If you’ve discovered a lump in your neck or undergone changes in your voice, you might belong to the group confronting thyroid nodules. The presence of these small lumps can induce concern and uncertainty, triggering queries about health and subsequent courses of action.
Intriguingly, most thyroid nodules are not detrimental, but awareness of this reality does not always diminish the unease associated with the finding of a nodule.
This article provides a comprehensive overview about thyroid nodules – their composition, their occurrence, their diagnosis, and their treatment. We’ll scrutinize both medical interventions and natural methodologies for effectively dealing with these nodules.
Your education about this prevalent condition begins here. Eager to gain more knowledge? Continue reading!
Key Takeaways
- Most thyroid nodules are not cancerous and do not cause symptoms, but about 5% can be malignant.
- Diagnosing thyroid nodules may include physical exams, imaging tests like ultrasounds or CT scans, and sometimes a biopsy to check for cancer cells.
- Treatment options range from observation and medication to minimally invasive procedures and surgery, depending on the nodule’s size, symptoms, and risk of cancer.
- Supplements such as vitamin D, selenium, iodine, and lifestyle changes can support thyroid health.
- Regular check-ups are essential for monitoring thyroid nodules over time to ensure they don’t grow larger or become problematic.
Understanding Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules are lumps in your thyroid gland. Some can cause problems, while others might not be harmful.
Definition
Thyroid nodules are solid or fluid-filled lumps located on the thyroid gland in the neck. These growths can be either single or multiple and may vary greatly in size. Most of these nodules do not cause any symptoms and are benign, meaning they’re not cancerous.
Despite this, a small fraction—about 5%—can be malignant, posing a risk for thyroid cancer.
Understanding thyroid nodules is crucial for early detection and treatment. While most are harmless, staying informed helps identify when medical intervention is needed.
Types
Moving from what defines thyroid nodules, it’s important to understand the various types that can appear on the thyroid gland. Thyroid nodules can be either solid or fluid-filled lumps.
Most of these are benign and won’t cause any symptoms, making them less concerning for those who have them. Despite this reassurance, a small percentage might be cancerous, which calls for a different approach in management and treatment.
Solid nodules consist of tissue mass within the thyroid gland while fluid-filled ones, also known as cysts, contain liquid. This distinction is crucial during diagnosis as it guides doctors on the next steps—for instance, deciding whether a biopsy is necessary.
Given most thyroid nodules don’t lead to discomfort or noticeable symptoms, their discovery often happens during routine check-ups or unrelated imaging tests.
Symptoms
Thyroid nodules are lumps in your neck. Many people don’t feel them and they cause no pain. Some signs that you might have thyroid nodules include having trouble swallowing, feeling a lump in your throat when you touch it, or your voice becoming hoarse for no clear reason.
These symptoms happen because the nodule is big enough to press on other parts of your neck.
Feeling very hot, losing weight without trying, having high blood pressure or a fast heartbeat could mean hyperthyroidism. This condition can occur if the thyroid nodule makes too much thyroid hormone.
Most nodules aren’t serious and don’t lead to cancer; only a small number do.
Causes
Several factors can lead to the growth of thyroid nodules. One main cause is an imbalance in hormone production within the thyroid gland itself. Iodine deficiency also plays a significant role, as iodine is crucial for healthy thyroid function.
Autoimmune diseases, where the body mistakenly attacks its tissues, can contribute too. Radiation exposure, especially in childhood, increases the risk.
Genetics matter as well—some people inherit a tendency to develop these nodules from their family members. Lastly, aging makes nodules more likely; they’re found more often in older adults.
With most cases being benign and not leading to symptoms, it’s essential to understand these causes for better prevention and treatment planning.
Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules
Detecting a thyroid nodule involves careful examination and testing, guiding the way to effective treatment. Keep reading to understand each step of the process.
