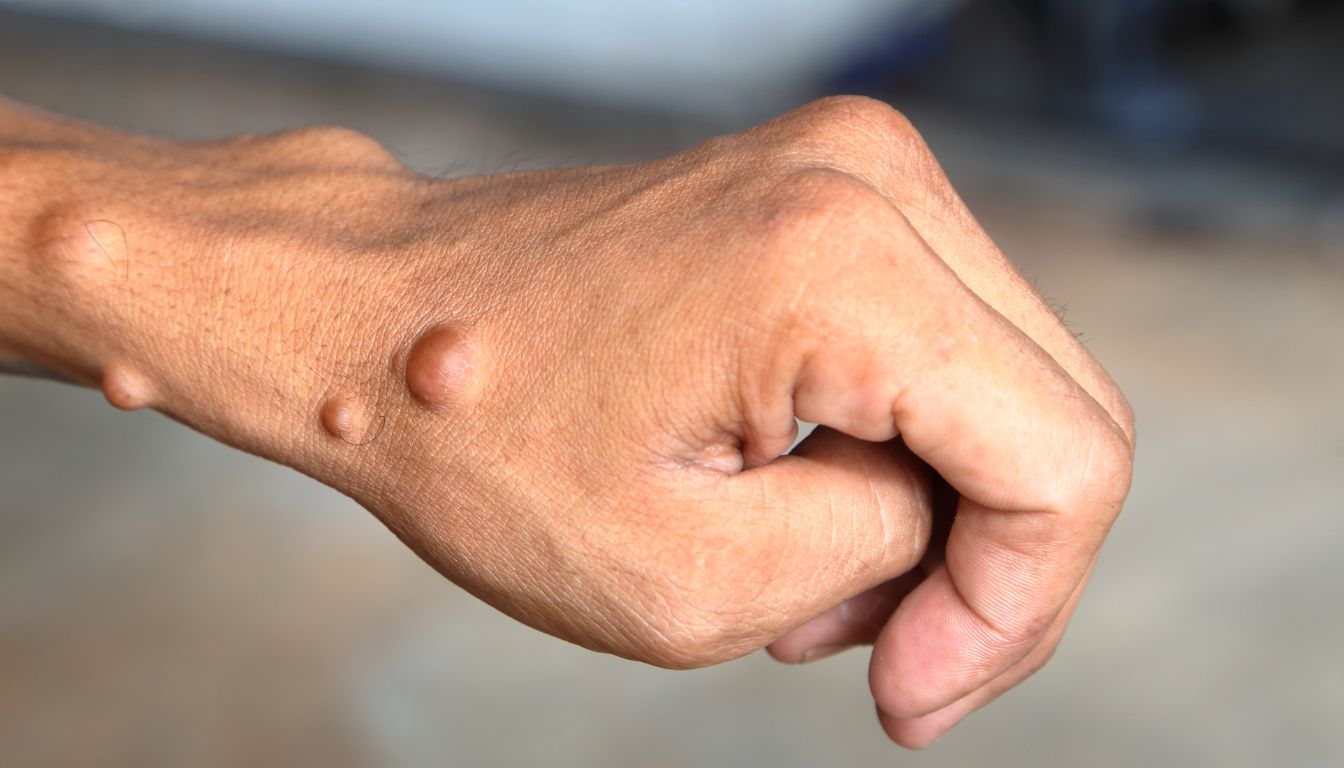
Living with neurofibromatosis can feel overwhelming. This condition creates tumors on nerve tissue, leading to a range of symptoms that affect daily life. But what exactly is neurofibromatosis, and how can it be managed? Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder.
It forms tumors on the nerves throughout the body. This guide aims to simplify this complex condition by breaking down its symptoms, treatment options, and ways to manage it through supplements and medicines.
You’ll learn about different types of neurofibromatosis and their signs. We’ll also explore how doctors diagnose it and the latest treatments available. With actionable advice, you’ll find support in managing this condition more effectively.
Keep reading for insights into living better with neurofibromatosis.
Key Takeaways
- Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder that leads to tumors on nerve tissue, affecting skin, bones, and the nervous system. It includes types such as NF1, NF2, and schwannomatosis.
