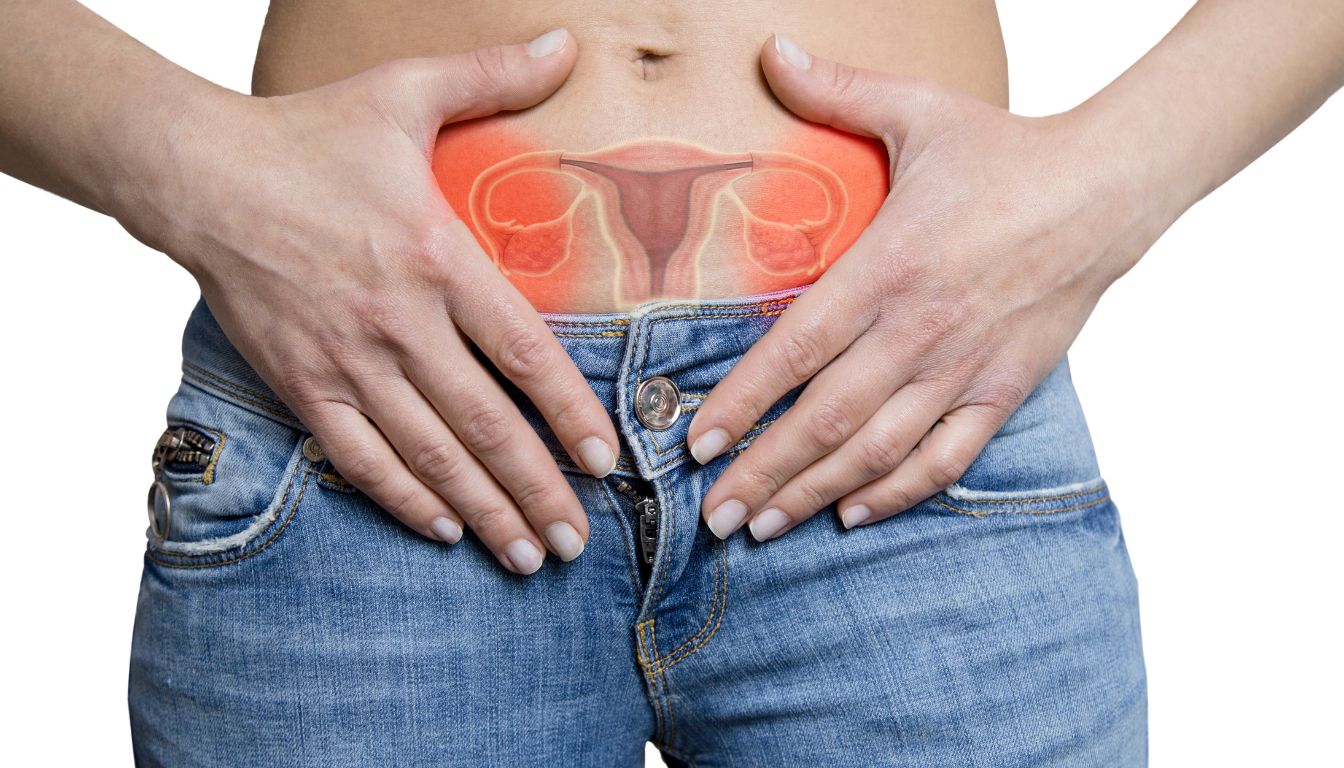
Many people are looking for clear, straightforward information about ovarian cancer but get lost in medical jargon and complex explanations. Ovarian cancer, a challenge many women face, may not show signs early on, making it crucial to understand both symptoms and treatments.
One key fact to note is that early detection significantly improves treatment success rates. This blog aims to demystify ovarian cancer by offering a complete guide on its symptoms, available treatments including supplements and medicines, targeted drugs’ effectiveness, complementary therapies, coping strategies, and resources for patients.
Keep reading — your guide starts here.
Key Takeaways
- Ovarian cancer starts in the ovaries and can be hard to detect early because it often doesn’t show symptoms until it has spread.
- Surgery and chemotherapy are main treatments for ovarian cancer. Doctors also use targeted therapy, hormone therapy, and immunotherapy to fight the disease.
- Patients should talk to their doctors about all treatment options, including clinical trials and complementary therapies like acupuncture or yoga.
