Dealing with skin abscesses can be quite the headache, especially when they’re related to drugs. Many folks find themselves lost, not knowing how to tackle this issue which causes discomfort and worries about appearance and health.
Here’s a fact that might surprise you: treatment options vary widely, from antibiotics to natural supplements, each designed for different kinds of skin abscesses.
This guide aims to shed light on effective strategies – covering everything from recognizing symptoms to exploring medical treatments and preventive measures. You’ll get insights into antibiotics known for tackling such infections, natural supplements that could aid recovery, and the latest in investigational medicines promising new hope in care.
Ready for relief? Let’s explore together.
Key Takeaways
- Skin abscesses are painful, pus-filled lumps caused by infections. They need careful treatment with antibiotics like cefazolin, clindamycin, or doxycycline depending on how severe they are.
- Natural supplements such as vitamin C, turmeric, and garlic can help the body fight skin abscesses. These supplements support healing and may reduce infection when used with medical treatments.
- Keeping a healthy lifestyle boosts your body’s ability to deal with skin abscesses. Eating well, staying active, and managing conditions like diabetes help prevent future infections.
- Regular check-ups and following doctor’s advice for wound care are important in healing from an absess. This includes taking all prescribed medications even if symptoms improve early on.
- Preventing skin abscesses starts with good hygiene and proper care of wounds. Avoid sharing personal items that can spread bacteria and keep any cuts clean and covered until fully healed.
What are Skin Abscesses?
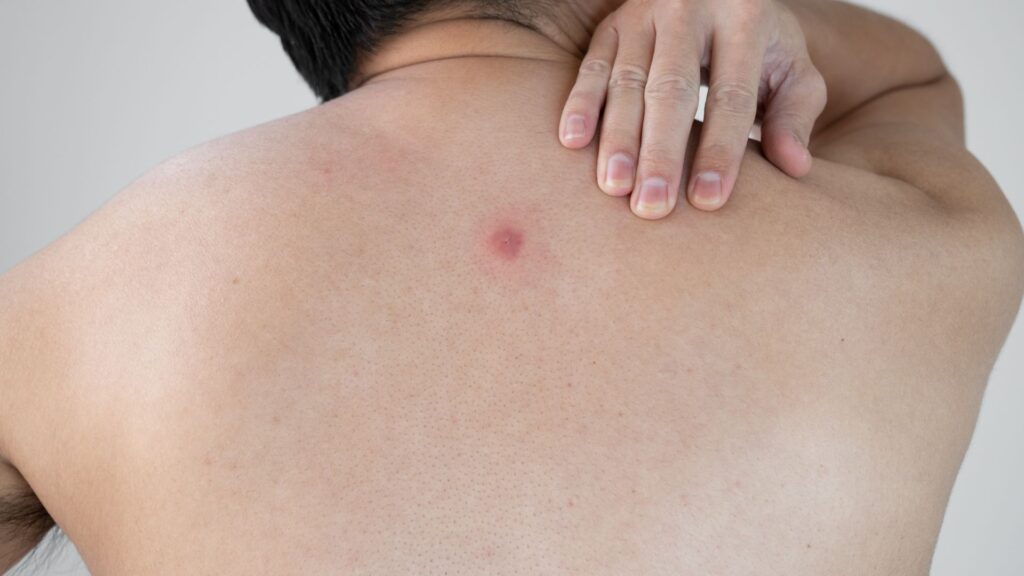
Skin abscesses are painful, pus-filled bumps under the skin caused by infections. They turn red and swollen as your body fights off the germs.
Overview
Skin abscesses are painful, pus-filled bumps under the skin caused by bacteria. These can range from small to large and occur in various parts of the body. Commonly due to infections or clogged sweat glands, they represent a key area of concern within dermatology and infectious diseases.
Treatments involve antibiotics like doxycycline or clindamycin for widespread cases, highlighting the importance of choosing the right medication based on specific symptoms and severity.