Physical examination
Doctors start diagnosing thyroid nodules with a simple check. They feel the neck to find any lumps or swelling. This helps them see if the thyroid gland looks bigger or has nodules.
If they find something, they might ask about symptoms like trouble swallowing, a lump in your neck, or voice changes.
Most thyroid nodules are benign and do not cause symptoms.
Next steps often include more tests to learn about the nodule’s nature. The goal is always clear—to figure out if the nodule needs treatment or just regular checks.
Imaging tests
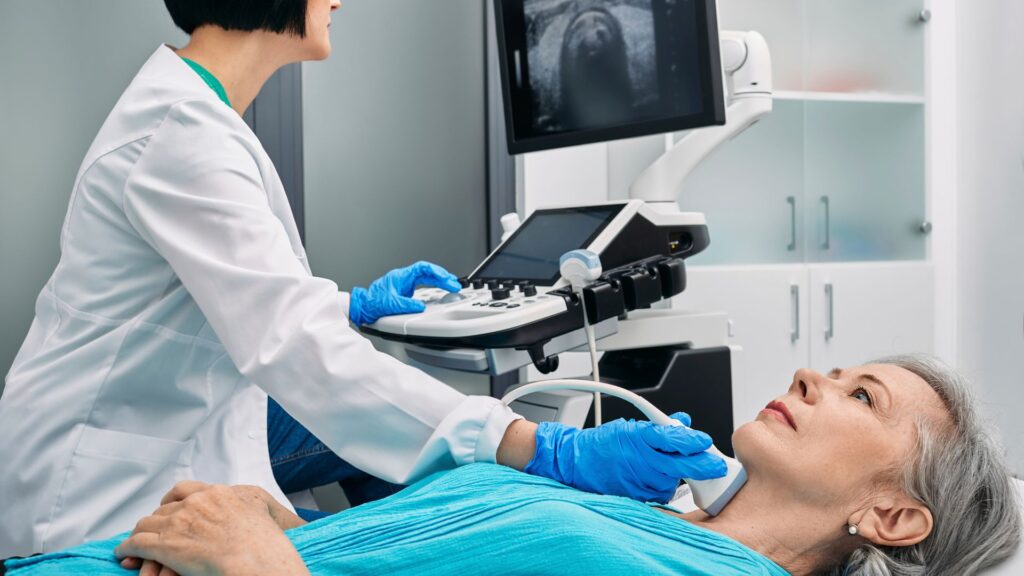
After a careful physical assessment, the subsequent step for diagnosing thyroid nodules incorporates imaging examinations. These tests supply thorough images of the thyroid, assisting physicians in comprehending the dimensions, form, and placement of nodules.
- Ultrasound: This is the typical imaging examination for thyroid nodules, utilizing sound waves to generate thyroid images on a screen. Ultrasounds can display if a nodule is solid or filled with fluid and assist in detecting any unusual aspects that could imply cancer.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): On occasion, physicians resort to CT scans to obtain a wider understanding of the thyroid and nearby formations. This test merges numerous X-ray images shot from varying perspectives to produce cross-sectional views. It’s particularly beneficial for scrutinizing larger nodules and assessing their influence on adjacent tissues.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRIs are used less frequently but can be beneficial in particular instances, notably if further details about the nodule’s composition is necessary or if the patient isn’t suitable for other imaging types due to allergies or other health complications.
- Thyroid Scintigraphy: This examination involves introducing a minor amount of radioactive iodine into the body, which the thyroid gland absorbs. A special camera then photographs the gland to gauge its functionality and to identify nodules that absorb more or less iodine compared to normal tissue.
- PET Scan (Positron Emission Tomography): This scan isn’t routinely used for initial diagnosis but can be suggested if there are doubts of cancer spreading outside the thyroid gland. The test includes injecting a radioactive sugar into the body which cancer cells absorb more than standard cells, making them visible in the scan.