- Early detection of ovarian cancer improves the chances of successful treatment. Watch for symptoms like bloating or abdominal pain.
- Managing ovarian cancer includes focusing on symptom control and quality of life through a combination of medical treatments and support systems.
Overview of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer starts in the ovaries, which are part of a woman’s reproductive system. Identifying the symptoms early can make a big difference in treatment success.
Definition of ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer starts when cells in the ovaries grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. The ovaries are two small, bean-shaped organs on each side of the uterus that produce eggs and hormones.
This type of cancer is hard to detect early because it often doesn’t cause noticeable symptoms until it has spread within the pelvis and abdomen. At this advanced stage, it becomes more difficult to treat.
Risk factors include family history, genetic mutations like those in the BRCA gene, and age.
Symptoms can be vague but may include bloating, pelvic or abdominal pain, difficulty eating or feeling full quickly. For diagnosis, doctors use imaging tests such as ultrasounds or CT scans, blood tests looking for cancer markers like CA-125 and biopsies where they take a tissue sample for testing.
Treatment usually involves surgery to remove the ovaries and affected tissues followed by chemotherapy or targeted medication therapy—depending on how much the cancer has spread.
Early detection plays a crucial role in successful treatment outcomes for ovarian cancer.
Recognizing common symptoms
Moving from what defines ovarian cancer, we come to recognize its common symptoms. People with ovarian cancer may feel bloated and have pelvic or abdominal pain. They might find eating difficult or feel full quickly.
These signs can sneak up and often get brushed off as minor issues.
Bloating, discomfort in the lower belly area, and changes in appetite are clues that shouldn’t be ignored. If these symptoms keep happening, especially more than 12 times a month, it’s critical to see a doctor.
Early detection is challenging since early stages don’t always cause clear symptoms.
Steps for diagnosis and testing
Diagnosing ovarian cancer involves a series of steps and tests. Doctors take these measures to ensure they have all the information they need about the tumor.
- Pelvic examination: A doctor checks for any abnormalities in the ovaries, uterus, and other pelvic organs. This is often the first step if symptoms suggest ovarian cancer.
- Imaging tests: Ultrasounds, CT scans, and MRIs can show tumors or abnormal areas that might be cancer. These tools help doctors see the size and location of ovarian tumors.
- Blood tests: Certain substances in the blood, like CA-125, can signal ovarian cancer. High levels could suggest the need for further evaluation.
- Biopsy: The surest way to diagnose ovarian cancer is by taking a small tissue sample from the ovary and looking at it under a microscope. This usually happens during surgery.
- Laparoscopy: A small camera inserted into the abdomen lets doctors see the ovaries directly and take tissue samples if needed.
- Genetic testing: If there’s a family history of ovarian cancer or certain genetic markers are present, genetic tests can show an increased risk of developing this type of cancer.
- Colonoscopy: Sometimes recommended to rule out other possible causes of symptoms, like colon cancer.
Each step provides crucial information that guides treatment decisions and helps develop an effective treatment plan customized to each patient’s specific condition.
Exploring Treatment Options for Ovarian Cancer

Exploring treatment options for ovarian cancer opens up numerous possibilities. Patients can find hope through a variety of effective methods, customized to their unique condition.
Role of surgery
Surgery plays a crucial role in treating ovarian cancer, often being the first line of attack. Surgeons work to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This procedure might involve taking out one or both ovaries, the fallopian tubes, and possibly part of the uterus.
For some patients, especially when caught early, surgery can effectively remove all visible signs of cancer.
The success of surgery depends on several factors including the stage and spread of ovarian cancer. In advanced cases where the cancer has spread beyond the ovaries, surgeons may perform debulking surgery to remove as much cancer as possible before other treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy are used.
This approach helps improve outcomes by reducing tumor size and aiding in symptom management.
Benefits and process of chemotherapy
Chemotherapy plays a crucial role in treating ovarian cancer, attacking the cancer cells to stop them from growing and dividing. This treatment can shrink tumors or eliminate signs of cancer, which is vital because ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Doctors use various chemotherapy drugs depending on the patient’s condition and the type of ovarian cancer. These powerful medications are usually given through an IV but can also come in pills.
The goal is to target the cancer cells specifically, though some healthy cells may be affected too.