For milder nonpurulent infections–where there is no pus–healthcare professionals might opt for antibiotics such as cefazolin, ceftriaxone, or penicillin. This approach underscores the clinical development guidelines that steer acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection treatments.
Managing drug-related skin abscesses requires proper wound care alongside medical supervision to prevent further complications. Such conditions demand a collaborative management strategy involving those with lived substance use experience, harm reductionists, nursing students, and medical professionals for effective treatment and prevention efforts within communities facing these challenges.
Causes
Bacteria getting into a break in the skin often causes abscesses. These breaks might be tiny, like a needle mark from drug use or a small cut, and can allow bacteria to enter. Various types of bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, play key roles in skin infections leading to abscesses.
Many times, these conditions begin as minor bacterial infections around hair follicles or oil glands. If left untreated, they can grow into deeper layers of the skin and accumulate pus forming an abscess.
Abscess treatment strategies highlight the importance of addressing both the infection with antibiotics—such as cefazolin, clindamycin for mild cases—and managing more severe instances with drugs like doxycycline.
The clinical development of new treatments follows specific guidelines designed to combat acute bacterial skin and structure infections effectively. A collaborative approach that involves healthcare professionals familiar with substance use issues is crucial when treating drug-related skin abscesses.
Symptoms
Skin abscess symptoms include a painful, red lump on the skin. You might notice it feels warm to the touch. Over time, this lump can grow and start to hurt more. Some people see pus or a fluid-filled area in the center of the lump.
If the infection spreads, you could feel sick all over—fever and chills are common signs that your body is fighting hard.
Feeling tired or just not right can be another clue that an abscess is taking a toll on your health. Swollen lymph nodes near the abscess show your immune system is responding. These warning signs mean you should get medical help soon to prevent worse problems.
Treatment of Skin Abscesses
Treating skin abscesses requires prompt attention. You can start with basic home care, but seeking medical advice is a smart move for proper healing.
Self-care at home
Taking care of a skin abscess at home can be an effective first step before seeking professional medical help. It’s crucial to do this carefully to avoid further complications. Here’s how:
- Keep the area clean and dry at all times. Wash with gentle soap and water, then pat dry with a soft towel.
- Apply warm compresses to the abscess for 20 minutes several times a day. This helps increase blood flow, encouraging healing.
- Avoid poking or pressing the abscess. Squeezing it can push the infection deeper into your skin.
- Elevate the affected area if possible to reduce swelling.
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen to ease discomfort and swelling, but always follow the dosage instructions on the package.
- Monitor for signs of spreading infection, such as increased redness, pain, or fever. If any of these symptoms occur, seek medical help right away.
- Change bandages regularly if you’re advised by healthcare providers to keep the abscess covered.
- Balance your diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables to strengthen your immune system.
Next up is how medical treatment takes the healing process further…
Medical treatment
After trying some self-care methods at home, you might need medical treatment if the skin abscess doesn’t improve. Here’s what that involves:
- Visit a healthcare provider who can assess the severity of your skin abscess. They’ll determine whether it needs drainage or if antibiotics are necessary.
- Incision and drainage (I&D) is often the first-line treatment for skin abscesses. A doctor carefully cuts the abscess to let it drain, which can quickly relieve pain and start healing.
- Antibiotics might be prescribed, especially if the infection seems severe or spreads. Cefazolin, ceftriaxone, clindamycin, and penicillin are common options for nonpurulent infections.
- For widespread abscesses, oral antibiotics like doxycycline or clindamycin may be recommended to help fight off the infection throughout your body.
- Proper wound care follows I&D to ensure the area heals well and prevents further infection. This care includes keeping the wound clean, changing bandages regularly, and possibly using antiseptic solutions.
- Pain management is also important since both the abscess and its treatment can cause discomfort. Pain relief methods might include over-the-counter medicines or prescribed painkillers from your doctor.
- Follow-up appointments are crucial to check on your healing progress. Your healthcare provider will want to make sure the infection is clearing up as expected.