Each set of imaging tests have a vital role in accurately diagnosing thyroid nodules—leading the next steps for evaluations with blood tests and biopsies if required—and building an efficient treatment plan adjusted to each patient’s individual requisite.
Biopsy
Following the imaging tests, a biopsy is often the next step in diagnosing thyroid nodules. Doctors use this procedure to take a small sample of the nodule tissue. They then examine it under a microscope to see if it’s cancerous.
This test is crucial because only a few thyroid nodules are malignant.
For this process, doctors commonly perform a fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy. It involves inserting a thin needle into the nodule to collect cells. The discomfort level is generally low and the procedure doesn’t take long.
A pathologist looks at the cell samples to check for cancer cells, helping decide on the best treatment plan if needed.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Nodules
Exploring the alternatives for thyroid nodules treatment offers prospects and resolutions. Be it medication or surgery, each method targets the preservation of your health and wellness.
Observation
Doctors often choose to closely watch thyroid nodules instead of rushing into treatment. This approach, known as observation, is common for small, noncancerous nodules that don’t cause symptoms.
Most thyroid nodules fall into this category. They are solid or fluid-filled lumps that rarely signal a serious problem. During observation, doctors check the nodule’s size and look for any changes over time.
Regular ultrasound exams may be part of the process.
Patients under observation won’t need immediate surgery or medication. This method helps avoid unnecessary treatments for harmless nodules. If a nodule grows or starts causing symptoms like difficulty swallowing or hoarseness, the doctor may then suggest other actions such as biopsy, medication, or even surgery.
Observation prioritizes patient safety while minimizing the stress and side effects that can come from more aggressive procedures.
Medications
Medications for thyroid nodules often aim to treat symptoms or underlying issues, especially if the nodules cause hyperthyroidism. Doctors might prescribe thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
This helps balance hormone levels in the body, addressing symptoms like unexplained weight loss, fever, high blood pressure, and heart palpitations. For benign nodules that don’t need immediate surgery but may affect thyroid function, medication can provide effective management.
In cases where reducing the size of the nodule is necessary or when trying to avoid surgery, doctors may use other medicines as well. These treatments help manage the patient’s condition while minimizing risks associated with more invasive procedures.
Continuous monitoring through regular check-ups is crucial to adjust medications as needed and ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
Minimally invasive procedures
Minimally invasive procedures provide a balanced solution for treating thyroid nodules. They are less extreme than surgery, but more direct than medication or observation.
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) applies high-frequency radio waves to warm up and eliminate abnormal thyroid tissue. A slender needle inserted into the nodule under ultrasound supervision transfers the energy, focusing only on the affected area whilst safeguarding healthy adjacent tissues.
- Ethanol ablation consists of injecting alcohol right into the thyroid nodule. The ethanol prompts the nodule cells to dehydrate and perish, leading to a decrease in nodule size. This method is exceptionally useful for cystic nodules that are predominantly filled with fluid.
- Laser therapy enlists concentrated light to warm up and eradicate unwanted thyroid tissue. Comparable to RFA, a fiber optic cable dispatches the laser energy through a needle, ensuring precise treatment of the nodule with minimal interference with other tissues.
- Percutaneous microwave ablation is an additional method that uses microwaves to warm up and eliminate thyroid nodules. It’s similar to RFA but deploys microwave energy as opposed to radio waves, suggesting an alternate solution for nodules not receptive to RFA.
These procedures have more rapid recuperation periods in comparison to traditional surgery, with the majority of individuals resuming their regular activities within a few days.
Proceeding forward, let’s transition to natural methods that could supplement these treatments…
Surgery
Doctors recommend surgery for thyroid nodules that are cancerous or cause symptoms. This treatment involves removing part or all of the thyroid gland. Surgeons often opt for this route when nodules are large, uncomfortable, or affect breathing and swallowing.
Surgery aims to get rid of harmful nodules while trying to maintain healthy thyroid function.
