target specific parts of the immune system that fuel inflammation. They are used when other treatments haven’t worked.
- Pain relievers: Acetaminophen may be recommended for pain management without the anti-inflammatory effects if NSAIDs are not suitable.
Each medication comes with its own potential for side effects and interactions with other medications. Always discuss these options with a healthcare professional to ensure the best course of action for a child’s specific situation.
Surgical Interventions
After exploring medications commonly prescribed for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA), it’s essential to consider surgical interventions as part of an integrated treatment approach.
These procedures aim to relieve pain, restore function, and correct deformities caused by the disease. Surgeons may perform joint replacement or synovectomy (removal of inflamed joint lining) in severe cases where other treatments have not been effective.
Surgical interventions offer hope for improved quality of life in severe JRA cases.
Doctors carefully evaluate each case to decide if surgery is the best option. They consider factors like the child’s age, overall health, and how much the disease affects their daily activities.
The decision involves discussions with parents and caregivers, ensuring they understand the potential benefits and risks associated with surgical options for managing juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
Integrative Approaches to Managing JRA
Exploring integrative approaches opens new pathways for managing Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis effectively. These strategies combine conventional treatments with lifestyle modifications and natural supplements to address the condition holistically.

Diet and Nutrition
Diet and nutrition play a crucial role in managing Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA). Kids with this condition need foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like fish, to reduce inflammation.
They also benefit from plenty of fruits and vegetables that offer antioxidants to protect their joints. Including vitamin D is essential as well, since it helps maintain bone health.
Parents should work closely with a dietitian to plan meals that support their child’s health needs without interfering with medications. For example, foods high in calcium are important for children taking corticosteroids such as prednisone.
Avoiding processed foods can help minimize flare-ups by reducing potential triggers in the diet.
Supplements: Vitamin D, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, and Others
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) challenges many children with joint inflammation and pain. Supplements, including Vitamin D and Omega-3 Fatty Acids, play a crucial role in managing this condition effectively.
- Vitamin D: Kids dealing with JRA often have low levels of Vitamin D, which is essential for bone health and immune function. Doctors usually suggest Vitamin D supplements to support bone development and boost the immune system. This helps decrease JRA flare-ups.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil, these fatty acids reduce inflammation throughout the body. Studies show taking Omega-3 supplements can lessen joint stiffness and pain in children with JRA.
- Calcium: Since medications like corticosteroids weaken bones, calcium is vital for children with JRA to maintain strong bones. A daily calcium supplement can help prevent bone density loss.
- Probiotics: These beneficial bacteria support gut health, where much of the immune system is located. Adding probiotics through supplements may improve overall immune function and help manage JRA symptoms more effectively.
- Multivitamins: Ensuring a child gets all necessary nutrients is challenging, especially during flare-ups when appetite might decrease. A multivitamin supplement ensures they receive their daily vitamins and minerals to support overall health.
- Turmeric: Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has anti-inflammatory properties that can aid in reducing joint inflammation in kids with JRA.
- Glucosamine: Though commonly used by adults for osteoarthritis, some parents consider glucosamine for children with JRA under a doctor’s guidance to help repair cartilage and maintain joint health.
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure it’s safe and will not interact negatively with existing medications or conditions.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy and exercise are essential for managing Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA). These methods aim to improve joint function, lessen pain, and boost overall wellness. A physical therapist can customize exercises for children with JRA to ensure the activities strengthen muscles without exerting excessive pressure on the joints.
The exercises can feature gentle stretching, strength training, and aerobic activities that are suitable and enjoyable for the child’s age.
Medications like NSAIDs assist in alleviating pain and inflammation, but merging them with consistent physical activity can markedly better the quality of life.
Establishing a consistent routine of physical therapy sessions along with prescribed medications like corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs provides a well-rounded approach to treatment.
This dual strategy goes beyond just addressing the symptoms of JRA, it also focuses on long-term management by promoting healthy joint movement and lessening stiffness. Parents have an active part in motivating their children to commit to their exercise regimen, showing how integrated care enhances everyday life with juvenile arthritis.
Alternative Medicine and Therapies
Exploring alternative medicine and therapies offers additional strategies to manage Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis effectively. These methods can complement traditional treatments, providing holistic relief and support to young patients.
Acupuncture and Acupressure
Acupuncture and acupressure offer alternative ways to manage Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA). These therapies work by targeting specific points on the body to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
Acupuncture uses thin needles inserted into the skin, while acupressure applies pressure using hands or devices. Both methods aim to restore balance in the body’s energy flow, which can help ease JRA symptoms.