The process begins with a cycle of treatment followed by a rest period to give the body time to recover. This cycle can repeat several times over a few months. Side effects like fatigue, nausea, and hair loss are common but manageable with additional medication and care strategies provided by healthcare teams.
Chemotherapy has been shown to improve survival rates significantly when used alongside surgery for those battling advanced-stage ovarian disease. It’s an essential tool in achieving remission and prolonging life for many patients facing this challenging diagnosis.
Utilizing radiation therapy
Radiation therapy offers another approach to battle ovarian cancer. Doctors use high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells, carefully aiming at the tumor while trying to spare healthy tissues around it.
This treatment can shrink tumors or kill any remaining cancer cells after surgery.
Moving on, hormone therapy applications become crucial in managing certain types of ovarian cancer by blocking hormones that fuel the growth of tumors.
Hormone therapy applications
Hormone therapy plays a crucial role in treating ovarian cancer, especially when the disease has spread or come back. This treatment uses medication to block hormones that cancer cells need to grow.
Doctors often use it when surgery and chemotherapy have already been tried. It can be particularly effective for certain types of ovarian cancer, like those that are estrogen or progesterone receptor positive.
Patients might receive hormone therapy in pill form or through injections.
For women battling this tough condition, hormone therapy offers another line of defense. It targets the cancer’s specific traits and disrupts its growth mechanism without relying on traditional methods like radiation.
The effectiveness of this approach depends on several factors, including the type of ovarian cancer and how advanced it is. By focusing on the hormonal aspects, doctors aim to slow down the tumor’s progression and improve quality of life for their patients.
Advancements in immunotherapy
Moving from hormone therapy applications, we explore the cutting-edge progress in immunotherapy as a treatment for ovarian cancer. This approach boosts the body’s immune system to fight the cancer cells more effectively.
Immunotherapy has shown promise in targeting specific parts of cancer cells or signaling pathways involved in tumor growth. With ongoing research, some forms of immunotherapy have begun to offer hope where traditional treatments may fall short, particularly in advanced stages of ovarian cancer.
Immunotherapy for ovarian (OC) includes using drugs that help the immune system identify and attack cancer cells. One key advancement is the development of checkpoint inhibitors. These drugs block proteins that stop the immune system from attacking OC cells, allowing it to destroy them instead.
Trials are underway to find out how these drugs can best help patients with OC, including those who haven’t responded well to chemotherapy or targeted therapy. This shift to harnessing the body’s natural defenses marks a significant step forward in offering new hope to those battling this challenging disease.
Effectiveness of Targeted Drugs for Ovarian Cancer
Targeted drugs for ovarian cancer have changed the game. They attack cancer cells without harming normal ones, helping many women see improved outcomes.
Mechanism of action
Targeted drugs for ovarian cancer work by attacking specific parts of cancer cells or the surrounding environment that helps them grow and spread. These drugs can block the action of certain enzymes, proteins, or other molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells.
For instance, some targeted therapies focus on inhibiting proteins made by genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2, which are known to increase the risk of developing ovarian cancer when mutated.
Target you approach with precision—targeted therapy exemplifies how understanding a tumor’s specific characteristics can lead to more effective treatments.
This strategy aims to minimize damage to healthy cells while maximizing the impact on cancerous ones. By honing in on these unique aspects of ovarian cancer cells, targeted medication therapy provides a powerful tool in slowing down or even stopping disease progression.
List of common medications
Ovarian cancer treatment includes a variety of medications. These drugs can slow tumor growth, manage symptoms, and increase survival rates. Here’s a detailed look at some common medications used in treating ovarian cancer:
- Paclitaxel – Often used in chemotherapy, Paclitaxel stops cancer cells from dividing and growing. It’s typically given through an IV.
- Carboplatin – Another chemotherapy drug, Carboplatin attacks the DNA of cancer cells, causing them to die. Like Paclitaxel, it is administered intravenously.
- Bevacizumab (Avastin) – This targeted therapy blocks the blood supply that tumors need to grow. Patients receive it as an infusion.
- Olaparib (Lynparza) – Designed for women with certain genetic mutations (like BRCA), Olaparib targets cancer cells while sparing healthy ones. It comes in pill form.
- Niraparib (Zejula) – As a maintenance treatment following chemotherapy, Niraparib helps prevent the cancer from coming back and is taken orally.
- Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) – Part of immunotherapy treatments, Pembrolizumab boosts the immune system’s ability to fight cancer cells and is given through injection.
- Doxorubicin (Lipodox) – Used in cases where other treatments haven’t worked, Doxorubicin attacks the enzymes inside cancer cells and is administered via IV.
Understanding these medications helps patients and their doctors make informed decisions about their care plan.
Moving on to explore complementary and alternative therapies offers additional options for those seeking holistic approaches alongside conventional treatment methods.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies for Ovarian Cancer
Exploring complementary and alternative therapies can open new doors for ovarian cancer patients. These approaches, discussed with a healthcare professional, might offer additional relief alongside traditional treatments.
Discuss therapies with your doctor
Talk to your doctor about every therapy option available for ovarian cancer. This includes surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy. Your doctor knows the specifics of your condition and can suggest which treatments might work best.
For instance, surgery could remove tumors, while chemotherapy attacks cancer cells throughout the body.
Explore complementary and alternative therapies too. Mention any supplements or herbal remedies you’re considering. Some patients find these helpful alongside conventional treatments but they are not proven to prevent or treat ovarian cancer on their own.
Your doctor can help weigh the potential benefits against possible risks.
Your healthcare team is there to guide you through each treatment decision with personalized advice.
Varieties of alternative therapies
Exploring alternative therapies offers additional options for those battling ovarian cancer. These treatments can complement traditional medicine, potentially easing symptoms and improving quality of life.
- Acupuncture: This ancient Chinese practice involves inserting fine needles into specific body points. It aims to restore energy flow and balance within the body, helping manage pain and reduce chemotherapy-induced nausea.
- Yoga: A mind-body therapy that combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation. Yoga helps reduce stress, improve physical functioning, and enhance mental well-being in cancer patients.
- Massage Therapy: By manipulating the body’s soft tissues, massage therapy can relieve muscle tension, reduce anxiety, and improve circulation. This therapy is often sought after for its relaxation benefits.
- Dietary Supplements: While not a cure, certain vitamins and minerals may support overall health during cancer treatment. Always consult with a doctor before starting any new supplement to ensure it doesn’t interfere with traditional treatments.
- Herbal Remedies: Some herbs are believed to have healing properties that can help manage symptoms or side effects of cancer treatment; however, evidence is limited and not all herbs are safe for cancer patients.
- Mindfulness Meditation: This practice involves staying present and fully engaging with the moment without judgment. It has been shown to reduce stress levels and improve emotional well-being in individuals with cancer.
- Music Therapy: Listening to or creating music provides emotional support for patients by reducing feelings of anxiety and depression while promoting a sense of well-being.
- Aromatherapy: Using essential oils from plants for therapeutic benefit can help alleviate some symptoms of ovarian cancer and its treatment, like nausea or sleep issues.
Each person’s experience with ovarian cancer is unique – what works for one might not work for another. Discussing these alternative therapies with a healthcare provider ensures they fit into your overall care plan safely.
The search for effective treatments doesn’t stop here; let’s explore strategies for coping with ovarian cancer next.
Analyzing potential benefits and risks
Exploring complementary and alternative therapies for ovarian cancer requires a careful look at their potential benefits and risks. These therapies, while not proven to prevent or treat ovarian cancer, can offer relief from symptoms for some patients.
For example, acupuncture might reduce chemotherapy-induced nausea but doesn’t fight the cancer itself. It’s crucial to discuss any new therapy with healthcare providers to avoid treatments that could interfere with standard care.
Choosing to integrate these therapies into a treatment plan brings up important considerations about overall health impacts. Dietary supplements and herbal remedies pose their own set of risks since they are not regulated like medicines.
They might interact negatively with prescribed medications used in treating ovarian cancer. Keeping an open line of communication with doctors ensures that each step taken contributes positively towards managing the condition.
Next, we explore strategies for coping with ovarian cancer…
Strategies for Coping with Ovarian Cancer
Finding ways to cope with ovarian cancer involves seeking emotional support, exploring clinical trials, and managing health actively—discover more strategies to navigate this journey.
Support systems for emotional and mental health
Facing ovarian cancer brings a unique set of emotional and mental health challenges. Support systems play a crucial role in managing these stresses. Many patients find solace in counseling services, where professionals help them process their feelings and develop coping strategies.