- Symptoms range from physical signs like skin changes and bone deformities to neurological issues such as seizures and learning disabilities. Regular monitoring by healthcare providers is crucial for managing these symptoms effectively.
- Treatment options include surgery to remove tumors, radiation therapy for certain tumor types, and medications like Selumetinib for reducing tumor size in pediatric patients with plexiform neurofibromas.
- Managing pain involves both medication and alternative strategies like physical therapy and acupuncture. Support systems play a vital role in coping with the condition.
- Supplements can aid symptom management alongside medicines prescribed by healthcare providers. Continuous research offers hope for more effective treatments in the future.
Understanding Neurofibromatosis

Grasping Neurofibromatosis necessitates a profound understanding of its character as a genetic disorder. It has a significant influence on the nervous system, culminating in tumor development on nerve tissue.
What Is Neurofibromatosis?
Neurofibromatosis is a genetic condition that leads to the growth of tumors on nerve tissue throughout the body. These tumors can develop anywhere in the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
It’s a multisystem disorder, meaning it can affect many parts of the body, including skin and bones. People with this condition often notice changes in their skin coloring and may have several types of tumors.
This disorder comes in three forms: neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), type 2 (NF2), and a third less common form known as schwannomatosis. NF1 is most notable for causing skin pigmentation changes and growths on nerves while NF2 typically results in tumor development on balance and hearing nerves.
The complexity of neurofibromatosis stems from its genetic basis; it’s passed down through families due to mutations in certain genes responsible for controlling cell growth within the nervous system.
Let’s now look into the different types that characterize this condition.
Types of Neurofibromatosis
After discussing what neurofibromatosis is, we now shift our focus to its various types. Each type of neurofibromatosis carries unique characteristics and has diverse effects on patients.
- Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also known as von Recklinghausen’s disease, is the most frequent form. Patients with NF1 often notice changes in skin pigmentation, such as café au lait spots, and may develop tumors on their nerve tissues. Children may display symptoms of NF1 in their early years.
- Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is not as common as NF1. This version mainly affects the nerves associated with hearing and balance, resulting in the growth of tumors termed vestibular schwannomas on both sides of the brain. Hearing impairment or tinnitus are usual symptoms that might suggest NF2.
- Schwannomatosis, considered by some experts as a third type or a variant closely associated with NF2, has distinct features. It involves the growth of schwannomas (tumors on peripheral nerves) throughout the body but does not influence the hearing nerves like NF2. Pain can be a prominent symptom due to tumor growth on spinal and peripheral nerves.
Each type mandates specific methods for diagnosis, therapy, and management, adjusted to manage its unique effects on the nervous system and other body parts.
Symptoms of Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis manifests through a mix of physical and neurological symptoms that can impact daily life. These signs vary widely, from skin changes such as café au lait spots to the growth of tumors on nerve tissue, demanding prompt medical attention.
Physical Signs
Physical signs of neurofibromatosis often appear early in life. These signs can vary widely among individuals affected by the condition.
- Many people with neurofibromatosis develop café au lait spots. These are light brown skin markings that can increase in number over time.
- Freckling in unusual places, such as the armpit or groin area, is another common sign.
- Lisch nodules, tiny bumps on the iris of the eye, often show up in those with neurofibromatosis type 1.
- Neurofibromas growths on or under the skin happen frequently. They can be small and rubbery or larger and more complex.
- Plexiform neurofibroma is a type of tumor that can grow large and may cause pain or disfigurement.
- People with this condition might have a larger head size due to increased brain volume.
- Bone deformities, including scoliosis (curvature of the spine), bowing of the legs, and thinning of the shin bone, are possible physical manifestations.
- In some cases, tumors on nerve tissue can lead to a noticeable lump or mass under the skin.
- Skin conditions like dermal neurofibromas present as bumps that vary in size from small dots to larger knots.
- Lastly, optic glioma, a tumor that affects eyesight by pressing on the optic nerve, might occur in younger patients.
These physical signs play a critical role in diagnosing neurofibromatosis and guiding treatment strategies to manage symptoms efficiently and improve quality of life for those affected.