Surgery is a key treatment option for thyroid nodules that pose a risk of cancer or cause significant discomfort.
This method has high success rates in handling problematic nodules, especially those few that turn out to be cancerous. Post-surgery, patients might need thyroid hormone replacement therapy to help their bodies regulate metabolism without the full gland’s function.
Regular follow-up care ensures recovery goes smoothly and helps monitor for any signs of recurrence.
Natural Approaches to Managing Thyroid Nodules
Exploring natural approaches can offer additional support in managing thyroid nodules—discover how vitamins, lifestyle changes, and other remedies play a role. Keep reading to learn more about these gentle yet powerful options.
Vitamins and minerals that may help
Managing thyroid nodules requires a thorough strategy. Supplements can contribute positively to this strategy, providing natural aid for your thyroid health. Here’s an in-depth view at vitamins and minerals that may help those coping with thyroid nodules:
- Vitamin D – The Sunshine vitamin has a crucial role in immune health and regulates the thyroid gland. Low levels of vitamin D have a connection with an increased risk of thyroid problems.
- Vitamin B12 – This nutrient is vital for nerve function, energy creation, and the production of DNA. Many individuals with thyroid dysfunctions find themselves lacking in B12, leading to the possible advantage of supplementation.
- Selenium – A mineral of great significance for the creation of thyroid hormones and protection against oxidative damage inside the gland. Selenium can assist in balancing thyroid function and has demonstrated a decrease in nodule size in certain situations.
- Iodine – The thyroid gland requires iodine for hormone production. Though shortage is uncommon in developed countries owing to iodized salt, the upkeep of adequate iodine levels is essential for thyroid health.
- Zinc – Participating in hormone creation throughout the body, zinc bolsters healthy thyroid function. It aids in converting T4 into a more active T3 form.
- Iron – Iron deficiency is associated with lessened thyroid function and health as it’s necessary for efficient production of thyroid hormone.
- Magnesium – Magnesium helps activate vitamin D and also has a role in muscle function and mood regulation, which thyroid disorders can influence.
- Copper – Needed only in minimal amounts, copper collaborates with iron to maintain healthy red blood cells and back up thyroid metabolism.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids (found in fish oil) – These necessary fats may lower inflammation and aid overall hormone equilibrium, including that of the thyroid gland.
- L-Tyrosine – An amino acid functioning as a building block for both dopamine and thyroxine (T4); low levels may contribute to symptoms of an underactive thyroid.
- Ashwagandha – While not a vitamin or mineral, this herb is mentioned for its adaptogenic qualities that might bolster better stress response synthesis closely related to enhanced adrenal and thus indirect support in solving root causes behind nodules’ existence or growth.
Including these supplements into your daily regimen could provide additional support for managing your condition, but it’s always wise to consult with healthcare professionals before initiating any new supplement regimen, especially on matters involving intricate systems like your endocrine function in relation to your thyroids.
Lifestyle factors
Taking care of your thyroid does not merely hinge on medication and doctor visits. Simple lifestyle adaptations can also aid in the efficient handling of thyroid nodules.
- Consuming a well-rounded diet teeming with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains benefits overall thyroid health. These foods are laden with the vital nutrients necessary for the smooth operation of the thyroid gland.
- Alleviating stress through methods like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can positively influence thyroid health. Stress hampers hormonal equilibrium, a factor pivotal in dealing with thyroid nodules.
- Regular physical activity stimulates metabolism and promotes hormonal equilibrium, thereby aiding in the alleviation of symptoms tied to thyroid nodules.
- Refraining from smoking and moderating alcohol consumption are crucial actions as well. Toxins from cigarettes and excessive alcohol can damage the thyroid gland.
- Ensuring sufficient nightly sleep—aim for 7 to 8 hours—promotes the balance of bodily hormones. Sleep deprivation can exacerbate symptoms of thyroid nodules.
- Tackling persistent health issues like diabetes and high blood pressure is also essential as they can influence thyroid health indirectly.