- Hidradenitis suppurativa patients, who experience chronic skin conditions forming abscesses, may require ongoing antibiotic therapy among other treatments guided by their doctors.
- Comprehensive management sometimes includes addressing any underlying health conditions contributing to frequent infections or poor wound healing.
- Lastly, a collaborative approach with various professionals ensures thorough care—doctors may work alongside harm reductionists and nurses, especially when treating individuals with lived experience of substance use affecting their health.
Follow-up steps
Taking care of your skin after an abscess is crucial for healing. Follow these steps to help your skin recover and prevent future infections.
- Keep the area clean: Wash the affected skin gently with mild soap and water. This helps remove harmful bacteria.
- Change dressings regularly: If your doctor used packing material or applied a dressing, change it as often as they recommend. Fresh dressings keep the wound clean and absorb any pus or fluids.
- Monitor for signs of infection: Watch for increased redness, swelling, pain, or pus. These could be signs that the infection is getting worse.
- Take all medications as directed: If you were prescribed antibiotics or pain management drugs, make sure to complete the entire course, even if you start feeling better early on.
- Attend follow-up appointments: Your healthcare provider will want to check on your progress. They can make sure the abscess is healing properly and adjust treatment if necessary.
- Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet: Good nutrition supports your immune system and helps your body fight off infections.
- Avoid squeezing or trying to drain the abscess at home: This can push the infection deeper into your skin.
- Protect the area from further injury: Avoid tight clothing or activities that could irritate the abscess site until it has fully healed.
- Consider lifestyle changes if needed: If recurrent abscesses are a problem, look into possible causes like diet, hygiene habits, or health conditions that might be contributing factors.
Now let’s explore how antibiotics play a role in treating skin abscesses.
Prevention
Preventing skin abscesses starts with understanding how they form and taking steps to avoid their causes. Good hygiene and proper wound care are your first lines of defense against these painful infections. Here’s a closer look at what you can do:
- Keep the skin clean and dry, especially after sweating or being in dirty environments, to prevent bacteria from entering through small cuts or scratches.
- Wash hands regularly with soap and water, particularly before eating, after using the bathroom, and when coming home from public places.
- Cover open wounds with a clean, dry bandage until they heal fully. This protects against bacteria and helps reduce the chance of infection.
- Avoid sharing personal items like towels, razors, or needles that can carry bacteria or other pathogens from one person to another.
- Maintain a healthy diet and stay hydrated to support your immune system’s ability to fight off potential infections before they start.
- Exercise regularly but make sure to clean any gym equipment before use and shower soon after exercising to remove sweat and bacteria.
- Manage chronic health conditions such as diabetes properly, as high blood sugar levels can weaken the body’s ability to heal wounds.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption since both can impair your immune system’s function and slow down wound healing.
- Wear protective clothing if you’re working in environments where cuts or abrasions are more likely – for example, gardening gloves when working with soil or sturdy shoes on rough terrain.
- Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider; keeping an eye on your overall health helps identify issues that could increase your risk of developing skin abscesses.
Now let’s explore antibiotics often used for treating skin abscesses once they’ve developed…
Antibiotics for Skin Abscesses
Choosing the right antibiotics for skin abscesses can make a big difference in healing. Doctors weigh the pros and cons of each option to find the best fit for your situation.
Antibiotic options
Doctors often choose antibiotics for treating skin abscesses, especially when they spread or are severe. Mild to moderate nonpurulent infections might get treated with cefazolin, ceftriaxone, clindamycin, or penicillin.
These medications fight the infection and help heal the abscess. For more serious cases, oral antibiotics like doxycycline or clindamycin can be prescribed. Each antibiotic works differently and targets various bacteria causing the infection.
Patients with widespread skin abscesses need careful medication selection by healthcare providers. Doctors consider factors such as the patient’s overall health, the severity of the abscess, and potential side effects before prescribing antibiotics.
Cefazolin and ceftriaxone attack a broad range of bacteria while being gentle on most people’s bodies. Clindamycin is a good option for those allergic to penicillin. Choosing the right antibiotic ensures effective treatment and quick recovery from skin infections like hidradenitis suppurativa or other drug-related skin conditions.