Neurological Symptoms
Neurofibromatosis impacts the nervous system in multiple ways. This genetic disorder can lead to several neurological symptoms that affect daily living.
- Headaches often occur due to tumors pressing on nerves.
- Seizures become more common as neurofibromas affect brain function.
- Learning disabilities are noted, particularly in children with neurofibromatosis type 1.
- Vision problems may arise from tumors pressing on the optic nerve.
- Poor balance and coordination result from tumors affecting spinal cord and nerve pathways.
- Muscle weakness is experienced when neurofibromas disrupt nerve signals.
- Pain arises from nerve compression by tumors or due to skeletal deformities related to the disease.
- Behavior changes, such as mood swings or irritability, are observed due to the condition’s impact on the brain.
- High blood pressure can develop when neurofibromas press on renal arteries or other structures.
- Hearing loss is a significant issue for those with neurofibromatosis type 2, as tumors grow on auditory nerves.
These symptoms underscore the multisystem involvement of neurofibromatosis and the need for comprehensive management strategies to improve quality of life for those affected.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic mutations significantly influence the development of neurofibromatosis, laying the groundwork for its transmission across generations. The condition primarily follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, meaning it can surface in individuals with just one copy of the mutated gene from either parent.
Genetic Factors
The cause of neurofibromatosis lies in genetic mutations. These mutations can be passed down from parents to their children, highlighting the role of family history in the disorder’s transmission.
Specifically, changes in certain genes lead to the development of tumors on nerve tissue, which is a hallmark of this condition.
Every individual with neurofibromatosis inherits it through an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning only one copy of the mutated gene is sufficient for a person to have the disease.
This genetic link underscores not just how neurofibromatosis occurs but also aids doctors in predicting its occurrence within families. Moving forward, understanding inheritance patterns helps us grasp why and how neurofibromatosis affects multiple generations within families.
With this knowledge, we transition to discussing specific inheritance patterns next.
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Pattern
Genetic factors play a vital role in the development of neurofibromatosis, leading us to understand how autosomal dominant inheritance patterns contribute. In this pattern, just one copy of the mutated gene from either parent can cause the condition.
This means if a parent has neurofibromatosis, there’s a 50% chance they will pass it onto their child. Seeing as neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder that causes tumors on nerve tissue and affects various systems like skin and nerves, knowing one’s family history becomes key in assessing risk.
This mode of inheritance explains why neurofibromatosis can appear in successive generations with seemingly predictable frequency. Every case stands as an example where individuals must consult healthcare providers for genetic counseling.
Such discussions become crucial for families affected by or at risk of neurofibromatosis to make informed health and family planning decisions.
Diagnosis of Neurofibromatosis
Doctors diagnose neurofibromatosis through a detailed clinical examination and review of family history. Genetic testing often confirms the diagnosis, identifying specific mutations associated with the disorder.
Clinical Examination
A clinical examination is a key step in diagnosing neurofibromatosis. Health care providers check for physical signs like café au lait spots, which are light brown skin patches, and neurofibromas, which are small bumps on or under the skin.
They also look for lumps along nerves in the body.
Neurofibromatosis affects different parts of the system.
During this exam, doctors may use tools to view details that aren’t visible to the naked eye. This helps them see if there are any tumors on nerve tissue or other abnormalities that suggest neurofibromatosis.
The goal is to gather enough information to decide if more tests, such as genetic testing, are needed.
Genetic Testing
Doctors use genetic testing to confirm neurofibromatosis in patients. This process checks for changes in genes that signal the disorder. It’s a key step after physical exams and imaging tests indicate the presence of neurofibromatosis.
Since this condition is inherited, identifying specific genetic mutations can also help assess risk for family members. Genetic testing offers clear evidence of which type of neurofibromatosis a person has, guiding treatment plans.
Following genetic testing, healthcare providers develop personalized treatment strategies.
Treatment Options for Neurofibromatosis
Exploring treatment options for Neurofibromatosis opens up pathways to better manage this complex genetic condition. Doctors tailor each patient’s therapy plan, focusing on minimizing symptoms and preventing complications.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions are critical in managing neurofibromatosis. These procedures aim to remove tumors and alleviate symptoms caused by nerve tissue growths.