- Minimizing contact with environmental toxins wherever feasible is beneficial, as certain chemicals can disrupt the endocrine system, thus affecting the thyroid gland.
- Maintaining hydration by drinking ample water throughout the day helps sustain optimal health and bolster the body’s natural detoxification processes.
These lifestyle modifications contribute not just to the management of thyroid nodules but to a broader improvement in overall well-being too.
Follow-Up Care and Monitoring
Checking your thyroid nodules regularly is key to stay healthy. Talk with your doctor often about the best way to keep an eye on them.
Importance of regular check-ups
Having regular medical examinations with your doctor is significant in managing thyroid nodules. Even though the majority are benign and symptom-free, it is vital to monitor any shift that might indicate risk.
These consultations facilitate continuous assessment of the nodule’s measurements and properties via imaging tests or blood examinations. Swift discovery of any drift into hyperthyroidism or growth in size can prompt timely intervention, potentially preventing more serious conditions.
During these regular updates, doctors often evaluate treatment possibilities, modifying plans as required based on the most recent results. Whether choosing medication, contemplating surgery, or merely extending observation, well-informed choices stem from current data on your health condition.
Maintaining consistent appointments ensures both you and your doctor keep ahead of any potential issues that may occur.
Precaution is preferable to treatment.
Discussing treatment options with doctors
Talking with your doctor about treatment options for thyroid nodules is key. They can guide you through choosing the best path, whether it’s watchful waiting, medication, or surgery.
Since most thyroid nodules are benign and don’t show symptoms, your doctor might suggest a wait-and-see approach at first. If the nodule grows or causes symptoms like difficulty swallowing or a noticeable lump in your neck, they might recommend more active treatments.
Doctors use tests—like imaging and biopsies—to learn more about your nodule. Based on these results, they may advise taking supplements like vitamins D and B, selenium, or iodine to support thyroid health.
For those few nodules that are cancerous or cause hyperthyroidism symptoms such as weight loss or heart palpitations, stronger interventions like surgery could be necessary. Your endocrinologist will tailor treatment to your specific needs and monitor the nodule over time to ensure the best outcome.
Potential Complications of Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules can lead to some serious health issues, including hyperthyroidism or even thyroid cancer. Keeping an eye on these lumps is critical for your health and well-being.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism rears its head when your thyroid gland, sitting at the front of your neck, goes into overdrive, producing too much hormone. This condition can kick-start symptoms like unexplained weight loss, heart palpitations that make your chest feel like a drum solo, high blood pressure that sends readings off the charts, and fever – turning up the heat without a thermostat in sight.
Hyperthyroidism turns up life’s pace without asking.
This fast-forward mode doesn’t just stop with feeling unusually warm or watching the scale drop; it revs up your entire system. From making your heart race to slimming down without trying – it signals that something’s up with those thyroid hormones.
Keep an eye on these signs; because if hyperthyroidism goes unchecked, it could lead you down a road needing more than just lifestyle tweaks to get back to normal rhythms.
Risk of cancer
Most thyroid nodules are not cancerous. In fact, only a small percentage turn out to be cancer. Doctors often find these lumps on the thyroid gland during routine check-ups or imaging tests for other reasons.
Even though most nodules do not pose a serious threat, it’s crucial to identify which ones could be harmful.
A biopsy helps doctors determine if a nodule is cancerous. This procedure involves taking a small sample of the nodule and examining it closely in a lab. If cancer is found, treatment options like surgery or radioactive iodine therapy become necessary steps to manage the condition and protect health.
Conclusion
Thyroid nodules — commonplace and yet potentially disconcerting — create a unique challenge within healthcare. These bumps on the thyroid gland necessitate consideration for diagnosis and treatment, prompting many to find comprehensive information on symptoms, treatments, supplements, and medicines.
Expert endocrinologist, Dr. Aiden Smith, shares valuable knowledge on this matter.