Comparison of benefits and harms
Evaluating the treatment options for skin abscesses involves a keen understanding of the benefits and harms associated with antibiotics. With a range of antibiotics at our disposal, from cefazolin to doxycycline, making an informed choice is crucial. Here, we dissect the advantages and potential disadvantages, providing insights into the best practices for managing skin abscesses.
| Antibiotic | Benefits | Harms | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cefazolin | Effective against a wide range of bacteria. Generally well-tolerated. | Possible allergic reactions. May not cover all strains of MRSA. | Mild to moderate nonpurulent infections. |
| Ceftriaxone | Single-dose treatment possible. Broad-spectrum coverage. | Potential for gastrointestinal disturbances. Risk of antibiotic resistance with overuse. | Acute bacterial skin infections needing robust intervention. |
| Clindamycin | Good MRSA coverage. Can be used in patients allergic to penicillin. | Risk of Clostridium difficile infection. Liver toxicity in rare cases. | More widespread skin abscesses and those caused by MRSA. |
| Penicillin | Highly effective against susceptible strains. Minimal side effects. | Limited spectrum. Not effective against MRSA. | Mild infections not involving MRSA. |
| Doxycycline | Effective against a broad range of bacteria, including MRSA. Oral administration. | Photosensitivity. Not recommended for pregnant women or children. | Widespread skin abscesses, including those resistant to other antibiotics. |
This table illustrates the strategic choice of antibiotics, balancing their efficacy with potential drawbacks. Cefazolin and ceftriaxone offer broad-spectrum coverage, making them suitable for a range of bacterial infections. Clindamycin stands out for its MRSA coverage, particularly vital for managing drug-resistant strains. Penicillin, while less effective against MRSA, remains a staple for treating susceptible strains, owing to its minimal side effects. Lastly, doxycycline provides a robust option for tackling MRSA, with its ease of oral administration marking it as a preferred choice for widespread abscesses.
Selecting the right antibiotic entails a careful consideration of the abscess’s characteristics and the patient’s overall health. Armed with this knowledge, healthcare providers can tailor their approach, ensuring effective management while minimizing potential harms.
Population-specific recommendations
Doctors often choose antibiotics like cefazolin, ceftriaxone, clindamycin, and penicillin for mild to moderate nonpurulent skin abscesses. Each patient’s health condition, like hidradenitis suppurativa or underlying chronic illnesses, shapes the treatment plan.
The goal is always clear—pick the best antibiotic that targets the infection without causing more harm.
For widespread skin infections, pills such as doxycycline or clindamycin might be prescribed. Health experts consider factors like age, allergies, and overall health before deciding on medication.
They also emphasize proper wound care and follow-up steps to avoid complications.
A collaborative approach helps tailor treatments for drug-related skin abscesses.
Natural Supplements for Skin Abscesses
Discover how natural supplements can aid in healing skin abscesses, and see what options could work best for you.
Potential benefits
Natural supplements can help fight skin abscesses. They boost the body’s healing powers and might reduce inflammation. Some even have properties that support fighting infections. With these benefits, natural supplements serve as a helpful companion to traditional treatments.
Incorporating natural supplements into your care plan may enhance recovery from skin abscesses, complementing prescribed antibiotics and proper wound care.
Recommended supplements
Understanding the potential benefits of natural supplements offers a foundation for managing skin abscesses. These supplements can work alongside traditional treatments to support healing and skin health.
- Vitamin C is known for its immune-boosting properties, making it a valuable ally in fighting infections that lead to skin abscesses.
- Turmeric contains curcumin, which has powerful anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects, helping to reduce swelling and fight off infection.
- Garlic possesses natural antimicrobial properties that can assist in combating bacteria responsible for skin infections.
- Tea tree oil, when applied topically after dilution, acts as a natural antiseptic to cleanse wounds and promote healing.
- Zinc supplements can support immune system function and aid the body in resisting infections like those causing abscesses.