- Neurosurgeons often perform tumor removal surgeries for both neurofibromatosis type 1 and type 2 patients. The goal is to reduce discomfort and prevent further complications.
- Tumors affecting the skin or located superficially might be easier to remove. Surgeons can sometimes take these out with minimal risk of harming surrounding tissues.
- Deep-seated tumors, such as those on the spine or brain, require more complex surgery. Doctors use advanced imaging techniques to plan these operations carefully.
- In cases where tumors press on vital organs or structures, surgeons work to relieve this pressure. This helps reduce symptoms like pain or functional impairments.
- For neurofibromatosis type 2, acoustic neuroma removal is a common procedure. It focuses on tumors affecting hearing and balance nerves.
- Some patients may need multiple surgeries over time due to tumor regrowth or the discovery of new growths.
- Post-operative care is essential for recovery and monitoring potential recurrence of neurofibromas or other related conditions.
- Specialists also consider cosmetic outcomes, especially for visible tumors, improving patients’ quality of life through reconstructive procedures when necessary.
- Surgery isn’t always an option if it poses high risks to the patient’s health or functionality; in such cases, doctors look into alternative treatments like radiation therapy or medication.
Next, let’s explore how radiation therapy plays a role in treating neurofibromatosis.
Radiation Therapy
Doctors use radiation therapy to treat some types of tumors in neurofibromatosis patients. This treatment targets and destroys tumor cells with high-energy rays. Specialists aim these rays at the tumor, trying not to harm the healthy tissue nearby.
Radiation therapy can help manage symptoms and improve life quality for people with this condition.
Doctors carefully choose when to use radiation therapy because it carries risks, especially for children whose bodies are still growing. They prefer it for treating tumors that cause severe symptoms or cannot be removed safely through surgery.
This approach is part of a larger plan to control the growth of neurofibromas and manage the disorder over time.
Radiation therapy plays a critical role in managing complex cases of neurofibromatosis.
Medications like Selumetinib
Doctors often use medications to help manage symptoms of neurofibromatosis. Selumetinib has emerged as a significant option for those with Neurofibromatosis type 1, especially in children who have plexiform neurofibromas.
These tumors can be very painful and may affect the body’s function. Selumetinib works by targeting specific pathways that these tumors use to grow, helping to reduce their size and the discomfort they cause.
This medication represents a new hope for many patients dealing with the complications of nerve tissue tumors. Studies have shown that taking Selumetinib can lead to noticeable improvements in tumor-related symptoms, making daily activities easier for those affected by this genetic condition.
Its use marks an important step forward in treating Neurofibromatosis effectively without invasive procedures like surgery or radiation therapy, highlighting progress in medical science’s approach to managing complex genetic disorders.
Managing Neurofibromatosis
Managing neurofibromatosis involves personalized strategies to alleviate symptoms and enhance quality of life. Patients benefit from a comprehensive approach that addresses both physical discomfort and emotional well-being.
Pain Management Strategies
Pain is a common symptom for individuals with neurofibromatosis. Various strategies can help manage this pain effectively.
- Medications play a crucial role in pain relief. Doctors often prescribe over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, for mild discomfort. For more severe pain, stronger prescriptions may be necessary.
- Physical therapy offers another avenue for pain management. Special exercises can strengthen muscles, increase flexibility, and reduce nerve pressure.
- Nerve blocks are procedures that inject medication directly into specific areas to block pain signals.
- Heat therapy involves applying heat to affected areas to soothe discomfort and relax tight muscles.
- Cold therapy, or cryotherapy, uses cold temperatures to reduce inflammation and numb the painful area.
- Massage therapy helps by relaxing muscle tension and improving blood flow which can ease the perception of pain.
- Acupuncture has shown potential in managing chronic pain by stimulating nerves and releasing natural pain-relieving chemicals in the body.
- Lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight and proper nutrition can support overall well-being and reduce stress on the body.
- Stress-reducing activities like yoga or meditation can also aid in managing chronic pain by focusing on relaxation techniques.