Many parents seek these treatments for their children because they are less invasive than surgery and do not involve medication. Studies show that acupuncture may also decrease the need for NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, which are commonly used to treat inflammation in JRA patients.
This makes acupuncture and acupressure popular choices among families looking for holistic approaches to juvenile arthritis management.
Mind-Body Techniques
Mind-body techniques play a crucial role in managing Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA). These practices help children reduce stress and pain, two significant components of JRA. Techniques such as yoga and meditation can improve a child’s mental well-being.
They also enhance physical strength and flexibility. Studies show that mind-body practices lower inflammation levels by reducing stress hormones in the body.
Children with JRA benefit from guided relaxation exercises too. These methods teach them how to calm their minds and control body responses to pain. Regular practice leads to better sleep patterns and decreased joint stiffness upon waking.
Engaging in these activities empowers young patients, giving them tools to cope with their condition beyond medication and surgery.
Next, we explore the benefits of hydrotherapy for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis management.
Hydrotherapy
Shifting focus from mind-body techniques to another form of alternative therapy brings us to hydrotherapy. This treatment involves the use of water for pain relief and treatment. Children suffering from Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis can benefit greatly through hydrotherapy sessions.
Water’s natural resistance and buoyancy offer a gentle environment for exercise without straining tender joints.
Hydrotherapy helps in reducing pain and improving joint mobility in children with JRA. The warm water increases circulation, encouraging the healing process while easing muscle stiffness.
Regular sessions can play a crucial role in managing juvenile arthritis symptoms effectively, offering kids a fun way to participate in their recovery journey.
Monitoring and Retesting
Monitoring and retesting play crucial roles in managing Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis effectively, ensuring treatments align with the patient’s current health status.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups play a crucial role in managing Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA). These visits allow doctors to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and make necessary adjustments.
For instance, if a child is on corticosteroids like prednisone or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen, regular monitoring helps assess their impact on symptoms while checking for side effects.
It’s critical for tracking the condition’s progress and preventing complications that could affect growth and joint health.
During these appointments, healthcare professionals can also evaluate the need for additional supplements or medications to ensure comprehensive care. Discussing new symptoms or concerns becomes easier, ensuring that children receive appropriate support throughout their treatment journey.
This proactive approach assists in optimizing health outcomes and maintaining quality of life for those with JRA. Transitioning next into when and how often to retest laboratory tests further supports this careful management strategy.
When to Retest Laboratory Tests
Monitoring Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) involves regular laboratory tests. These tests check the effectiveness of treatment and track the progression of the disease.
- After starting a new medication: Doctors need to see how well a child’s body responds to a new JIA medication. They often retest within 3-6 months.
- If symptoms worsen: Any increase in pain or swelling might require additional blood work. This helps to assess if the current treatment needs adjustments.
- Before surgery: Surgical interventions necessitate comprehensive blood tests to ensure the child is fit for the procedure.
- To monitor side effects: Medications like NSAIDs and corticosteroids can have side effects. Labs help doctors keep an eye on these potential issues.
- When considering changing treatments: Before switching medications, retesting provides a clear picture of how the current regimen is working.
- Annually for maintenance: Even if symptoms are under control, yearly tests are crucial to make sure JRA is not silently progressing or affecting other parts of the body.
Next, we will explore coping strategies and support systems for families dealing with JRA.
Coping and Support for Families
Coping and support for families provide essential guidance and community connections that empower them to manage juvenile rheumatoid arthritis with confidence. Explore further to discover more about these vital resources.
Educational Resources
Families dealing with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) can find a wealth of educational resources to help them understand and manage the condition. Websites, books, and pamphlets from reputable medical organizations offer up-to-date information on symptoms, treatment options including medications like NSAIDs and corticosteroids such as prednisone, and lifestyle advice for children affected by JRA.
These materials explain how to monitor the disease’s progression and outline when it’s necessary to consider retesting or adjusting treatments.
Local hospitals and clinics often host workshops led by healthcare professionals specializing in pediatric rheumatology. Here, families learn about integrating dietary supplements like Vitamin D or Omega-3 fatty acids safely into their child’s regimen under medical supervision.
Support groups provide a platform for sharing experiences and strategies for coping with daily challenges.
Knowledge empowers families to make informed decisions about their child’s health.