- Echinacea is often used to enhance the immune response, potentially speeding up recovery from skin infections.
- Aloe vera soothes the skin and has antimicrobial and healing properties that are beneficial for wound care.
- Honey, particularly Manuka honey, serves as a natural antibiotic due to its potent antimicrobial properties, making it an effective topical treatment for minor abscesses.
- Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil can reduce inflammation in the body, including around infected or inflamed skin areas.
- Probiotics help balance good bacteria in the gut, which plays a role in overall immunity and may impact the body’s ability to fight off skin infections.
Each of these supplements offers unique benefits that can contribute to the management and healing of skin abscesses when used appropriately alongside prescribed medical treatments.
Maintaining Overall Well-Being
Keeping your body and mind healthy boosts healing from skin abscesses. Explore more ways to stay well!
Importance of a healthy lifestyle
Living a healthy lifestyle keeps your body strong, especially when fighting infections like skin abscesses. Eating well, staying active, and getting enough sleep boosts your immune system.
This way, your body can better handle antibiotics for skin absolutions or heal faster if you need incision and drainage. It’s all about giving your body the upper hand against infections.
Regular check-ups are key too. They help manage underlying health conditions that might make it harder for you to fight infections. Conditions like hidradenitis suppurativa require ongoing care to prevent complications such as skin abscesses.
By managing these conditions early on, you reduce the risk of severe infections that need complex treatments like surgical intervention or specialized antibiotic therapy.
Managing underlying health conditions
Managing underlying health conditions is crucial in the fight against skin abscesses. Taking control of your health can prevent complications and support recovery.
- Keep a close eye on blood sugar levels if you have diabetes. High sugar can weaken your immune system, making it harder to fight off infections.
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals. Foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean meats support your body’s defense mechanisms.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Proper hydration helps your body function at its best.
- Exercise regularly to boost your circulation and immune system strength. Even walking for 30 minutes a day can make a difference.
- Monitor any chronic conditions closely, such as heart disease or asthma, and follow your doctor’s advice to manage them effectively.
- Don’t skip regular check-ups with your healthcare provider, especially if you’re managing long-term health issues.
- Take all medications as prescribed, without missing doses. This includes treatments for both your skin condition and any underlying diseases.
- New research keeps offering insights into how best to tackle abscesses; staying informed helps you play an active role in your care plan.
The next section will explore antibiotics for treating skin abscesses…
New and Investigational Antibiotics for Skin Abscesses
Scientists are developing exciting new antibiotics to fight skin abscesses, promising better treatment options ahead. Keep an eye out for these breakthroughs!

Aminomethylcyclines
Aminomethylcyclines are a new class of antibiotics showing promise in treating skin abscesses. They work by stopping bacteria from growing, which helps the body overcome infection.
Their development follows guidelines for acute bacterial skin and structure infections. This makes them an important option for those dealing with drug-related skin issues.
Researchers focus on these drugs to combat resistant strains of bacteria. Aminomethylcyclines could be beneficial for patients who haven’t responded well to traditional antibiotics like doxycycline or clindamycin.
As skin abscesses get trickier to treat due to resistance, having effective options is crucial.
Pleuromutilins
Pleuromutilins play a key role in the fight against acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections. These antibiotics break new ground by stopping bacteria from growing, which helps heal skin abscesses.
Researchers are working on new pleuromutilin-based drugs to treat these infections more effectively. This effort aligns with clinical development guidelines that recommend specific treatments for skin abscesses.
These investigations show promise for future advancements in antibiotic therapy, focusing on improving patient outcomes while managing drug-related side effects. As studies continue, doctors hope to find even better ways to use pleuromutilins against stubborn infections.
The journey toward developing these novel antibiotics marks a significant step forward in dermatology and infectious disease management.
Current understanding
Scientists are developing new antibiotics for skin abscesses, like Aminomethylcyclines and Pleuromutilins. These drugs could change how we treat infections. Today, doctors often use antibiotics such as cefazolin, ceftriaxone, clindamycin, and penicillin for mild to moderate cases.