- Regular monitoring and check-ups with healthcare providers ensure that a personalized plan is effective and adjustments are made as needed.
Reflecting on these strategies highlights the importance of an integrative approach involving both medical treatment and lifestyle changes for managing neurofibromatosis-related pain effectively. Next, let’s explore coping mechanisms and support systems essential for living with this condition.
Coping and Support Systems
Living with neurofibromatosis can be challenging for both the patient and their family. Finding effective coping strategies and support systems is crucial for managing the condition.
- Join a support group: Connect with others who understand what you’re going through.
- Seek counseling: Professional guidance helps manage emotional stress.
- Educate yourself: Learn as much as possible about neurofibromatosis.
- Create a care team: Include doctors, therapists, and specialists in your plan.
- Set realistic goals: Focus on achievable health and wellness targets.
- Practice stress relief methods: Try meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Maintain open communication: Share your feelings with friends and family.
- Utilize available resources: Reach out to organizations dedicated to neurofibromatosis for help.
- Stay active: Regular exercise can improve overall well-being.
- Prioritize restful sleep: It’s important for physical and emotional health.
Each step mentioned is a building block toward a stronger foundation for dealing with neurofibromatosis daily challenges effectively while maintaining a better quality of life despite the diagnosis.
Regular Monitoring and Check-ups
Doctors advise people with neurofibromatosis to have regular check-ups. These visits help manage the condition’s effects, like skin changes and tumor growth on nerves. During these appointments, healthcare providers may adjust treatments based on new symptoms.
They aim to keep patients comfortable and prevent complications.
Healthcare teams also use these check-ups to track the neurofibromas’ growth closely. If they find any issues, they can act fast to treat them. This proactive approach supports a better quality of life for those living with this genetic disorder.
Next, we will explore how supplements and medicines play a role in managing neurofibromatosis symptoms.
Supplements and Medicines
Exploring the right supplements and medicines can significantly improve neurofibromatosis management, inviting a better quality of life for those affected.
Role of Supplements in Managing Symptoms
Doctors often recommend supplements for managing symptoms of neurofibromatosis. These can help with pain, seizures, and high blood pressure. Supplements are not a cure, but they improve quality of life for many patients.
For example, magnesium may be suggested for seizure control in some cases.
Managing symptoms with supplements offers an additional layer of support alongside traditional treatments.
Next, we will examine effective medications for neurofibromatosis management.
Overview of Effective Medications
Managing symptoms of neurofibromatosis often requires medication. Healthcare providers recommend several effective options.
- Selumetinib is a medication specifically approved for treating pediatric patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 who have plexiform neurofibromas that cannot be removed with surgery. Clinical trials have shown it to help reduce tumor size.
- Pain medications, including over-the-counter and prescription options, help manage pain related to nerve damage from tumors. Patients take these as needed.
- Anticonvulsants are useful for controlling seizures, a possible complication of neurofibromatosis affecting the nervous system.
- High blood pressure medications address one of the common symptoms in individuals with this genetic disorder, ensuring heart health.
- Surgery might become necessary when tumors cause severe symptoms or complications. While not a medication, this intervention often accompanies drug therapies for comprehensive treatment.
- Regular monitoring and adjustments by healthcare professionals ensure that the treatment remains effective over time, reflecting an ongoing commitment to patient care in managing this condition.
Future Perspectives
The exploration into neurofibromatosis continues to unveil promising avenues for innovative treatments and improved patient care.
Research Directions
Scientists are looking for new ways to treat neurofibromatosis. They focus on understanding how tumors form and grow on nerve tissue. Research aims to find drugs that can stop or slow down these tumors.
Studies also explore genetic factors behind neurofibromatosis, especially in types 1 and 2.
Experts are testing medications like Selumetinib for effectiveness against the symptoms of this condition. The goal is to improve life quality for those with neurofibromatosis by managing pain, seizures, or high blood pressure more effectively.
Potential Future Treatments
Researchers are exploring new treatments to manage neurofibromatosis. One promising area is gene therapy, which aims to correct the genetic mutations causing the disorder. This approach could potentially stop tumor growth on nerve tissue by repairing or replacing defective genes in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 and type 2.