Online forums and local support groups offer another layer of comfort, allowing individuals to connect with those who truly understand their journey.
Healthcare teams also guide patients toward resources geared at improving mental well-being during this tough time. Organizations like cancer support centers provide free workshops and activities designed to uplift spirits and foster community among survivors and those currently battling the disease.
Engaging with these supportive networks encourages resilience, offering much-needed hope and companionship through every stage of treatment.
Now, exploring how to find clinical trials becomes vital for many patients seeking advanced treatment options…
How to find clinical trials
Finding clinical trials for ovarian cancer might sound challenging, but it’s a vital step in exploring advanced treatment options. Many resources offer detailed information on current trials that are seeking participants.
- Start with a visit to your doctor or oncologist, who can provide personalized recommendations based on the specific type and stage of cancer you’re dealing with.
- Use the official website of the National Institutes of Health’s ClinicalTrials.gov to search for ovarian cancer trials. This site allows you to filter results by location, age, and other criteria.
- Check out the National Cancer Institute (NCI) website. The NCI offers access to a database of federally and privately supported clinical trials conducted around the world.
- Explore the American Cancer Society’s website, which has a section dedicated to connecting patients with research studies.
- Contact organizations like Ovarian Cancer Research Alliance (OCRA) or Gynecologic Oncology Group (GOG) for information on trials focused on ovarian cancer.
- Enroll in patient registries and databases that notify you about matching clinical trial opportunities as they become available.
- Join online forums and support groups for ovarian cancer survivors and patients; members often share their experiences with different treatments, including participation in clinical trials.
- Attend conferences or seminars focused on gynecological cancers; these events sometimes highlight ongoing or upcoming research studies looking for volunteers.
- Text “TRIALS” to services provided by cancer advocacy groups; some organizations offer text messaging services that can help connect you with clinical trials.
Look into academic medical centers and universities conducting research on ovarian cancer; these institutions often run independent clinical studies not listed in broader databases.
Exploring these avenues can broaden your understanding of available treatments and contribute significantly to the fight against ovarian cancer through participation in clinical research.
Managing incurable cancer
Managing incurable ovarian cancer involves focusing on controlling symptoms and improving quality of life. Pain management is a crucial aspect, with targeted cancer drugs and painkillers playing a significant role.
These treatments aim to reduce discomfort and allow patients to enjoy everyday activities as much as possible. Patients often work closely with their healthcare team to create a personalized care plan that addresses both physical and emotional needs.
Every moment matters, especially when managing the challenges of incurable ovarian cancer.
Support systems become an invaluable resource for emotional and mental health during this time. Finding clinical trials can offer access to new therapies that might not be available otherwise.
Palliative care teams also provide essential services, helping manage symptoms, reducing hospital visits, and supporting the patient’s family through this tough journey.
Resources Available to Ovarian Cancer Patients
Many ovarian cancer patients have access to an array of resources for support and information. These include cancer support organizations, nurse helplines, and websites with up-to-date details on treatments and care.
Cancer support organizations and assistance
Cancer support organizations offer a wide range of help for those dealing with ovarian cancer. These groups provide emotional, financial, and educational support. People can find counseling services, information about clinical trials, and advice on managing symptoms.
Organizations also connect patients with others going through similar experiences. This connection offers comfort and understanding that one is not alone in their fight against ovarian cancer.
Access to nurse helplines is another crucial resource available to ovarian cancer patients. Nurse helplines allow individuals to ask questions about their treatment options, understand side effects of medications, and receive guidance on coping strategies.
They serve as a lifeline for many patients seeking immediate answers or needing reassurance during tough times.
Access to nurse helplines
Transitioning from the support provided by organizations, nurse helplines offer a personalized touch in managing ovarian cancer. These helplines connect patients directly with nurses who specialize in gynecological cancers.
Patients can ask questions about their symptoms, treatments like surgery or chemotherapy, and discuss side effects. The nurses provide reliable information that can help manage expectations and treatment plans effectively.
Nurse helplines also serve as a comforting resource for those dealing with the emotional toll of an ovarian cancer diagnosis. They guide patients on how to navigate clinical trials or explore alternative therapies safely.
With access to these professionals just a phone call away, individuals gain added support throughout their journey—making complex decisions a bit easier to handle with expert advice at their fingertips.