For severe abscesses, they might turn to pills like doxycycline or clindamycin. Research is ongoing to find better treatments.
The clinical development of drugs for acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections follows specific recommendations.
Healthcare professionals need effective options because the wrong treatment can lead to complications or drug resistance. As scientists learn more about these infections and how they respond to different therapies, patients will get better care.
This effort includes understanding which antibiotic works best for each type of abscess—knowledge that saves lives and improves recovery times.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate field of drug-related skin abscesses, supplements, and medicines takes a keen eye for detail and a deep knowledge of dermatology. Enter Dr. Rachel Simmons, a leading expert with over two decades of experience in infectious diseases and dermatological research.
With a Ph.D. from Harvard University in microbial biology and numerous awards for her groundbreaking work on antibiotic resistance, Dr. Simmons has contributed significantly to both clinical practice and public health policy related to managing skin infections.
Dr. Simmons highlights the importance of recognizing skin abscesses early — their causes, symptoms, and effective treatments are crucial for proper care. “Medications such as cefazolin or doxycycline,” she points out, “play pivotal roles in treating these conditions when used appropriately.” She stresses the significance of combining medical treatment with prevention strategies like good hygiene practices to reduce recurrence risks.
On safety and ethics, Dr. Simmons doesn’t mince words: transparency is key. She accentuates how honesty about possible side effects of antibiotics ensures that patients can make informed decisions regarding their health care options.
For integrating treatments into daily life, she recommends simple yet effective steps—like keeping wounds clean—to complement prescribed medications or supplements effectively.
With natural supplements gaining popularity for immune support amidst traditional antibiotic therapy, she cautions users to approach these alternatives with evidence-based skepticism while acknowledging their potential benefits when used judiciously alongside conventional medicine.
Evaluating pros and cons carefully, Dr. Simmons offers guidance on selecting appropriate interventions by comparing effectiveness against potential complications such as antibiotic resistance—a growing concern in global health care.
Her final verdict underscores the comprehensive value offered by an educated approach toward treating drug-related skin abscesses; understanding not just medications but also lifestyle adjustments needed promotes healing while preventing future issues.
FAQs
1. What are drug-related skin abscesses?
Drug-related skin abscesses are a type of skin infection that can occur due to the use of certain drugs or supplements, often resulting in painful, swollen areas filled with pus.
2. How do I recognize a drug-related skin abscess?
A drug-related skin abscess typically presents as a tender lump under your skin surface. It may be red, warm to touch and could potentially rupture releasing pus.
3. Can medicines help treat these types of abscesses?
Yes, various types of medicines including antibiotics can play an essential role in treating drug-related skin abscesses by combating the underlying infection.
4. Are there any particular supplements that might cause such problems?
While it’s not common for supplements to directly cause an abscess, some might lead to adverse reactions in people who have specific sensitivities or allergies—always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
General Facts
- There are different types of abscesses, including skin abscesses, and it is important to understand their symptoms and treatment.
- Treatment options for mild to moderate nonpurulent infections include antibiotics such as cefazolin, ceftriaxone, clindamycin, and penicillin.
- For more widespread skin abscesses, healthcare providers might prescribe antibiotic pills such as doxycycline or clindamycin.
- The clinical development of drugs for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections is guided by specific recommendations.
- Antibiotics are commonly prescribed for the treatment of skin abscesses, and it is important to be familiar with the types and names of these medications.
- Proper wound care and medical triage are essential for the treatment of drug-related skin abscesses.
- Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic skin condition that may require antibiotic treatment for management.
- The symptoms of skin abscesses and warning signs should be understood to seek timely medical treatment.
- The diagnosis and treatment of skin abscesses involve a combination of medical management and possible surgical intervention.
- A collaborative approach involving individuals with lived experience of substance use, nursing students, harm reductionists, and medical professionals can contribute to a comprehensive guide for drug-related skin abscesses and their management.