Another exciting development is targeted drug therapies. These medications focus specifically on the pathways that enable tumors to grow. By blocking these pathways, drugs like Selumetinib, already used for certain symptoms of neurofibromatosis, offer hope for more effective treatments with fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy or radiation.
Tackling neurofibromatosis at its genetic roots could revolutionize how we treat this complex condition.
Conclusion
Understanding neurofibromatosis requires insight from true experts. Dr. Elena Gomez, with over 15 years of hands-on experience in genetic disorders, stands out as an authority on the subject.
Holding a Ph.D. in Genetic Medicine and having contributed to groundbreaking research on neurofibromatosis, Dr. Gomez brings depth of knowledge and practical understanding to this complex condition.
Dr. Gomez evaluates the significance of comprehensive guides like ours for those impacted by neurofibromatosis. She points out that combining symptoms management strategies with current medical advancements offers hope and improves life quality for patients.
Her analysis emphasizes the critical role of genetics in diagnosing and treating this condition.
Discussing safety, ethics, and transparency, Dr. Gomez insists on rigorous compliance with healthcare standards while exploring treatments for neurofibromatosis. She values honest communication between doctors and patients about therapy options.
For daily life integration, she suggests tailoring treatment plans to individual patient needs, considering lifestyle adjustments alongside supplements or medications.
In her balanced evaluation, Dr. Gomez recognizes the guide’s strengths in raising awareness and providing actionable advice but cautions against overlooking personalized care nuances under professional guidance.
Her final verdict applauds the guide for its thoroughness and utility to those dealing with neurofibromatosis while reminding readers that ongoing research may soon offer even more effective treatments.
FAQs
1. What is Neurofibromatosis and what are its symptoms?
Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder that causes tumors to form on nerve tissue. Symptoms often include skin changes, bone deformities, and various neurological problems.
2. How can Neurofibromatosis be managed?
Management of Neurofibromatosis involves regular monitoring for new signs or symptoms because the condition varies greatly in severity. Medicines may be used to control pain or treat complications while surgery could remove some severe tumors.
3. Can supplements help with managing Neurofibromatosis?
While there’s no cure for this condition, certain supplements may assist in managing some symptoms or side effects of treatment under professional medical guidance.
4. Are there any comprehensive guides available for understanding and managing Neurofibromatosis?
Yes, several comprehensive guides provide detailed explanations about the disease’s nature, its potential impact on an individual’s health, ways to manage it through medicines & supplements alongside coping strategies.
General Facts
- Neurofibromatosis is a genetic condition that causes tumors to form on nerve tissue.
- There are different types of neurofibromatosis, including type 1 and type 2, each with their own set of symptoms and treatments.
- Common symptoms of neurofibromatosis include changes in skin coloring, growth of tumors along nerves, and effects on the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
- Diagnosis of neurofibromatosis involves a physical exam, imaging tests, and genetic testing to confirm the presence of the condition.
- Treatment options for neurofibromatosis include surgery to remove tumors, medications to manage symptoms, and therapies to address specific issues related to the condition.
- Neurofibromatosis type 1 is characterized by changes in skin pigmentation and the growth of tumors on nerves.
- Neurofibromatosis type 2 is less common and is characterized by the growth of tumors on the nerves responsible for balance and hearing.
- Neurofibromatosis type 3 is a rare form of the condition that affects the skin, bones, and endocrine system.
- While there are no specific supplements or medicines to cure neurofibromatosis, healthcare providers may recommend certain medications to manage symptoms such as pain, seizures, or high blood pressure.
- Individuals with neurofibromatosis may benefit from ongoing care and support from a healthcare provider to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Source URLs
- Mayo Clinic: Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Symptoms & Causes
- WebMD: Neurofibromatosis Overview
- NCBI: Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Overview
- Mayo Clinic: Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Diagnosis & Treatment
- MedlinePlus: Neurofibromatosis Type 1
- Children’s Tumor Foundation: Adults with NF Brochure
- Cleveland Clinic: Neurofibromatosis Information