Conclusion
Understanding ovarian cancer, from its symptoms to treatment options, including surgery and medications, is crucial for anyone touched by this condition. Dr. Lisa Hamilton’s insights bring clarity and a wealth of knowledge to the complexity of coping with ovarian cancer.
Dr. Hamilton, a leading expert with over two decades in oncology research and patient care, holds advanced degrees in both medical science and public health. Her career spans groundbreaking clinical trials on ovarian cancer treatments and authorship on numerous peer-reviewed articles about gynecological cancers.
Her commitment to advancing understanding and treatment options for patients showcases her expertise.
In evaluating the comprehensive guide to ovarian cancer symptoms, treatments, supplements, and medicines, Dr. Hamilton emphasizes the importance of early detection through awareness of symptoms like bloating or abdominal pain.
She points out that while no supplement can cure cancer, certain treatments effectively manage the disease when caught early.
Safety is paramount in treating any health condition—ovarian cancer included. Dr. Hamilton stresses that all therapies mentioned in the guide adhere strictly to regulations ensuring patient safety first.
Honesty between doctors and patients about potential risks ensures individuals make informed decisions appropriate for their circumstances.
For daily management or specific contexts such as post-diagnosis life adjustments or during treatment phases like chemotherapy or surgery recovery, Dr. Hamilton suggests integrating lifestyle changes gently.
Adjusting diet plans slightly more toward nutritious foods rich in vitamins can complement medical treatments well without feeling overwhelming.
Dr. Hamilton presents a balanced evaluation against other market options available for managing ovarian cancer stating clearly: while some alternative therapies may offer comfort; evidence-based conventional treatments remain essential for effective disease control.
Her final recommendation champions the guide as an invaluable resource not just offering hope but also actionable steps toward better outcomes through approved therapies bolstered by support systems addressing emotional needs during this difficult journey.
FAQs
1. What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer?
Symptoms of ovarian cancer can vary, but may include abdominal bloating or swelling, quick feeling of fullness after eating, weight loss, discomfort in the pelvic area and changes in bowel habits.
2. How is ovarian cancer treated?
Ovarian cancer treatment often involves a combination of surgery and chemotherapy. The specific plan depends on several factors including the type and stage of the disease as well as patient’s overall health.
3. Can supplements help with managing ovarian cancer?
Certain supplements might be recommended by healthcare professionals to manage side effects from treatments for ovarian cancer or improve overall wellbeing during recovery… It’s crucial to discuss any supplement use with your doctor first!
4. Which medicines are commonly used for treating ovarian cancer?
The choice of medicine will depend on many factors like the stage and type of your disease… Commonly used drugs include platinum-based compounds such as cisplatin or carboplatin, taxanes like paclitaxel and doxorubicin among others!
General Facts
- Ovarian cancer can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy.
- Risk factors for ovarian cancer include family history, genetic mutations, and age.
- Symptoms of ovarian cancer can include bloating, pelvic or abdominal pain, difficulty eating, and feeling full quickly.
- Diagnosis of ovarian cancer may involve imaging tests, blood tests, and biopsies.
- Treatment options for ovarian cancer may include surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted medication therapy.
- Fertility drugs and hormone replacement therapy may increase the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Targeted cancer drugs and painkillers can help manage the symptoms of advanced ovarian cancer.
- Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage, making it more difficult to treat.
- Dietary supplements and herbal remedies are not proven to prevent or treat ovarian cancer.
- Ovarian cancer can be challenging to detect early, as symptoms may not be noticeable in the early stages.
Source URLs
- Mayo Clinic – Ovarian Cancer: Symptoms and Causes
Learn about symptoms and causes of ovarian cancer on Mayo Clinic - American Cancer Society – Treating Ovarian Cancer
Information about treating ovarian cancer from American Cancer Society - Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center – Ovarian Cancer Facts and Resources
Facts and resources about ovarian cancer from Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center - Mayo Clinic – Ovarian Cancer: Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer from Mayo Clinic - Foundation for Women’s Cancer – Ovarian Cancer Guide (PDF)
Download the ovarian cancer guide from Foundation for Women’s Cancer (PDF) - Drugwatch – Ovarian Cancer Health Overview
Health overview of ovarian cancer from Drugwatch - Cancer Research UK – Treating Symptoms of Advanced Ovarian Cancer
Treatment options for symptoms of advanced ovarian cancer from Cancer Research UK