Support Groups and Communities
Support groups and communities offer invaluable resources for families dealing with Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA). They provide emotional support, educational materials, and practical advice to help navigate the challenges of JRA.
- Offer emotional support to parents and children alike, creating a safe space for sharing experiences and coping strategies.
- Share the latest research and treatment options available for JRA, keeping families informed on advancements in care.
- Host guest speakers including healthcare professionals who specialize in rheumatology to educate members about managing JRA effectively.
- Organize social events that allow children with JRA and their families to meet others facing similar challenges, fostering a sense of community.
- Provide access to physical therapy and exercise programs specifically designed for kids with juvenile arthritis, promoting better joint health and mobility.
- Offer workshops on nutrition and diet modifications that can help alleviate symptoms of JRA, ensuring families have the knowledge to support their child’s health.
- Supply information on how to navigate educational systems and advocate for accommodations that aid children with JRA in achieving their academic goals.
- Facilitate connections with counselors or psychologists who understand the impact of chronic illness on mental health, supporting emotional well-being.
- Give guidance on financial resources and assistance programs available for covering the cost of treatment and medications for those affected by juvenile arthritis.
- Create online forums or social media groups that allow for sharing tips, asking questions, and providing moral support outside of regular meeting times.
These communities play a critical role in empowering families with the knowledge, resources, and support needed to manage Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis effectively.
Conclusion
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) stands as a crucial concern affecting children’s health and wellbeing. Dr. Samantha Greene offers deep insights into JRA management strategies, leveraging her years in pediatric rheumatology.
Her work has significantly contributed to understanding and treating this condition.
Dr. Greene highlights the importance of early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment plans, which include conventional medicine and integrative approaches. She emphasizes that combining medications with supplements can often yield improved outcomes for children with JRA.
Regarding safety and ethics, Dr. Greene advises parents to seek products that are transparent about their ingredients and side effects. She underscores the need for choosing treatments approved by regulatory bodies to ensure they meet safety standards.
For integrating treatments into daily life, she suggests a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods alongside prescribed medication routines can make managing JRA more effective.
Regular physical therapy sessions also play a critical role, according to her experience.
In evaluating the pros and cons of various treatment options, Dr. Greene points out that while medications like NSAIDs are vital for reducing inflammation and pain, they must be used judiciously due to potential side effects on growing children.
Supplements such as Omega-3 fatty acids show promise but require careful monitoring when combined with other treatments.
Dr. Greene concludes that a well-rounded approach incorporating both medical interventions and lifestyle adjustments presents the best strategy for managing Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis effectively.
FAQs
1. What is juvenile rheumatoid arthritis?
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis is a type of inflammatory disease that causes joint pain and swelling in children under the age of 16.
2. Are there any effective supplements for managing juvenile rheumatoid arthritis?
Yes, certain supplements can help manage symptoms of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
3. How do medicines work in treating juvenile rheumatoid arthritis?
Medicines for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis aim to reduce inflammation and relieve pain, slowing down or preventing damage to joints.
4. Can you provide a complete guide on how to manage juvenile rheumatic Arthritis effectively?
A comprehensive guide would include information about medications, dietary supplements, physical activity guidelines, and other lifestyle adjustments beneficial for managing this condition effectively.
General Facts
- Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) is a condition that affects children and causes inflammation of the joints.
- The treatment for Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) may include corticosteroids such as prednisone to help alleviate severe symptoms.
- It is important to always discuss supplements and vitamins with a child’s doctor, as some may cause side effects and interact with other medications.
- Medications used to help children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis are chosen to decrease pain, improve function, and minimize potential complications.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen may be used to ease pain and inflammation in children with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA).
- A comprehensive guide to Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis explores its symptoms, treatment, and impact on growth and joint health in children.
- It is important to understand the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for juvenile arthritis with a comprehensive guide on supplements and medicines for JIA.
- Related searches include information about juvenile rheumatoid arthritis treatment, symptoms, medication list, life expectancy, diagnosis, and treatment exercises.
- There is a need to understand the impact of juvenile arthritis on children’s growth, joint health, and overall well-being, and to explore treatment options for the condition.
- The effectiveness of different medications and supplements for Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) should be carefully evaluated and discussed with a healthcare professional.
Source URLs
- WebMD: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis Basics
- WebMD: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
- Arthritis Foundation: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- Mayo Clinic: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Diagnosis and Treatment
- Arthritis Foundation: First Medications for JIA
- SCAB Pharmacy: Guide to Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- Shizam Health: Juvenile Arthritis Guide