With a distinguished background that involves groundbreaking research on thyroid health at esteemed institutions and multiple publications to his credit, Dr. Smith offers insightful understanding about thyroid nodule management.
He emphasizes the need to comprehend the character of these nodules — stressing that while most are benign and lack symptoms, an attentive approach for diagnosis and treatment is imperative.
Dr. Smith underscores the significance of early symptom identification in planning effective treatments. The use of imaging tests and biopsies assists in deciding the suitable course of treatment — whether that means monitoring or intervention via medication or surgery.
He points out that technological advancements in minimally invasive procedures indicate progress but also necessitate judicious selection of patients.
Regarding the safe and ethical aspects of thyroid nodule treatment options — including vitamin D, B12, selenium, iodine supplementation, and medical methods like ethanol ablation or thyroid hormone replacement therapy; Dr. Smith highlights that clarity and compliance with regulatory standards are fundamental principles.
As for integrating treatments into daily routines or controlling benign nodules without immediate surgery; he proposes lifestyle modifications along with regulated supplement intake might serve as helpful additions to prescribed medical treatments.
Deep comparisons between various treatments convey that no universal solution exists; factors like individual health state significantly influence the decision-making process around treatment options such as watchful waiting, medication, minimally invasive procedures or surgery, each having its own advantages and disadvantages requiring an individual evaluation, as voiced by Dr. Smith.
Wrapping up his analysis, Dr. Smith points out that decisions made jointly between patients and their healthcare providers provide the optimal route forward. Aiming to not merely eradicate the imminent risk posed by possible carcinogenic nodules, but also safeguard long-term well-being of patients affected by this condition.
As the landscape of thyroid nodule management continuously evolves, the expertise of professionals like Dr. Smith remains an invaluable asset for those dealing with the difficulties related to this condition.
FAQs
1. What are thyroid nodules and what symptoms should I look out for?
Thyroid nodules are small lumps that form within your thyroid gland, often harmless but can sometimes cause noticeable symptoms. These may include a visible lump in the neck, difficulty swallowing, or changes in voice.
2. How do doctors typically treat thyroid nodules?
Treatment options range from watchful waiting to medication or even surgery, depending on the size and type of the nodule as well as any symptoms it might be causing.
3. Can supplements help manage thyroid nodules?
Certain dietary supplements might support overall thyroid health; however, they aren’t a standalone treatment for thyroid nodules. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
4. Are there specific medicines recommended for treating thyroid nodules?
Yes – if your doctor determines that your nodule is causing hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid), he or she may prescribe anti-thyroid medications to control hormone production.
General Facts
- Thyroid nodules are solid or fluid-filled lumps found on the thyroid gland in the neck.
- Most thyroid nodules are benign and do not cause symptoms.
- Only a small percentage of thyroid nodules are cancerous.
- Treatment options for benign nodules include watchful waiting and medication.
- Symptoms of hyperthyroidism can include unexplained weight loss, fever, high blood pressure, and heart palpitations.
- Thyroid nodules can occur in the thyroid gland and may need treatment if found to be cancerous.
- Thyroid nodules are typically harmless, but some may require medical intervention.
- Symptoms of thyroid nodules can include difficulty swallowing, a lump in the neck, and hoarseness.
- Diagnosis of thyroid nodules involves imaging tests, blood tests, and biopsies.
- Treatment for thyroid nodules may involve surgery, medication, or supplements.
Source URLs
- Understanding Thyroid Nodules – WebMD
- Thyroid Nodules Diagnosis and Treatment – Mayo Clinic
- Thyroid Nodule Information – Cleveland Clinic
- Thyroid Nodules Symptoms and Causes – Mayo Clinic
- Thyroid Nodules: What You Need to Know – Medical News Today
- Thyroid Nodules Overview – Verywell Health
- Thyroid Nodules Health Resource – Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi

